Abstract
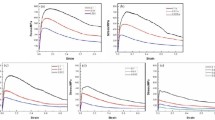
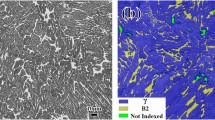
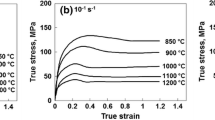
The high-temperature flow behavior and flow stress sensitivity of BT25y alloy were investigated. Results show that hot deformation is accompanied by the dynamic competition between work hardening and flow softening. The strain rate sensitivity exponent m tends to decrease with the strain rate after a first rise, and reaches the maximum at strain rate of 0.1 s−1. There is a large temperature range exhibiting m values above 0.2 at strain rates of 0.01–0.1 s−1. The temperature sensitivity exponent s shows an overall dropping trend with elevated temperature. The strain hardening exponent n first decreases and then increases with the strain at strain rate of 0.01 s−1. Large positive n values lie in areas with high strain rate, and small negative n values are located in areas with lower temperature and small strain rate. Secondary lamellar α appears near the phase transition temperature. The microstructure presents elongated characteristics at high strain rate.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
E.O. Ezugwu and Z.M. Wang: Titanium alloys and their machinability—A review. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 68 (3), 262 (1997).
T. Wang, H.Z. Guo, Y.W. Wang, X.N. Peng, Y. Zhao, and Z.K. Yao: The effect of microstructure on tensile properties, deformation mechanisms and fracture models of TG6 high temperature titanium alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 528 (6), 2370 (2011).
X. Ma, W.D. Zeng, F. Tian, and Y.G. Zhou: The kinetics of dynamic globularization during hot working of a two phase titanium alloy with starting lamellar microstructure. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 548, 6 (2012).
X.M. Yang, H.Z. Guo, H.Q. Liang, Z.K. Yao, and S.C. Yuan: Flow behavior and constitutive equation of Ti–6.5Al–2Sn–4Zr–4Mo–1W–0.2Si titanium alloy. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 25 (4), 1347 (2016).
V.N. Moiseyev: Titanium Alloys: Russian Aircraft and Aerospace Applications (CRC Press, New York, USA, 2006); p. 21.
K.X. Wang, W.D. Zeng, Y.Q. Zhao, Y.J. Lai, and Y.G. Zhou: Dynamic globularization kinetics during hot working of Ti17 alloy with initial lamellar microstructure. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 527, 2559 (2010).
X. Ma, W.D. Zeng, F. Tian, Y. Sun, and Y.G. Zhou: Modeling constitutive relationship of BT25 titanium alloy during hot deformation by artificial neural network. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 21 (8), 1591 (2012).
Y. Nan, Y.Q. Ning, H.Q. Liang, H.Z. Guo, Z.K. Yao, and M.W. Fu: Work-hardening effect and strain-rate sensitivity behavior during hot deformation of Ti–5Al–5Mo–5V–1Cr–1Fe alloy. Mater. Des. 82, 84 (2015).
H.Q. Liang, Y. Nan, Y.Q. Ning, H. Li, J.L. Zhang, Z.F. Shi, and H.Z. Guo: Correlation between strain-rate sensitivity and dynamic softening behavior during hot processing. J. Alloys Compd. 632, 478 (2015).
Y.H. Liu, Y.Q. Ning, X.M. Yang, Z.K. Yao, and H.Z. Guo: Effect of temperature and strain rate on the workability of FGH4096 superalloy in hot deformation. Mater. Des. 95, 669 (2016).
J. Luo and M.Q. Li: Strain rate sensitivity and strain hardening exponent during the isothermal compression of Ti60 alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 538, 156 (2012).
W.S. Lee, C.F. Lin, T.H. Chen, and H.H. Hwang: Effects of strain rate and temperature on mechanical behavior of Ti–15Mo–5Zr–3Al alloy. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 1 (4), 336 (2008).
S.T. Chiou, H.L. Tsai, and W.S. Lee: Impact mechanical response and microstructural evolution of Ti alloy under various temperatures. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 209 (5), 2282 (2009).
W.S. Lee and C.F. Lin: High-temperature deformation behavior of Ti6Al4V alloy evaluated by high strain-rate compression tests. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 5 (1–3), 127 (1998).
