Abstract
Dilute magnetic semiconductors (DMS) show promise as materials that can exhibit ferromagnetism at room temperature (RT). However, the nature of ferromagnetism in this material system must be well understood in order to allow intelligent design of RT spintronic devices. This work investigates the magnetic properties of the as-grown films and the effect of Mn incorporation on crystal integrity and device performance. Ga1-xMnxN films were grown by MOCVD on c-plane sapphire substrates with varying thickness and Mn concentration. Homogenous Mn incorporation throughout the films was verified with Secondary Ion Mass
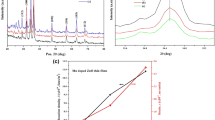
Spectroscopy (SIMS), and no macroscopic second phases (MnxNy) were detected using X-ray diffraction (XRD). Superior crystalline quality in the MOCVD-grown films relative to Mn-implanted GaN epilayers was confirmed via Raman spectroscopy. Vibrating sample magnetometry (VSM) measurements showed an apparent room temperature ferromagnetic hysteresis in the as-grown epiayers. Similarly, a marked decrease in the magnetization was observed with annealing and silicon doping, as well as in post-growth annealed Mg-codoped samples. The observed decrease in üB per Mn with increasing Mn concentration is explained by Raman spectroscopy results, which show a decrease in long-range lattice ordering and an increase in nitrogen vacancy concentration with increasing Mn concentration. Light emitting diodes (LEDs) containing a Mn-doped active region have also been produced. Devices were fabricated with different Mn-doped active layer thicknesses, and I-V characteristics show that the devices become more resistive as thickness of the Mn-doped active layer increases. The electroluminescence of the Mn-containing layers is red-orange vice blue. Under ultraviolet illumination, there is an increase in the measured VSM signal from Mn-containing layers.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
T. Dietl, H. Ohno, et al., Science 287 (2000) 1019.
S. A. Wolf, D. D. Awschalom, et al., Science 294 (2001) 1488.
K. C. Ku, S. J. Potashnik, et al., Appl. Phys. Lett. 82 (2003) 2302.
Y.-J. Zhao, P. Mahadevan, et al., Appl. Phys. Lett. 84 (2004) 3753.
K. Sato and H. Katayama-Yoshida, Semicond. Sci. Technol. 17 (2002) 367.
J. Kang, K. J. Chang, et al., Journal of Superconductivity 18 (2005) 55.
V. I. Litvinov, Phys. Rev. B 72 (2005) 195209.
M. L. Reed, N. A. El-Masry, et al., Appl. Phys. Lett. 79 (2001) 3473.
N. Theodoropoulou, A. F. Hebard, et al., Appl. Phys. Lett. 78 (2001) 3475.
M. E. Overberg, C. R. Abernathy, et al., Appl. Phys. Lett. 79 (2001) 1312.
M. H. Kane, A. Asghar, et al., Semicond. Sci. Technol. 20 (2005) L5.
S. Dhar, O. Brandt, et al., Appl. Phys. Lett. 82 (2003) 2077.
R. Giraud, S. Kuroda, et al., Europhysics Letters 65 (2004) 553.
B. K. Rao and P. Jena, Phys. Rev. Lett. 89 (2002) 185504.
Y. L. Soo, S. Kim, et al., Appl. Phys. Lett. 84 (2004) 481.
M. Yokoyama, H. Yamaguchi, et al., J. Appl. Phys. 97 (2005) 10D317.
F. E. Arkun, M. J. Reed, et al., Appl. Phys. Lett. 85 (2004) 3809.
S. Sonoda, I. Tanaka, et al., (2005) Submitted.
M. J. Reed, F. E. Arkun, et al., Appl. Phys. Lett. 86 (2005) 102504.
U. Haboeck, H. Siegle, et al., Physica Status Solidi C 0 (2003) 1710.
W. Limmer, W. Ritter, et al., Appl. Phys. Lett. 72 (1998) 2589.
A. Sato, K. Azumada, et al., Appl. Phys. Lett. 87 (2005) 021907.
H. Munekata, Physica E 25 (2004) 160.
Acknowledgments
M.S. gratefully acknowledges the support of the Alexander von Humboldt-Foundation. One author (M.K.) was supported by a graduate fellowship from the National Science Foundation. This work was supported in part by grants from the National Science Foundation (ECS#0224266, U. Varshney) and the Air Force Office of Scientific Research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kane, M.H., Fenwick, W., Strassburg, M. et al. Structural, Optical, and Magnetic Behavior of in-situ Doped, MOCVD-Grown Ga1-xMnxN Epilayers and Heterostructures. MRS Online Proceedings Library 892, 504 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1557/PROC-0892-FF07-04-EE05-04
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/PROC-0892-FF07-04-EE05-04