Abstract
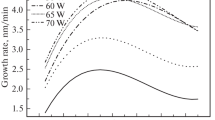
The paper correlates the growth and structure formation with the properties of indium-tin-oxide (ITO) films fabricated by pulsed reactive magnetron deposition onto amorphous substrates held at elevated temperatures ranging from room temperature to 510 °C. The evolution of the microstructure is consistent with the well-known structure zone model. The temperature dependence of the film texture is described with consideration of the interplay between the shadowing and surface-diffusion processes. It is shown that deposition at elevated temperatures lowers the crystallization threshold and is more effective in reducing resistivity than the postdeposition vacuum annealing at comparable temperatures. The films grown at a substrate temperature of 400 and 510 °C have the lowest resistivity of 1.2 × 10−4 Ω cm, the highest free electron density of 1.2 to 1.0 × 1021 cm−3, and mobility of 35–42 cm2 V−1 s−1 and exhibit the strongest (222) texture with the largest grain size.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
B.G. Lewis D.C. Paine: Applications and processing of transparent conducting oxides. MRS Bull. 25(8), 22 2000
I. Hamberg C.G. Granqvist: Evaporated Sn-doped In2O3 films: Basic optical properties and applications to energy-efficient windows. J. Appl. Phys. 60, R123 1986
R.B.H. Tahar, T. Ban, Y. Ohya Y. Takahashi: Tin doped indium oxide thin films: Electrical properties. J. Appl. Phys. 83, 2631 1998
M. Kamei, Y. Shigesato, I. Yasui, N. Taga S. Takaki: Comparative study of heteroepitaxial and polycrystalline tin-doped indium oxide films. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 218, 267 1997
H. Wulff, M. Quaas H. Steffen: Investigation of plasma-deposited ITO films by GIXR and GIXRD. Thin Solid Films 355–356, 395 1999
M. Kamei, Y. Shigesato S. Takaki: Origin of characteristic grain-subgrain structure of tin-doped indium oxide films. Thin Solid Films 259, 38 1995
G. Frank H. Köstlin: Electrical properties and defect model of tin-doped indium oxide layers. Appl. Phys. A: Solids Surf. 27, 197 1982
G.B. Gonzalez, T.O. Mason, J.P. Quintana, O. Warschkow, D.E. Ellis, J-H. Hwang, J.P. Hodges J.D. Jorgensen: Defect structure studies of bulk and nano-indium-tin oxide. J. Appl. Phys. 96, 3912 2004
J. Ederth, P. Johnsson, G.A. Niklasson, A. Hoel, A. Hultaker, P. Heszler, C.G. Granqvist, A.R. van Doorn, M.J. Jongerius D. Burgard: Electrical and optical properties of thin films consisting of tin-doped indium oxide nanoparticles. Phys. Rev. B 68, 155410 2003
H. Fujivara M. Kondo: Effects of carrier concentration on the dielectric function of ZnO:Ga and In2O3:Sn studied by spectroscopic ellipsometry: Analysis of free-carrier and band-edge absorption. Phys. Rev. B 71, 075109 2005
A. Rogozin, N. Shevchenko, M. Vinnichenko, F. Prokert, V. Cantelli, A. Kolitsch W. Moeller: Real-time evolution of the indium tin oxide film properties and structure during annealing in vacuum. Appl. Phys. Lett. 85, 212 2004
A. Rogozin, N. Shevchenko, M. Vinnichenko, M. Seidel, A. Kolitsch W. Möller: Annealing of indium tin oxide films by electric current: Properties and structure evolution. Appl. Phys. Lett. 89, 061908 2006
A.I. Rogozin, M.V. Vinnichenko, A. Kolitsch W. Moeller: Effect of deposition parameters on properties of ITO films prepared by reactive middle frequency pulsed dual magnetron sputtering. J. Vac. Sci. Technol., A 22, 349 2004
A. Rogozin, M. Vinnichenko, N. Shevchenko, A. Kolitsch W. Moeller: Plasma influence on the properties and structure of indium tin oxide films produced by reactive middle frequency pulsed magnetron sputtering. Thin Solid Films 496, 197 2006
U. Kreissig, R. Gago, M. Vinnichenko, P. Fernández-Hidalgo, R.J. Martín-Palma J.M. Martínez-Duart: Heavy-ion ERDA and spectroscopic ellipsometry characterization of a SiOC:H layered structure as functional coating on polymeric lenses. Nucl. Instr. Methods Phys. Res. B 219–220, 908 2004
H-E. Cheng M-H. Hon: Texture formation in titanium nitride films prepared by chemical vapour deposition. J. Appl. Phys. 79, 8047 1996
JCPDS-ICDD No. 6-416. Joint Committee on Powder Diffraction Standards ASTM Philadelphia, PA 1991
J.C. Bravman R. Sinclair: The preparation of cross-section specimens for transmission electron-microscopy. J. Elect. Mic. Tech. 1, 53 1984
S.K. Choi J.I. Lee: Effect of film density on electrical properties of indium oxide films deposited by dc magnetron sputtering. J. Vac. Sci. Technol., A 19, 2043 2001
W. Fukarek H. Kersten: Application of dynamic in situ ellipsometry to the deposition of tin-doped indium oxide films by reactive direct-current magnetron sputtering. J. Vac. Sci. Technol., A 12, 523 1994
S. Berg T. Nyberg: Fundamental understanding and modeling of reactive sputtering processes. Thin Solid Films 476, 215 2005
J.A. Thornton: The microstructure of sputter-deposited coatings. J. Vac. Sci. Technol., A 4, 3059 1986
I. Petrov, P.B. Barna, L. Hultman J.E. Greene: Microstructural evolution during film growth. J. Vac. Sci. Technol., A 21, 1 2003
S. Muranaka: Crystallization of amorphous In2O3 films during film growth. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 30, L2062 1991
S. Muranaka, Y. Bando T. Takada: Influence of substrate temperature and film thickness on the structure of reactively evaporated In2O3. Thin Solid Films 151, 355 1987
C.W. Ow-Yang, D. Spinner, Y. Shigesato D.C. Paine: A time-resolved reflectivity study of the amorphous-to-crystalline transformation kinetics in dc-magnetron sputtered indium tin oxide. J. Appl. Phys. 83, 145 1998
P.C.P. Bronsveld, J.K. Rath, R.E.I. Schropp, T. Mates, A. Fejfar, B. Rezek J. Kočka: Internal structure of mixed phase hydrogenated silicon thin films made at 39 degrees C. Appl. Phys. Lett. 89, 051922 2006
U. Geyer, U. von Hülsen P. Thiyagarajan: Surface roughening and columnar growth of thin amorphous CuTi films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 70, 1691 1997
E. Nishimura, H. Ohkawa, P.K. Song Y. Shigesato: Microstructures of ITO films deposited by d.c. magnetron sputtering with H2O introduction. Thin Solid Films 445, 235 2003
S. Ishibashi, Y. Higuchi, Y. Ota K. Nakamura: Low resistivity indium-tin oxide transparent conductive films. I. Effect of introducing H2O gas or H2 gas during direct current magnetron sputtering. J. Vac. Sci. Technol., A 8, 1399 1990
J.E. Greene, J-E. Sundgren, L. Hultman, I. Petrov D.B. Bergstrom: Development of preferred orientation in polycrystalline TiN layers grown by ultrahigh vacuum reactive magnetron sputtering. Appl. Phys. Lett. 67, 2928 1995
Y.S. Jung S.S. Lee: Development of indium tin oxide film texture during DC magnetron sputtering deposition. J. Cryst. Growth 259, 343 2003
K. Ellmer, R. Mientus H. Rossner: In situ investigation by energy dispersive x-ray diffraction (EDXRD) of the growth of magnetron sputtered ITO films. Surf. Coat. Technol. 142–144, 1094 2001
M. Quaas, H. Steffen, R. Hippler H. Wulff: Influence of microstructure on oxygen diffusion in plasma-deposited In/Sn films. Thin Solid Films 420–421, 306 2002
N. Yamada, I. Yasui, Y. Shigesato, H. Li, Y. Ujihira K. Nomura: Effect of substrate temperature on the structural, electrical and optical properties of ITO films prepared by RF magnetron sputtering. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 39, 4158 2000
D.C. Paine, T. Whitson, D. Janiac, R. Beresford, C. Ow Yang B. Lewis: A study of low temperature crystallization of amorphous thin film indium–tin–oxide. J. Appl. Phys. 85, 8445 1999
H. Ohta, M. Orita, M. Hirano, H. Tanji, H. Kawazoe H. Hosono: Highly electrically conductive indium–tin–oxide thin films epitaxially grown on yttria-stabilized zirconia (100) by pulsed laser deposition. Appl. Phys. Lett. 76, 2740 2000
A. Suzuki, T. Matsushita, T. Aoki, Y. Yoneyama M. Okuda: Pulsed laser deposition of transparent conducting indium tin oxide films in magnetic field perpendicular to plume. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 40, L401 2001
A. Suzuki, T. Matsushita, T. Aoki M. Okuda: Highly conducting transparent indium tin oxide films prepared by pulsed laser deposition. Thin Solid Films 411, 23 2002
P. Nath, R.F. Bunshah, B.M. Basol O.M. Staffsud: Electrical and optical properties of In2O3: Sn films prepared by activated reactive evaporation. Thin Solid Films 72, 463 1980
I.A. Rauf: Low resistivity and high mobility tin-doped indium oxide films. Mater. Lett. 18, 123 1993
J.R. Bellingham, W.A. Phillips C.J. Adkins: Intrinsic performance limits in transparent conducting oxides. J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 11, 263 1992
S. Ray, R. Banerjee, N. Basu, A.K. Batabyal A.K. Barua: Properties of tin doped indium oxide thin films prepared by magnetron sputtering. J. Appl. Phys. 54, 3497 1983
T.J. Coutts, D.L. Young X. Li: Characterization of transparent conducting oxides. MRS Bull. 25(8), 58 2000
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The authors are grateful to H. Reuther for Auger analysis and to B. Schmidt for preparation of thermally oxidized Si wafers. The AFM studies were carried out with financial support from the Spanish Ministerio de Eduicacion y Ciencia Grant No. FIS2006-12253-C06-03.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rogozin, A., Vinnichenko, M., Shevchenko, N. et al. Effect of elevated substrate temperature on growth, properties, and structure of indium tin oxide films prepared by reactive magnetron sputtering. Journal of Materials Research 22, 2319–2329 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2007.0293
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2007.0293