T. Seshacharyulu, S.C. Medeiros, W.G. Frazier, and Y.V.R.K. Prasad: Hot working of commercial Ti–6Al–4V with an equiaxed α — β microstructure: Materials modeling considerations. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 284 (1–2), 184 (2000).
W.J. Jia, W.D. Zeng, Y.G. Zhou, J.R. Liu, and Q.J. Wang: High-temperature deformation behavior of Ti60 titanium alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 528, 4068 (2011).
Y.C. Lin and X.M. Chen: A critical review of experimental results and constitutive descriptions for metals and alloys in hot working. Mater. Des. 32 (4), 1733 (2011).
Y.C. Lin, M.S. Chen, and J. Zhang: Modeling of flow stress of 42CrMo steel under hot compression. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 499 (1–2), 88 (2009).
J. Cui, H. Yang, Z. Sun, H. Li, Z. Li, and C. Shen: Flow behavior and constitutive model using piecewise function of strain for TC11 alloy. Rare Met. Mater. Eng. 41 (3), 397 (2012).
J. Lin and F.P.E. Dunne: Modelling grain growth evolution and necking in superplastic blow-forming. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 43 (3), 595 (2001).
G.C. Wang and M.W. Fu: Maximum m superplasticity deformation for Ti–6Al–4V titanium alloy. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 192–193, 555 (2007).
A.K. Ghosh: On the measurement of strain-rate sensitivity for deformation mechanism in conventional and ultra-fine grain alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 463 (1–2), 36 (2007).
R. Hales, S.R. Holdsworth, M.P. O’Donnell, I.J. Perrin, and R.P. Skelton: A code of practice for the determination of cyclic stress-strain data. Mater. High Temp. 19 (4), 165 (2002).
W.A. Backfen, I.R. Turner, and D.H. Avery: Superplasticity in an Al–Zn alloy. ASM Trans. Q. 57, 980 (1964).
J. Luo, M.Q. Li, W.X. Yu, and H. Li: The variation of strain rate sensitivity exponent and strain hardening exponent in isothermal compression of Ti–6Al–4V alloy. Mater. Des. 31, 741 (2010).
L.M. Lei, X. Huang, M.M. Wang, L.Q. Wang, J.N. Qin, and S.Q. Lu: Effect of temperature on deformation behavior and microstructures of TC11 titanium alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 528 (28), 8236 (2011).
Y. Karpat: Temperature dependent flow softening of titanium alloy Ti6Al4V: An investigation using finite element simulation of machining. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 211 (4), 737 (2011).
Y. Zhao, H.Z. Guo, Z.F. Shi, Z.K. Yao, and Y.Q. Zhang: Microstructure evolution of TA15 titanium alloy subjected to equal channel angular pressing and subsequent annealing at various temperatures. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 211 (8), 1364 (2011).
X.H. Gong, Y. Wang, Y.M. Xia, P. Ge, and Y.Q. Zhao: Experimental studies on the dynamic tensile behavior of Ti–6Al–2Sn–Zr–3Mo–1Cr–2Nb–Si alloy with Widmanstatten microstructure at elevated temperatures. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 523 (1–2), 53 (2009).
L. Li and N. Zhou: Experimental investigation of hot deep drawability of EW94 heat resistant alloy sheet. J. Aeronaut. Mater. 33 (5), 22 (2013).
R. Ebrahimi and N. Pardis: Determination of strain-hardening exponent using double compression test. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 518 (1–2), 56 (2009).
J.H. Holloman: Tensile deformation. Trans. Metall. Soc. AIME 162, 268 (1945).
H.P. Stüwe and P. Les: Strain rate sensitivity of flow stress at large strains. Acta Mater. 46 (18), 6375 (1998).
X. Ma, W.D. Zeng, F. Tian, Y.G. Zhou, and Y. Sun: Optimization of hot process parameters of Ti–6.7Al–2Sn–2.2Zr–2.1Mo–1W–0.2Si alloy with lamellar starting microstructure based on the processing map. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 545, 132 (2012).
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
This study was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51205319).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, X., Guo, H., Yao, Z. et al. Strain rate sensitivity, temperature sensitivity, and strain hardening during the isothermal compression of BT25y alloy. Journal of Materials Research 31, 2863–2875 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2016.294
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2016.294