Abstract
The expediency of using precast spun concrete columns and other members of annular cross sections reinforced by high-strength steel bars is discussed. Test material properties and production, curing and testing procedures, response factors and ultimate compressive stresses of plain and reinforced spun concrete specimens are presented. The strength and strain features of compressed tubular reinforced concrete members are considered. Modeling of a bearing capacity of eccentrically loaded members of annular cross sections is based on the concepts of bending with an concentrical force and compression with a bending moment. The comparison of modeling and test data of concentrically and eccentrically loaded members is analysed.












Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- A c and A s :
-
Cross-sectional areas of concrete and reinforcement sections
- E c and E s :
-
Moduli of elasticity of concrete and reinforcement
- M E :
-
Applied total bending moment
- M R :
-
Resisting bending moment
- N E :
-
Applied total compressive force
- N EP :
-
Quasi-permanent compressive force
- N R :
-
Resisting compressive force
- d :
-
Outer diameter of annular cross sections
- e 0 :
-
First order eccentricity
- e = e 0η:
-
Second order eccentricity
- f′ c :
-
Sustained strength of concrete
- f c and f cm :
-
Cylinder (compressive) strength of concrete and its mean value
- f c1 :
-
Compressive strength of spun concrete hollow cylinders
- f c2 :
-
Compressive strength of spun concrete in reinforced members
- f st and f sc :
-
Conventional strengths of reinforcement in tension and compression
- h :
-
Height of tubular specimens
- f cc :
-
Compressive strength of spun concrete in tubular members
- f pr :
-
Prism strength of concrete
- f 0.2 :
-
0.2% proof-stress of reinforcement
- k c and k s :
-
Efficiency factors for compressive concrete and reinforcement sections
- k p :
-
Factor of a quasi-permanent load effect
- k 2 :
-
Conversion factor of a hollow cylinder effect
- r 1 and r 2 :
-
Radii of annular cross section circles
- r s :
-
Radius of the reinforcement circle
- t = r 2−r 1 :
-
Thickness of annular cross sections
- δ:
-
Coefficient of variation
- γ:
-
Partial safety factor
- ɛ c1 :
-
Compressive strain in the concrete at the peak stress f c1
- ɛ c2 and ɛ c3 :
-
Compressive strains in the concrete at the peak stress f c2 by typical and bi-linear stress-strain relations
- ɛ′ cu and ɛ cu :
-
Ultimate compressive strains in the concrete adjacent with steel bars of concentrically and eccentrically loaded columns
- ɛ′ s and ɛ s :
-
Ultimate compressive steel strains of concentrically and eccentrically loaded columns
- η:
-
Factor of second order moment effect
- θ:
-
Parameter which contains model uncertainties
- λ:
-
Additional angle of the compression zone
- ρ = A s /A c :
-
Reinforcement ratio
- σ′ sc and σ sc :
-
Ultimate compressive steel stresses of concentrically and eccentrically loaded columns
- ψ:
-
Angle of the total compression zone
References
Quast U (2002) Columns and masts of prestressed spun concrete 6th International symposium on utilization of high strength/high performance concrete. Leipzig, Germany, pp 519–526
MacGregor JG (1988) Reinforced concrete, mechanics and design. Practice-Hall International Inc.
Kudzys A, Kliukas R, Vadlūga R (1993) Utilization of high-strength spun concrete and reinforcing steel in compressive structures. High-Strength Concrete, Proceedings, Vol. 1. Norway, pp 259–268
Kaufmann JP, Hesselbarth Moser K and Terrasi GP (2005) Application of fiber reinforced high performance composites in spun-cast elements. Mater Struct 38:549–555
EN (1992–1), Eurocode 2: Design of concrete structures – Part 1: General rules and rules for buildings, Brussels
ACI Committee 318-05 (2005) Building code requirements for structural concrete. American Concrete Institute, Farmington Hills, Mich
Dilger WH, Rao SVKM (1997) High performance concrete mixtures for spun cast concrete poles. PCI J 42(4):82–89
González OM, Robles F, Díaz De Cossío (1974) Strength and deformation of prestressed concrete elements. Reinforced concrete engineering. John Wiley and Sons, New York, pp 194–301
Diniz SMC (2005) Effect of concrete age specification on the reliability of HSC columns. ICOSSAR, Augusti G, Schuëller GJ, Ciampoli M (eds) Millpress, Rotterdam, pp 565–572
Diniz SMC (2002) Long-term reliability of eccentrically-loaded HSC columns. 6th International symposium on utilization of high strength/high performance concrete. Leipzig, Germany, pp 1601–1615
Vadlūga R, Kliukas R, Garalevičius R (1996) Strength and deformability estimation of centrifuged concrete. Journal of Civil Engineering and Management (Statyba), 4(8), Vilnius, pp 73–83
Hussaini AAl, Regan PE, Hue H-Y, Ramdant K-E (1993) The behaviour of HSC columns under axial load. High-Strength Concrete, Proceedings, Vol. 1, Norway, pp 83–89
Vadlūga R (1983) The evaluation of strength of reinforced concrete members of ring cross-section. Concrete Structures, Proceedings 14, Vilnius, pp 94–102 (in Russian)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendix
Appendix
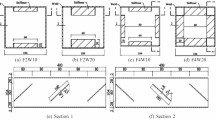
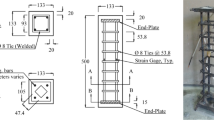
Tables 1 and 2 list essential properties of the reinforced spun concrete specimens. Each specimen has a numeric designation. The second letters A (Aksomitas) and K (Kliukas) relate to the names of researchers.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kudzys, A., Kliukas, R. The resistance of compressed spun concrete members reinforced by high-strength steel bars. Mater Struct 41, 419–430 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1617/s11527-007-9255-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1617/s11527-007-9255-8