Abstract
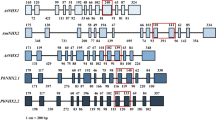
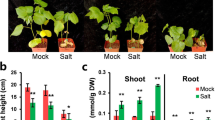
A novel vacuolar Na+/H+ exchanger, CgNHX1, was cloned from a halophytic species Chenopodium glaucum by using reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) and rapid amplification of cDNA ends (RACE) technique. Sequence alignment and phylogenetic analysis of 22 NHX genes from GenBank as well as the new CgNHX1 gene indicate that NHX genes shared a great degree of similarity, regardless of their glycophytic or halophytic origin. Expression of the CgNHX1 gene was induced by NaCl and peaked at 400 mmol/L NaCl. Overexpression of NHX1 genes in rice enhanced their tolerance to salt stress. However, there is no significant difference in salt tolerance among the transgenic rice plants overexpressing the NHX1 genes from either glycophytic or halophytic species. The Na+ content of both the wild type (WT) and transgenic plants increased when exposed to 50 and 100 mmol/L NaCl, and the Na+ concentration in transgenic plants was marginally higher than that of WT. Our data demonstrate that the overexpression of the NHX1 gene from either glycophytic or halophytic species resulted in the enhanced tolerance to salt stress at a similar level, suggesting that NHX gene per se might not be the reason accounting for the difference in salt tolerance between glycophytes and halophytes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Apse, M.P., Aharon, G.S., Snedden, W.A., Blumwald, E., 1999. Salt tolerance conferred by overexpression of a vacuolar Na+/H+ antiport in Arabidopsis. Science, 285(5431):1256–1258. [doi:10.1126/science.285.5431.1256]
Apse, M.P., Sottosanto, J.B., Blumwald, E., 2003. Vacuolar cation/H+ exchange, ion homeostasis, and leaf development are altered in a T-DNA insertional mutant of AtNHX1, the Arabidopsis vacuolar Na+/H+ antiporter. Plant J., 36(2):229–239. [doi:10.1046/j.1365-313X.2003.01871.x]
Aronson, P.S., 1985. Kinetic properties of the plasma membrane Na+-H+ exchanger. Ann. Rev. Physiol., 47(1): 545–560. [doi:10.1146/annurev.ph.47.030185.002553]
Brini, F., Hanin, M., Mezghani, I., Berkowitz, G.A., Masmoudi, K., 2007. Overexpression of wheat Na+/H+ antiporter TNHX1 and H+-pyrophosphatase TVP1 improve salt-and drought-stress tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana plants. J. Exp. Bot., 58(2):301–308. [doi:10.1093/jxb/erl251]
Chauhan, S., Forsthoefel, N., Ran, Y., Quigley, F., Nelson, D.E., Bohnert, H.J., 2000. Na+/myo-inositol symporters and Na+/H+-antiport in Mesembryanthemum crystallinum. Plant J., 24(4):511–522. [doi:10.1046/j.1365-313x.2000.00903.x]
Chen, S., Jin, W., Wang, M., Zhang, F., Zhou, J., Jia, Q., Wu, Y., Liu, F., Wu, P., 2003. Distribution and characterization of over 1000 T-DNA tags in rice genome. Plant J., 36(1):105–113. [doi:10.1046/j.1365-313X.2003.01860.x]
Counillon, L., Pouyssegur, J., Reithmeier, R.A., 1994. The Na+/H+ exchanger NHE-1 possesses N-and O-linked glycosylation restricted to the first N-terminal extracellular domain. Biochemistry, 33(34):10463–10469. [doi:10.1021/bi00200a030]
Flowers, T.J., Troke, P.F., Yeo, A.R., 1977. The mechanism of salt tolerance in halophytes. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol., 28(1):89–121. [doi:10.1146/annurev.pp.28.060177.000513]
Flowers, T.J., Haijibagheri, M.A., Clipson, N.J.W., 1986. Halophytes. Quart. Rev. Biol., 61(3):313–337. [doi:10.1086/415032]
Fukuda, A., Nakamura, A., Tanaka, Y., 1999. Molecular cloning and expression of the Na+/H+ exchanger gene in Oryza sativa. Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1446(1):149–155.
Gaxiola, R.A., Rao, R., Sherman, A., Grisafi, P., Alper, S.L., Fink, G.R., 1999. The Arabidopsis thaliana proton transporters, AtNhx1 and Avp1, can function in cation detoxification in yeast. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 96(4):1480–1485. [doi:10.1073/pnas.96.4.1480]
Greenway, H., Munns, R., 1980. Mechanisms of salt tolerance in non-halophytes. Ann. Rev. Plant Physiol., 31(1): 149–190. [doi:10.1146/annurev.pp.31.060180.001053]
Hamada, A., Shono, M., Xia, T., Ohta, M., Hayashi, Y., Tanaka, A., Hayakawa, T., 2001. Isolation and characterization of a Na+/H+ antiporter gene from the halophyte Atriplex gmelini. Plant Mol. Biol., 46(1):35–42. [doi:10.1023/A:1010603222673]
Hofmann, K.S.W., 1993. TM base—A database of membrane spanning proteins segments. Biol. Chem. Hoppe-Seyler, 347:166–172.
