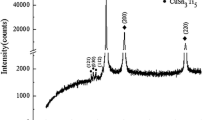
Abstract
Instrumented nanoindentation technique is a powerful approach for accurately measuring mechanical properties of materials in micron or even nanoscale. In this article, the effect of tin (Sn) content upon mechanical properties of the α-phase in Cu–Sn alloys was studied by using an instrumented nanoindentation. The experimental results revealed that: (i) the hardness of the α-phase exhibited a linear relationship with Sn content (C) increasing, i.e., H = 0.0757C + 0.8916, when it was less than the maximum solid solubility (15.8 wt.%), which is in good agreement with the Friedel–Mott–Suzuki theory; (ii) the variation of Young’s modulus in a narrow range of 120–130 GPa is attributed to orientation variation of the α-phase in casting Cu–Sn dendrites.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. Gordon and R. Knopf: Metallurgy of bronze used in tools from Machu Picchu, Peru. Archaeometry 48, 57 (2006).
J.S. Park, C.W. Park, and K.J. Lee: Implication of peritectic composition in historical high-tin bronze metallurgy. Mater. Charact. 60, 1268 (2009).
R.D. Joseph: Copper and Copper Alloys. (ASM International. Handbook Committee, 2001), pp. 44–46.
R. Selver and R. Varol: Some thermal and physical characteristics of sintered tin bronze bearings. Metall. 57, 28 (2002).
B.S. Ünlüa and E. Atik: Evaluation of effect of alloy elements in copper based CuSn10 and CuZn30 bearings on tribological and mechanical properties. J. Alloy. Comp. 489, 262 (2010).
T.K. He: Synthetic study on the alloying technique for bronze in the pre-QIN period. Studies in the History of Natural Sciences 16, 273 (1997) (Article in Chinese, Abstract in English).
D.A. Scott: Metallography and Microstructure of Ancient and Historic Metals. (The Getty Conservation Institute J. Paul Getty Museum, Malibu CA, 1991), p. 121.
J. Audy and K. Audy: Analysis of bell materials: Tin bronzes. China Foundry 5, 199 (2008).
J.B. Pethicai, R. Hutchings, and W.C. Oliver: Hardness measurement at penetration depths as small as 20 nm. Philos. Mag. A 48, 593 (1983).
W.C. Oliver and G.M. Pharr: An improved technique for determining hardness and elastic modulus using load and displacement sensing indentation experiments. J. Mater. Res. 7, 1564 (1992).
X.D. Li and B. Bhushan: A review of nanoindentation continuous stiffness measurement technique and its applications. Mater. Charact. 48, 11 (2002).
W.C. Oliver and G.M. Pharr: Measurement of hardness and elastic modulus by instrumented indentation: Advances in understanding and refinements to methodology. J. Mater. Res. 19, 3 (2004).
F. Riede and J.M. Wheeler: Testing the “Laacher See hypothesis”: Tephra as dental abrasive. J. Archaeol. Sci. 36, 2384 (2009).
L.A. Darnell, M.F. Teaford, K.J.T. Livi, and T.P. Weihs: Variations in the mechanical properties of Alouatta palliata molar enamel. Am. J. Phys. Anthropol. 141, 7 (2010).
G.D. Sanson, S.A. Kerr, and K.A. Gross: Do silica phytoliths really wear mammalian teeth? J. Archaeol. Sci. 34, 526 (2007).
H. Lerner, X.D. Du, A. Costopoulos, and M. Ostoja-Starzewski: Lithic raw material physical properties and use-wear accrual. J. Archaeol. Sci. 34, 711 (2007).
R. Fleischer and W. Hibbard: The Relation Between Structure and Mechanical Properties of Metals, Vol. 1. (H.M.S.O., London, 1963), p. 262.
N. Mott and F. Nabarro: Report on the Strength of Solids. (Physical Society, London, 1948), pp. 1–19.
N. Mott: Imperfections in Nearly Perfect Crystals. (John Wiley, New York, 1952), p. 173.
F. Nabarro: Dislocations and Properties of Real Materials. (The Institute of Metals, London, 1985), p. 152.
J. Friedel: Dislocations. (Addison-Wesley, New York, 1964), p. 224.
T. Suzuki, S. Takeuchi, and H. Yoshinaga: Dislocation Dynamics and Plasticity. (Springer-Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg, 1991), p. 32.
E. Schmidt and W. Boas: Plasticity of Crystals, English Translation. (Hughes and Co., London, 1950), p.191.
S.N. Dub, Y.Y. Lim, and M.M. Chaudhri: Nanohardness of high purity Cu (111) single crystals: The effect of indenter load and prior plastic sample strain. J. Appl. Phys. 107, 043510 (2010).
ISO 1577-1: “Metallic materials-Instrumented indentation test for hardness and materials parameter-Test method.” (ISO Central Secretariat, Geneva, Switzerland, 2002).
J. Chen and Y.S. Lai: Towards elastic anisotropy and strain-induced void formation in Cu-Sn crystalline phases. Microelectron. Reliab. 49, 264 (2009).
R. An, C.Q. Wang, Y.H. Tian, and H. Wu: Determination of the elastic properties of Cu3Sn through first-principles calculations. J. Electron. Mater. 37(4), 477 (2008).
Z.D. Guo, X.F. Wang, X.P. Yang, D.M. Jiang, X.M. Ma, and H.W. Song: Relationships between young’s modulus, hardness and orientation of grain in polycrystalline copper. Acta Metall. Sin. 44, 901 (2008).
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Department of Culture of Wuhan, China, and the Higher education of scientific research project Foundation of China (No. 20070486016).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., He, K., Liao, C. et al. Measurements of mechanical properties of α-phase in Cu–Sn alloys by using instrumented nanoindentation. Journal of Materials Research 27, 192–196 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2011.299
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2011.299