Abstract
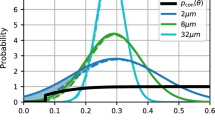
Based on computer-generated templates, percolation objects were fabricated. Random-site, semi-continuous swiss cheese, and semi-continuous inverse swiss-cheese percolation models above the percolation threshold were considered. The water-filled pore space was investigated by nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) imaging and in the presence of a pressure gradient, by NMR velocity mapping. The percolation backbones were determined using velocity maps. The fractal dimension of the backbones turned out to be smaller by about 17 % than that of the complete cluster. As a further relation of interest, the volume-averaged velocity was calculated as a function of the probe volume radius. In a certain scaling window, the resulting dependence can be represented by a power law. The experimental results favorably compare to computer simulations with the finite-element method (FEM) or the finite-volume method (FVM). Thermal convection in percolation clusters of different porosities was studied using the NMR velocity mapping technique. The velocity distribution is related to the convection roll size distribution. The maximum velocity as a function of the porosity clearly visualizes a closed-loop percolation transition if the Rayleigh number conditions are appropriate. Percolation theory suggests a relationship between the anomalous diffusion exponent and the fractal dimension of the cluster, i.e. between a dynamic and a structural parameter. Interdiffusion between two compartments initially filled with H2O and D2O, respectively, was examined by proton imaging. The results confirm the theoretical expectation. Finally, advection driven dispersive transport was investigated in the large Péclet number limit. The superdiffusive transport anomaly was demonstrated and discussed in terms of the non-local advection-diffusion and the fractional diffusion theories.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
D. Stauffer and A. Aharony, Introduction to Percolation Theory (Taylor Francis, 1992).
A. Bunde and S. Havlin, (Eds.), Fractals and Disordered Systems (Springer-Verlag, 1996).
H. Hermann, Stochastic Models of Heterogeneous Materials (Trans Tech Publ., 1991).
S. Feng, B. I. Halperin, and P. N. Sen, Phys. Rev. B 35, 197 (1987).
A. Klemm, H.-P. Müller, R. Kimmich, Phys. Rev. E 55, 4413 (1997).
R. Kimmich, NMR Tomography, Diffusometry, Relaxometry (Springer-Verlag, 1997).
D. A. Nield and A. Bejan, Convection in Porous Media (Springer-Verlag, 1992).
H.-P. Müller, J. Weis, and R. Kimmich, Phys. Rev. E 52, 5195 (1995).
H.-P. Müller, R. Kimmich, and J. Weis, Phys. Rev. E 54, 5278 (1996).
J. S. Andrade Jr, M. P. Almeida, J. Mendes Filho, S. Havlin, B. Suki, and H. E. Stanley, Phys. Rev. Letters 79, 3901 (1997).
F. Klammler and R. Kimmich, Phys. Med. Biol. 35, 67 (1990).
S. L. Codd, B. Manz, J. D. Seymour, and P. T. Callaghan, Phys. Rev. E 60, R3491 (1999).
A. Kapitulnik, A. Aharony, G. Deutscher, and D. Stauffer, J. Phys. A: Math. Gen. 16, L269 (1983).
M. Porto, A. Bunde, S. Havlin, and H. E. Roman, J. Phys. Rev. E 56, 1667 (1997).
M. D. Shattuck, R. P. Behringer, G. A. Johnson, and J. G. Georgiadis, Phys. Rev. Letters 75, 1934 (1995).
S. Alexander and R. Orbach, J. Physique-Lettres (Paris) 43, L625 (1982).
D. C. Hong, S. Havlin, H. J. Herrmann, and H. E. Stanley, Phys. Rev. B 30, 4083 (1984).
J. G. Zabolitzky, Phys. Rev. B 30, 4077 (1984).
G. I. Taylor, Proc. Roy. Soc. Lond. A 219, 186 (1953).
R. Aris, Proc. Roy. Soc. Lond. A 235, 67 (1956).
H. Brenner, J. Stat. Phys. 62, 1095 (1991).
C. van den Broeck, Physica A 168, 677 (1990).
J. H Cushman, B.X. Hu and T.R. Ginn, J. Stat. Phys. 75, 859 (1994).
D.L. Koch and J.F. Brady, J. Fluid Mech. 200, 173 (1987).
J. Koplik, S. Redner and D. Wilkinson, Phys. Rev. A 37, 2619 (1988).
M. Sahimi, Rev. Mod. Phys, 65, 1393 (1993).
H.A. Makse, J.S. Andrade and H.E. Stanley, Phys. Rev. E 61, 583 (2000).
R. Metzler and J. Klafter, Europhys. Lett. 51, 492 (2000).
W. R. Schneider and W. Wyss, J. Math. Phys. 30, 134 (1989).
J. D. Seymour and P. T. Callaghan, Al ChE J. 43, 2096 (1997).
O. J. Poole and D. W. Salt, J. Phys. A; Math. Gen. 29, 7959 (1996).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kimmich, R., Klemm, A., Weber, M. et al. Flow, Diffusion, Dispersion, and Thermal Convection in Percolation Clusters: NMR Experiments and Numerical FEM/FVM Simulations. MRS Online Proceedings Library 651, 271 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1557/PROC-651-T2.7.1
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/PROC-651-T2.7.1