Abstract
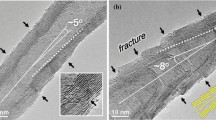
In this work, we report a method to synthesize a peculiar composite structure of tubular carbon nanofibers (CNFs) growing on a microsized tin (Sn) whisker. The material used is a commercially available copper clad laminate (CCL). The CCL is composed of a surface copper (Cu) layer and a bottom polymer (phenol-formaldehyde resin) board, in which the polymer board is used as the carbon source. Using lithography and lift-off techniques, the Cu layer was patterned to a stripelike Cu trace. A Sn thin film was then evaporated on the polymer board near the Cu trace. To release the residue stress that resulted from the evaporation; Sn whiskers with diameters of about 2 to 5 μm were formed on the Sn thin film after evaporation. By passing an electric current through the Cu trace, the Cu trace was heated due to Joule heating and served as a heating source for the thermal decomposition of phenol-formaldehyde. After heat treatment, the CNFs grew on the surface of the Sn whiskers with tubular hollow-cored structure. The diameter of the tubular CNFs is about hundreds of nanometers and their length can reach several micrometers. The growth mechanism of the brushlike composite structure is also discussed.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
S.H. Yoon, C.W. Park, H. Yang, Y. Korai, I. Mochida, R.T.K. Baker, N.M. Rodriguez: Novel carbon nanofibers of high graphitization as anodic materials for lithium ion secondary batteries. Carbon 42, 21 2004
R.L. Price, M.C. Waid, K.M. Haberstroh, T.J. Webster: Selective bone cell adhesion on formulations containing carbon nanofibers. Biomaterials 24, 1877 2003
M. Tsuji, M. Kubokawa, R. Yano, N. Miyamae, T. Tsuji, M.S. Jun, S. Hong, S. Lim, S.H. Yoon, I. Mochida: Fast preparation of PtRu catalysts supported on carbon nanofibers by the microwave-polyol method and their application to fuel cells. Langmuir 23, 387 2007
V. Vicky, T. Katerina, C. Nikos: Carbon nanofiber-based glucose biosensor. Anal. Chem. 78, 5538 2006
K. Kamada, T. Ikuno, S. Takahashi, T. Oyama, T. Yamamoto, M. Kamizono, S. Ohkura, S. Honda, M. Katayama, T. Hirao, K. Oura: Surface morphology and field-emission characteristics of carbon nanofiber films grown by chemical vapor deposition on alloy catalyst. Appl. Surf. Sci. 212–213, 383 2003
M. Rzepka, E. Bauer, G. Reichenauer, T. Schliermann, B. Bernhardt, K. Bohmhammel, E. Henneberg, U. Knoll, H.E. Maneck, W. Braue: Hydrogen storage capacity of catalytically grown carbon nanofibers. J. Phys. Chem. B 109, 14979 2005
S. Iijima: Helical microtubules of graphitic carbon. Nature 354, 56 1991
Y.H. Wang, S.C. Chiu, K.M. Lin, Y.Y. Li: Formation of carbon nanotubes from polyvinyl alcohol using arc-discharge method. Carbon 42, 2535 2004
H. Kajiuraa, H. Huanga, S. Tsutsuia, Y. Murakamib, M. Miyakoshi: High-purity fibrous carbon deposit on the anode surface in hydrogen DC arc-discharge. Carbon 40, 2423 2002
N. Krishnankutty, N.M. Rodriguez, R.T.K. Baker: Effect of copper on the decomposition of ethylene over an iron catalyst. J. Catal. 158, 217 1996
R.L.V. Wala, T.M. Ticichb, V.E. Curtis: Substrate–support interactions in metal-catalyzed carbon nanofiber growth. Carbon 39, 2277 2001
Y.W. Yen, M.D. Huang, F.J. Lin: Synthesize carbon nanotubes by a novel method using chemical vapor deposition-fluidized bed reactor from solid-stated polymers. Diamond Relat. Mater. 17, 567 2008
K.N. Tu, J.C.M. Li: Spontaneous whisker growth on lead-free solder finishes. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 409, 131 2005
M.E. Williams, K-W. Moon, W.J. Boettinger, D. Josell, A.D. Deal: Hillock and whisker growth on Sn and SnCu electrodeposits on a substrate not forming interfacial intermetallic compounds. J. Electron. Mater. 36, 214 2007
A.T. Huang, A.M. Gusak, K.N. Tu, Y.S. Lai: Thermomigration in SnPb composite flip chip solder joints. Appl. Phys. Lett. 88, 141911 2006
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to acknowledge the financial support of National Science Council of Taiwan, Republic of China (ROC) through Grant NSC 96-2221-E-005-064-MY3. This work is supported in part by the Ministry of Education, Taiwan, ROC under the ATU plan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Cm., Shih, Py. A peculiar composite structure of carbon nanofibers growing on a microsized tin whisker. Journal of Materials Research 23, 2668–2673 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1557/JMR.2008.0326
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/JMR.2008.0326