Jones, R.G.W., 1981. Salt Tolerance. In: Johnson, C.B. (Ed.), Physiological Processes. Limiting Plant Productivity. Butterworths, Iondon, p.271–292.
Li, J.Y., Zhang, F.C., Ma, J., Cai, L., Bao, Y.G., Wang, B., 2003. Using RT-PCR to amplify the NHX gene fragment in Atriplex dimorphostegia. Plant Physiol. Commun., 6(6):585–588 (in Chinese).
Ma, X.L., Zhang, Q., Shi, H.Z., Zhu, J.K., Zhao, Y.X., Ma, C.L., Zhang, H., 2004. Molecular cloning and different expression of a vacuolar Na+/H+ antiporter gene in Suaeda salsa under salt stress. Biol. Plantarum, 48(2):219–225. [doi:10.1023/B:BIOP.0000033448.96998.44]
Ohta, M., Hayashi, Y., Nakashima, A., Hamada, A., Tanaka, A., Nakamura, T., Hayakawa, T., 2002. Introduction of a Na+/H+ antiporter gene from Atriplex gmelini confers salt tolerance to rice. FEBS Lett., 532(3):279–282. [doi:10.1016/S0014-5793(02)03679-7]
Orlowski, J., Grinstein, S., 1997. Na+/H+ exchangers of mammalian cells. J. Biol. Chem., 272(36):22373–22376. [doi:10.1074/jbc.272.36.22373]
Qiu, Q.S., Guo, Y., Dietrich, M.A., Schumaker, K.S., Zhu, J.K., 2002. Regulation of SOS1, a plasma membrane Na+/H+ exchanger in Arabidopsis thaliana, by SOS2 and SOS3. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 99(12):8436–8441. [doi:10.1073/pnas.122224699]
Quintero, F.J., Blatt, M.R., Pardo, J.M., 2000. Functional conservation between yeast and plant endosomal Na+/H+ antiporters. FEBS Lett., 471(2–3):224–228. [doi:10.1016/S0014-5793(00)01412-5]
Shi, H., Zhu, J.K., 2002. Regulation of expression of the vacuolar Na+/H+ antiporter gene AtNHX1 by salt stress and abscisic acid. Plant Mol. Biol., 50(3):543–550. [doi:10.1023/A:1019859319617]
Shi, H., Ishitani, M., Kim, C., Zhu, J.K., 2000. The Arabidopsis thaliana salt tolerance gene SOS1 encodes a putative Na+/H+ antiporter. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 97(12):6896–6901. [doi:10.1073/pnas.120170197]
Shi, H., Quintero, F.J., Pardo, J.M., Zhu, J.K., 2002. The putative plasma membrane Na+/H+ antiporter SOS1 controls long-distance Na+ transport in plants. Plant Cell, 14(2):465–477. [doi:10.1105/tpc.010371]
Shi, H., Lee, B.H., Wu, S.J., Zhu, J.K., 2003. Overexpression of a plasma membrane Na+/H+ antiporter gene improves salt tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana. Nat. Biotechnol., 21(1):81–85. [doi:10.1038/nbt766]
Xiong, L.M., Zhu, J.K., 2002. Salt Tolerance. In: Somerville, C.R., Meyerowitz, E.M. (Eds.), The Arabidopsis Book. American Society of Plant Biologists, Rockville, MD, p.1–22. [doi:10.1199/tab.0048]
Xu, M., Zhu, L., Shou, H., Wu, P., 2005. A PIN1 family gene, OsPIN1, involved in auxin-dependent adventitious root emergence and tillering in rice. Plant Cell Physiol., 46(10):1674–1681. [doi:10.1093/pcp/pci183]
Zhang, H.X., Blumwald, E., 2001. Transgenic salt-tolerant tomato plants accumulate salt in foliage but not in fruit. Nat. Biotechnol., 19(8):765–768. [doi:10.1038/90824]
Zhu, J.K., 2001. Plant salt tolerance. Trends Plant Sci., 6(2):66–71. [doi:10.1016/S1360-1385(00)01838-0]
Zorb, C., Noll, A., Karl, S., Leib, K., Yan, F., Schubert, S., 2005. Molecular characterization of Na+/H+ antiporters (ZmNHX) of maize (Zea mays L.) and their expression under salt stress. J. Plant Physiol., 162(1):55–66. [doi:10.1016/j.jplph.2004.03.010]
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
The two authors contributed equally to this work
Project supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 30471118 and 30460015) and the Key Project of Education Ministry of China (No. 205178)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Jy., He, Xw., Xu, L. et al. Molecular and functional comparisons of the vacuolar Na+/H+ exchangers originated from glycophytic and halophytic species. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 9, 132–140 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B0710445
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B0710445