Abstract
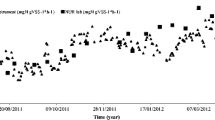
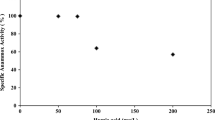
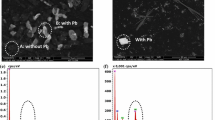
Performance of biological phosphorus removal in the oxic-settling-anaerobic (OSA) process was investigated. Cell staining and fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH) were used to analyze characteristics and microbial community of sludge. Experimental results showed that phosphorus removal efficiency was near 60% and the amount of biological phosphorus accumulation in aerobic sludge of the OSA system was up to 26.9 mg/g. Biological phosphorus removal efficiency was partially inhibited by carbon sources in the continuous OSA system. Contrasted to the OSA system, biological phosphorus removal efficiency was enhanced by 14% and the average total phosphorus (TP) contents of aerobic sludge were increased by 0.36 mg/g when sufficient carbon sources were supplied in batch experiments. Staining methods indicated that about 35% of microorganisms had typical characteristics of phosphorus accumulating organisms (PAOs). FISH analysis demonstrated that PAOMIX-binding bacteria were predominant microbial communities in the OSA system, which accounted for around 28% of total bacteria.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
APHA (American Public Health Association/American Water Works Association/Water Environment Federation), 1995. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater. Washington, DC, USA.
Bond, P.L., Erhart, R., Wagner, M., Keller, J., Blackall, L.L., 1999. Identification of some of the major groups of bacteria in efficient and nonefficient biological phosphorus removal activated sludge systems. Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 65(9):4077–4084.
Chen, G.H., An, K.J., Saby, S., Brois, E., Djafer, M., 2003. Possible cause of excess sludge reduction in an oxic-settling-anaerobic activated sludge process (OSA process). Water Res., 37(16):3855–3866. [doi:10.1016/S0043-1354(03)00331-2]
Chudoba, P., Chang, J., Capedeville, B., 1991. Synchronized division of activated sludge microorganisms. Water Res., 25(7):817–822. [doi:10.1016/0043-1354(91)90161-I]
Chudoba, P., Chudoba, J., Capdeville, B., 1992. The aspect of energetic uncoupling of microbial growth in the activated sludge process: OSA system. Water Sci. Technol., 26:2477–2480.
Crocetti, G.R., Hugenholtz, P., Bond, P.L., Schuler, A., Keller, J., Jenkins, D., Blackall, L.L., 2000. Identification of polyphosphate accumulating organisms and design of 16S rRNA-directed probes for their detection and quantitation. Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 66(3):1175–1182. [doi:10.1128/AEM.66.3.1175-1182.2000]
Kong, Y., Nielsen, J.L., Nielsen, P.H., 2005. Identity and ecophysiology of uncultured actinobacterial polyphosphate-accumulating organisms in full-scale enhanced biological phosphorus removal plants. Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 71(7):4076–4085. [doi:10.1128/AEM.71.7.4076-4085.2005]
Lee, D.S., Jeon, C.O., Park, J.M., 2001. Biological nitrogen removal with enhanced phosphate uptake in a sequencing batch reactor using single sludge system. Water Res., 35(16):3968–3976. [doi:10.1016/S0043-1354(01)00132-4]
Liu, Y., Lin, Y.M., Tay, J.H., 2005a. The elemental compositions of P-accumulating microbial granules developed in sequencing batch reactors. Process Biochem., 40(10): 3258–3262. [doi:10.1016/j.procbio.2005.03.002]
Liu, Y., Zhang, T., Fang, H.H.P., 2005b. Microbial community analysis and performance of a phosphate-removing activated sludge. Bioresour. Technol., 96(11):1205–1214. [doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2004.11.003]
Murray, R.G.E., Doetsch, R.N., Robinow, C.F., 1994. Determinative and Cytological Light Microscopy. In: Gehardt, P., Murray, R.G.E., Wood, W.A., Krieg, N.R. (Eds.), Methods for General and Molecular Bacteriology. American Society for Microbiology. Washington, DC, p.21–41.
Pijuan, M., Guisasola, A., Baeza, J.A., Carrera, J., Casas, C., Lafuente, J., 2006. Net P-removal deterioration in enriched PAO sludge subjected to permanent aerobic conditions. J. Biotechnol., 123(1):117–126. [doi:10.1016/j.jbiotec.2005.10.018]
Saby, S., Djafer, M., Chen, G.H., 2003. Effect of low ORP in anoxic sludge zone on excess sludge production in oxic-settling-anoxic activated sludge process. Water Res., 37(1):11–20. [doi:10.1016/S0043-1354(02)00253-1]
Sanz, J.L., Köchling, T., 2007. Molecular biology techniques used in wastewater treatment: an overview. Process Biochem., 42(2):119–133. [doi:10.1016/j.procbio.2006.10/003]
Serafim, L.S., Lemos, P.C., Levantesi, C., Tandoi, V., Santos, H., Reis, M.A.M., 2002. Methods for detection and visualization of intracellular polymers stored by polyphosphate-accumulating microorganisms. J. Microbiol. Methods, 51(1):1–18. [doi:10.1016/S0167-7012(02)-00056-8]
Tchobanoglous, G., Burton, F.L., Stensel, H.D., 2003. Wastewater Engineering Treatment and Reuse. Tsinghua University Publishing House, Beijing, p.565, 805–806.
Tsuneda, S., Ohno, T., Soejima, K., Hirata, A., 2006. Simultaneous nitrogen and phosphorus removal using denitrifying phosphate-accumulating organisms in a sequencing batch reactor. Biochem. Eng. J., 27(3):191–196. [doi:10.1016/j.bej.2005.07.004]
Wang, J.F., Jin, W.B., Zhao, Q.L., Liu, Z.G., Lin, J.K., 2007. Performance of treating wastewater and anti-impact in oxic-settling-anoxic (OSA) process for minimization of excess sludge. Environ. Sci., 28(11):2488–2493 (in Chinese).
Wei, Y.S., van Houten, R.T., Borger, A.R., Eikelboom, D.H., Fan, Y.B., 2003. Minimization of excess sludge production for biological wastewater treatment. Water Res., 37(18):4453–4467. [doi:10.1016/S0043-1354(03)-00441-X]
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Project (No. 2006BAC19B04) supported by the National Key Technology R&D Program of China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Jf., Zhao, Ql., Jin, Wb. et al. Performance of biological phosphorus removal and characteristics of microbial community in the oxic-settling-anaerobic process by FISH analysis. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. A 9, 1004–1010 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.A0820064
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.A0820064
Keywords
- Excess sludge reduction
- Biological phosphorus removal
- Phosphate accumulating organisms (PAOs)
- DAPI (4′,6′-diamidino-2-phenyl indol dihydrochloride)
- Fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH)