Abstract
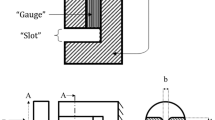
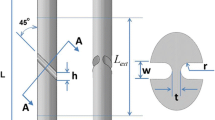
The Iosipescu shear test specimen geometry has been investigated by a number of research workers in recent years with conflicting results. The paper describes a numerical study of a compact shear test specimen, based on the Iosipescu geometry, which is proposed to investigate size effects in shear failure. A range of geometries has been studied and the extreme cases are reported. Results are presented for the largest absolute principal stresses together with a detailed study of the stresses between and around the roots of the two notches introduced in the test specimens. The results for the largest absolute principal stresses show that tensile stresses are created at the roots of the two notches. These tensile stresses may result in Mode I failure and probably account for the Mode I or mixed mode fracture observed in tests using the Iosipescu geometry. The results for the distribution of stresses between the roots of the two notches show that deep notches increase the likelihood of shear fracture prior to tensile failure. Shallow notches give a stress distribution similar to that developed in the indirect tensile test and hence tensile failure is likely to precede shear failure in such cases. Further numerical and experimental work is proposed.
Résumé
La géométrie de spécimen d’essai de cisaillement d’Iosipescu a été étudiée par un certain nombre de chercheurs ces dernières années avec des résultats contradictoires. Le sujet décrit une étude numérique d’un spécimen compact d’essai de cisaillement, basée sur la géométrie d’Iosipescu, qui est proposée pour étudier des effets de taille en rupture de cisaillement. Une gamme des géométries a été étudiée et les cas extrêmes sont rapportés. Des résultats sont présentés pour les plus grandes contraintes principales absolues ainsi qu’une étude détaillée des contraintes entre et autour des racines des deux entailles présentées dans les spécimens. Les résultats pour les plus grandes contraintes principales absolues prouvent que des contraintes de tensions sont créées aux racines des deux entailles. Ces contraintes de tension peuvent être les résultats de la rupture en mode I et expliquer probablement le mode I ou le mode mixte observé dans les essais employant le Iosipescu test spécimen géométrie. La distribution des contraintes entre les racines des deux entailles prouve que les entailles profondes augmentent la probabilité de la rupture de cisaillement avant la rupture de tension. Les entailles peu profondes donnent une distribution de contraintes semblables à celle développée dans l’essai de tension indirect et par conséquent la rupture en tension est susceptible de précéder la rupture de cisaillement dans ces cas-ci. Nous proposons beaucoup plus de travaux numériques et expérimentaux.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liu K, Barr B, Watkins J (1985) Mode II fracture of fibre reinforced concrete materials. Int J Cem Compos Lightweight Concr 7:93–101
Barr B (1987) The fracture characteristics of FRC materials in shear. In: Shah SP, Batson GB (eds) Fiber reinforced concrete properties and applications. American Concrete Institute, Detroit, MI, SP-105, pp 27–53
Bazant ZP, Pfeiffer PA (1985) Tests on shear fracture and strain––softening in concrete. Proceedings of the second symposium on the interaction of non-nuclear munitions with structures. Florida
Barr B, Thomas WF (1986) A study of the fracture characteristics of glass reinforced cement. Proceedings of the third international symposium on developments in FRC composites, Sheffield, England
Ingraffea ARM, Panthaki MJ (1985) Shear fracture tests of concrete beams. Proceedings of the seminar sponsored by the Japan society for the promotion science and the US National Science Foundation, Tokyo, Japan
Swartz SE, Taha NM (1987) Preliminary investigation of the suitability of the Iosipescu test specimen for determining mixed mode fracture properties of concrete. Special Report No.191, College of Engineering, Kansas State University
Barr B, Hasso, Khalifa S (1987) A study of mode II (shear) fracture of notched beams, cylinders and cores. Fracture of concrete and rock. SEM-RILEM international conference, Houston, USA
Carpinteri A (1987) Interaction between tensile strength failure and mixed mode crack propagation in concrete. Department of Structure Engineering, Politecnico di Torino, Italy
Aliabadi MH, Saleh AL (2002) Fracture mechanics analysis of cracking in plain and reinforced concrete using boundary element method. Engineering Fracture mechanics, London, England, pp 267–280
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
An erratum to this article is available at http://dx.doi.org/10.1617/s11527-009-9497-8.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Derradj, M., Kaci, S. Numerical study of compact shear (Mode II) type test specimen geometry. Mater Struct 41, 1203–1210 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1617/s11527-007-9318-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1617/s11527-007-9318-x