Abstract
Objective
To investigate the amounts of extractable organic nitrogen (EON), and the relationships between EON and total extractable nitrogen (TEN), especially the amino acids (AAs) adsorbed by soils, and a series of other hydrolyzed soil nitrogen indices in typical land use soil types from southeast China. Under traditional agricultural planting conditions, the functions of EON, especially AAs in the rhizosphere and in bulk soil zones were also investigated.
Methods
Pot experiments were conducted using plants of pakchoi (Brassica chinensis L.) and rice (Oryza sativa L.). In the rhizosphere and bulk soil zone studies, organic nitrogen components were extracted with either distilled water, 0.5 mol/L K2SO4 or acid hydrolysis.
Results
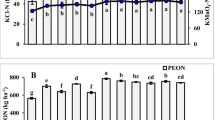
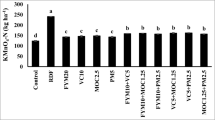
K2SO4-EON constituted more than 30% of TEN pools. K2SO4-extractable AAs accounted for 25% of EON pools and nearly 10% of TEN pools in rhizosphere soils. Overall, both K2SO4-EON and extractable AAs contents had positive correlations with TEN pools.
Conclusions
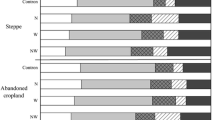
EON represented a major component of TEN pools in garden and paddy soils under traditional planting conditions. Although only a small proportion of the EON was present in the form of water-extractable and K2SO4-extractable AAs, the release of AAs from soil exchangeable sites might be an important source of organic nitrogen (N) for plant growth. Our findings suggest that the content of most organic forms of N was significantly greater in rhizosphere than in bulk soil zone samples. However, it was also apparent that the TEN pool content was lower in rhizosphere than in bulk soil samples without added N.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bai, H.Y., Xiao, J.Z., 1998. Experimental Research and StatisticalzAnalysis. World Book Press, Xi’an, China, p.120–128 (in Chinese).
Bray, R.H., Kurtz, L.T., 1945. Determination of total, organic, and available forms of phosphorus in soils. Soil Sci., 59(1):39–45. [doi:10.1097/00010694-194501000-00006]
Bregliani, M.M., Ros, G.H., Temminghoff, E.J.M., van Riemsdijk, W.H., 2010. Nitrogen mineralization in soils related to initial extractable organic nitrogen: effect of temperature and time. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal., 41(11):1383–1398. [doi:10.1080/00103621003759387]
Bremner, J.M., 1965. Organic Forms of Nitrogen. In: Black, C.A. (Ed.), Methods of Soil Analysis. American Society of Agronomy, Madison, p.1238–1255.
Cabrera, M.L., Beare, M.H., 1993. Alkaline persulfate oxidation for determining total nitrogen in microbial biomass extracts. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J., 57(4):1007–1012. [doi:10. 2136/sssaj1993.03615995005700040021x]
Chantigny, M.H., 2003. Dissolved and water-extractable organic matter in soils: a review on the influence of land use and management practices. Geoderma, 113(3–4):357–380. [doi:10.1016/S0016-7061(02)00370-1]
Chapin, F.S.III, Moilanen, L., Kielland, K., 1993. Preferential use of organic nitrogen for growth by a nonmycorrhizal arctic sedge. Nature, 361(6408):150–153. [doi:10.1038/361150a0]
Chen, C.R., Xu, Z.H., 2008. Analysis and behavior of soluble organic nitrogen in forest soils. J. Soils Sed., 8(6):363–378. [doi:10.1007/s11368-008-0044-y]
Christou, M., Avramides, E.J., Jones, D.L., 2006. Dissolved organic nitrogen dynamics in a Mediterranean vineyard soil. Soil Biol. Biochem., 38(8):2265–2277. [doi:10.1016/j. soilbio.2006.01.025]
