Abstract
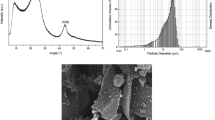
Composite phase change materials (PCM) were prepared by mixing exfoliated graphite nanoplatelets (xGnP) into paraffin wax. The two types of graphite nanoplatelets that were investigated were xGnP-1 having thickness of 10 nm and a diameter of 1 um and xGnP-15 having the same thickness with a platelet diameter of 15 um. Direct casting and two roll milling were used to prepare samples. Scanning electron microscopy images show that the nanofillers disperse very well in paraffin matrix without noticeable agglomeration. Paraffin/xGnP-15 PCM consistently exhibited higher thermal conductivity than xGnP-1 PCM. The improvement in thermal conductivity was as high as 5 fold for xGnP-15 composites and 2 fold for xGnP-1 composites at 4 vol%. The aspect ratio, particle orientation, and interface density between the conductive particles and the polymer matrix were found to be the critical parameters in determining the conductivities of the resulting nanocomposites. The thermal physical properties of the nanocomposites were investigated by differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) and thermal gravimetric analysis (TGA). It was found that the latent heat of nanocomposites was not negatively affected in the presence of xGnP particles and the thermal stability improved.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S.M. Hasnain. Energy Convers. Manage, 39, 1127 (1998)
S.M. Hasnain.; in Energy ‘93. Proc.5 th Intl. Energy Conference, Seoul, Korea 1993
K.K. Pillai.; B.J. Brinkworth. Appl. Energy. 2, 205 (1976)
A.S.Luyt, eXpress Polym. Lett, 2, 3, 147 (2008)
R.Velraj.; R.V. Seeniraj.; B.Hafner.; C.Faber.; K.Schwarzer. Sol.Energy. 60, 281 (1997)
S.M. Hasnain.; in Proc. COMSTECH NIST Workshop on New Trends and Break-throughs in Solar Energy Research. Islamabad, Pakistan, 1994
J. Fukai. Energy Convers. Manage. 41, 1543 (2000)
A. Elgafy.; K. Lafdi. Carbon, 43, 3067 (2005)
S. Pincemin., Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. C 92, 603 (2008)
S.Kim.; L.T.Drzal.; Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. C 93, 136 (2009)
H.Fukushima.; Ph.D Thesis, Michigan State University, East Lansing, MI, USA, 2003
K.Kalaitzidou, Ph.D. Thesis, Michigan State University, East Lansing, MI, USA, 2006
K.Kalaitzidou.; H.Fukushima.; L.T.Drzal, Carbon, 45 1446 (2007)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiang, J., Drzal, L.T. Enhanced Thermal Conductivity of Phase Change Materials Modified by Exfoliated Graphite Nanoplatelets. MRS Online Proceedings Library 1218, 610 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1557/PROC-1218-Z06-10
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/PROC-1218-Z06-10