DeAngelis, K.M., Lindow, S.E., Firestone, M.K., 2008. Bacterial quorum sensing and nitrogen cycling in rhizosphere soil. Fems. Microbiol. Ecol., 66(2):197–207. [doi:10. 1111/j.1574-6941.2008.00550.x]
Ding, T.P., Tian, S.H., Sun, L., Wu, L.H., Zhou, J.X., Chen, Z.Y., 2008. Silicon isotope fractionation between rice plants and nutrient solution and its significance to the study of the silicon cycle. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, 72(23):5600–5615. [doi:10.1016/j.gca.2008.09.006]
Ge, T.D., Song, S.W., Roberts, P., Jones, D.L., Huang, D.F., Iwasaki, K., 2009. Amino acids as a nitrogen source for tomato seedlings: the use of dual-labeled (13C, 15N) glycine to test for direct uptake by tomato seedlings. Environ. Exp. Bot., 66(3):357–361. [doi:10.1016/j.envexpbot.2009.05.004]
Haynes, R.J., 2005. Labile organic matter fractions as central components of the quality of agricultural soils: an overview. Adv. Agron., 85:221–268. [doi:10.1016/S0065-2113(04)85005-3]
Herman, D.J., Johnson, K.K., Jaeger, C.H., Schwartz, E., Firestone, M.K., 2006. Root influence on nitrogen mineralization and nitrification in Avena barbata rhizosphere soil. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J., 70(5):1504–1511. [doi:10.2136/sssaj2005.0113]
Hodge, A., 2001. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi influence decomposition of, but not plant nutrient capture from, glycine patches in soil. New Phytol., 151(3):725–734. [doi:10.1046/j.0028-646x.2001.00200.x]
Joergensen, R.G., Brookes, P.C., 1990. Ninhydrin-reactive nitrogen measurements of microbial biomass in 0.5 M K2SO4 soil extracts. Soil Biol. Biochem., 22(8):1023–1027. [doi:10.1016/0038-0717(90)90027-W]
Jones, D.L., Healey, J.R., Willett, V.B., Farrar, J.F., Hodge, A., 2005a. Dissolved organic nitrogen uptake by plants—an important N uptake pathway? Soil Biol. Biochem., 37(3):413–423. [doi:10.1016/j.soilbio.2004.08.008]
Jones, D.L., Shannon, D., Junvee-Fortune, T., Farrarc, J.F., 2005b. Plant capture of free amino acids is maximized under high soil amino acid concentrations. Soil Biol. Biochem., 37(1):179–181. [doi:10.1016/j.soilbio.2004.07.021]
Ke, Q.M., Lin, W.X., Huang, Z.F., Fang, J.L., Huang, M.Q., 2005. Simulation on the mathematical model of balanced fertilization in Pakchio vegetable crop. Chin. J. Eco-Agric., 13(1):119–121 (in Chinese).
Keeney, D.R., 1982. Nitrogen—Availability Indices. In: Page, A.L., Miller, R.H. (Eds.), Methods of Soil Analysis. Part 2: Chemical and Microbiological Properties. SSSA, Madison, p.711–730.
Keeney, D.R., Nelson, D.W., 1982. Nitrogen—Inorganic Forms. In: Page, A.L., Miller, R.H. (Eds.), Methods of Soil Analysis. Part 2, 2nd Ed. ASA and SSSA, Madison, WI, p.643–698.
Kelley, K.R., Stevenson, F.J., 1985. Characterization and extractability of immobilized 15N from the soil microbial biomass. Soil Biol. Biochem., 17(4):517–523. [doi:10. 1016/0038-0717(85)90019-7]
Kielland, K., McFarland, J.W., Ruess, R.W., Olson, K., 2007. Rapid cycling of organic nitrogen in taiga forest ecosystems. Ecosystems, 10(3):360–368. [doi:10.1007/s10021-007-9037-8]
Lipson, D., Näsholm, T., 2001. The unexpected versatility of plants: organic nitrogen use and availability in terrestrial ecosystems. Oecologia, 128(3):305–316. [doi:10.1007/s004420100693]
Lu, R.K., 1999. Soil Chemical Analysis Methods in Agriculture. China Agricultural Sciences and Technical Press, Beijing, China (in Chinese).
Lu, Y.H., Wassmann, R., Neue, H.U., Huang, C.Y., 2000. Dynamics of dissolved organic carbon and methane emissions in a flooded rice soil. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J., 64(6):2011–2017. [doi:10.2136/sssaj2000.6462011x]
Matsumoto, S., Ae, N., 2004. Characteristics of extractable soil organic nitrogen determined by using various chemical solutions and its significance for nitrogen uptake by crops. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr., 50(1):1–9. [doi:10. 1080/00380768.2004.10408446]
McDowell, W.H., Magill, A.H., Aitkenhead-Peterson, J.A., Aber, J.D., Merriam, J.L., Kaushal, S.S., 2004. Effects of chronic nitrogen amendment on dissolved organic matter and inorganic nitrogen in soil solution. For. Ecol. Manage., 196(1):29–41. [doi:10.1016/j.foreco.2004.03.010]
Murphy, D.V., Macdonald, A.J., Stockdale, E.A., Goulding, K.W.T., Fortune, S., Gaunt, J.L., Poulton, P.R., Wakefield, J.A., Webster, C.P., Wilmer, W.S., 2000. Soluble organic nitrogen in agricultural soils. Biol. Fert. Soils, 30(5-6):374–387. [doi:10.1007/s003740050018]
Näsholm, T., Kielland, K., Ganeteg, U., 2009. Uptake of organic nitrogen by plants. New Phytol., 182(1):31–48. [doi:10.1111/j.1469-8137.2008.02751.x]
Öhlund, J., Näsholm, T., 2001. Growth of conifer seedlings on organic and inorganic nitrogen sources. Tree Physiol., 21(18):1319–1326. [doi:10.1093/treephys/21.18.1319]
Olsen, S.R., Cole, C.V., Watanabe, F.S., Dean, L.A., 1954. Estimation of Available Phosphorus in Soils by Extraction with Sodium Bicarbonate. USDA Circular 939. US Department of Agriculture, Washington, DC, USA, p.1–18.
Raab, T.K., Lipson, D.A., Monson, R.K., 1996. Non-mycorrhizal uptake of amino acids by roots of the alpine sedge Kobresia myosuroides: implications for the alpine nitrogen cycle. Oecologia, 108(3):488–494. [doi:10. 1007/BF00333725]
Raab, T.K., Lipson, D.A., Monson, R.K., 1999. Soil amino acid utilization among species of the Cyperaceae: plant and soil processes. Ecology, 80(7):2408–2419. [doi:10.1890/0012-9658(1999)080[2408:SAAUAS]2.0.CO;2]
Reeve, J.R., Smith, J.L., Carpenter-Boggs, L., Reganold, J.P., 2009. Glycine, nitrate, and ammonium uptake by classic and modern wheat varieties in a short-term microcosm study. Biol. Fert. Soils, 45(7):723–732. [doi:10.1007/s00374-009-0383-x]
Ros, G.H., Hoffland, E., van Kessel, C., Temminghoff, E.J.M., 2009. Extractable and dissolved soil organic nitrogen: a quantitative assessment. Soil Biol. Biochem., 41(6): 1029–1039. [doi:10.1016/j.soilbio.2009.01.011]
Rothstein, D.E., 2009. Soil amino-acid availability across a temperate-forest fertility gradient. Biogeochemistry, 92(3):201–205. [doi:10.1007/s10533-009-9284-1]
Russell, R.S., 1982. Plant Root Systems, 1st Ed. McGraw-Hill, p.214.
Shi, G.R., 2004. Ecological effects of plant root exudates. Chin. J. Ecol., 23(1):97–101 (in Chinese).
Stevenson, F.J., 1982. Nitrogen-Organic Forms. In: Page, A.L. (Ed.), Methods of Soil Analysis, Part 2. Madison, WI, American Society Agronomy, p.625–641.
Stevenson, F.J., 1994. Humus Chemistry: Genesis, Composition, Reactions. John Wiley and Sons Inc., New York, p.443.
Willett, V.B., Green, J.J., Macdonald, A.J., Baddeley, J.A., Cadisch, G., Francis, S.M.J., Goulding, K.W.T., Saunders, G., Stockdale, E.A., Watson, C.A., et al., 2004. Impact of land use on soluble organic nitrogen in soil. Water Air Soil Poll., 4(6):53–60. [doi:10.1007/s11267-004-3013-5]
Wu, L.H., Mo, L.Y., Fan, Z.L., Tao, Q.N., Zhang, F.S., 2005. Absorption of glycine by three agricultural species under sterile sand culture conditions. Pedosphere, 15(3):286–292.
Yang, R., Yan, D.Y., Zhou, J.B., Wang, W.X., Ma, Q.A., 2007. Soluble organic nitrogen (SON) in different soils on the loess plateau of China. Acta Ecol. Sin., 27(4):1397–1403 (in Chinese).
Zheng, S.A., Zhang, M.K., 2011. Effect of moisture regime on the redistribution of heavy metals in paddy soil. J. Environ. Sci.-China, 23(3):434–443. [doi:10.1016/S1001-0742(10)60428-7]
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 30871595 and 31172032) and the Special Fund for Agro-Scientific Research in the Public Interest, China (No. 201003016)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Xy., Wu, Lh., Cao, Xc. et al. Organic nitrogen components in soils from southeast China. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 14, 259–269 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B1200104
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B1200104