Abstract
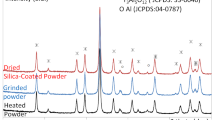
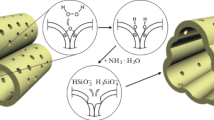
Cobalt nanoparticles were synthesized on silica thin films by heat treating Co/silica films spun on thermally oxidized Si substrates. The as-deposited films were calcined in vacuum (∼0.03 Torr) for 2 h at 500 °C, followed by reduction in hydrogen at 650 °C for up to 15 h. The reduction process is characterized as one of time-dependent evolution of nanoparticles in both physical appearance and phase nature, eventually leading to the formation of well-dispersed Co nanoparticles, as ascertained by x-ray photoelectron spectroscopy and scanning electron microscopy. Slow conversion of Co ions into metallic Co observed in this study is ascribed to the absence of a Co3O4 phase that forms predominantly during calcination in air. Atomic force microscopy revealed a marked increase in the surface roughness of the film due to the development of nanoparticles. A distinct duplex-layer structure was observed in the reduced film, which consisted of the upper layer laden with nanoparticles and the lower layer essentially particle-free. The growth of the upper layer appears to be controlled by the upward diffusion of Co2+ in the film during the reduction process.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
W.D. Zhang, Y. Wen, W.C. Tjiu, G.Q. Xu and L.M. Gan: Synthesis of vertically aligned carbon nanotubes on metal deposited quartz plates. Carbon 40, 1981 (2002).
A. Weidenkaff, S.G. Ebbinghaus, P. Mauron., A. Reller, Y. Zhang and A. Zuttel: Metal nanoparticles for the production of carbon nanotube composite materials by decomposition of different carbon sources. Mater. Sci. Eng., C 19, 119 (2002).
C.J. Lee and J. Park: Growth and structure of carbon nanotubes produced by thermal chemical vapor. Carbon 39, 1891 (2001).
S. Hofmann, B. Kleinsorge, C. Ducati, A.C. Ferrari and J. Robertson: Low-temperature plasma enhanced chemical vapour deposition of carbon nanotubes. Diamond Relat. Mater. 13, 1171 (2004).
T. Matsuzaki, K. Takeuchi, T.A. Hanoaka, H. Arakawa and Y. Sugi: Hydrogenation of carbon monoxide over highly dispersed cobalt catalysts derived from cobalt (II) acetate. Catal. Today 28, 251 (1996).
A. Kukoveca, Z. Konya, N. Nagaraju, I. Willems, A. Tamasi, A. Fonseca, J.B. Nagy and I. Kirisci: Catalytic synthesis of carbon nanotubes over Co, Fe and Ni containing conventional and sol.gel silica.aluminas. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2, 3071 (2000).
C.L. Cheung, A. Kurtz, H. Park and C.M. Lieber: Diameter controlled synthesis of carbon nanotubes. J. Phys. Chem. B 106, 2429 (2002).
O.A. Nerushev, S. Dittmar, R.E. Morjan, F. Rohmund and E.E.B. Campbell: Particle size dependence and model for iron-catalyzed growth of carbon nanotubes by thermal chemical vapor deposition. J. Appl. Phys. 93, 4185 (2003).
Y. Huh, J.Y. Lee, J. Cheon, Y.K. Hong, J.Y. Koo, T.J. Lee and C.J. Lee: Controlled growth of carbon nanotubes over cobalt nanoparticles by thermal chemical vapor deposition. J. Mater. Chem. 13, 2297 (2003).
M. Nath, B.C. Satishkumar, A. Govindaraj, C.P. Vinod and C.N.R. Rao: Formation of bundles of aligned carbon and carbon-nitrogen nanotubes on silica-supported iron and cobalt catalysts. Chem. Phys. Lett. 322, 333 (2000).
W.Z. Li, S.S. Xie, L.X. Qian, B.H. Chang, B.S. Zou, W.Y. Zhou, R.A. Zhao and G. Wang: Large-scale synthesis of aligned carbon nanotubes. Science 274, 1701 (1996).
H. Ago, T. Komatsu, S. Ohshima, Y. Kuriki and M. Yumura: Dispersion of metal nanoparticles for aligned carbon nanotube arrays. Appl. Phys. Lett. 77(1), 79 (2000).
M. Torrones, N. Grobert, J. Olivares, J.P. Zhang, H. Terrones, K. Kordatos, W.K. Hsu, J.P. Hare, P.D. Townsend, K. Prassides, A.K. Cheetham, H.W. Kroto and D.R.M. Walton: Controlled production of aligned-nanotube bundles. Nature 388, 52 (1997).
A.M. Cassell, S. Verma, L. Delzeit, M. Meyyappan and J. Han: Combinatorial optimization of heterogeneous catalysts used in the growth of carbon nanotubes. Langmuir 17, 260 (2001).
F.M. Cano, O.L.J. Gijzeman, F.M.F. de Groot and B.M. Weckhuysen: Manganese promotion in cobalt-based Fischer–Tropsch catalysis. Stud. Surf. Sci. Catal. 147, 271 (2004).
J.M. Jablonski, J. Okal, Potoczna-D. Petru and L. Krajczyk: High temperature reduction with hydrogen, phase composition, and activity of cobalt/silica catalysts. J. Catal. 220, 146 (2003).
R.C. Reuel and C.H. Bartholomew: Effects of support and dispersion on the CO hydrogenation activity/selectivity properties of Cobalt. J. Catal. 85, 78 (1984).
L.B. Backman, A. Rautiainen, M. Lindblad and A.O.I. Krause: Effect of support and calcination on the properties of cobalt catalysts prepared by gas phase deposition. Appl. Catal., A 191, 55 (2000).
S. Sun, N. Tsubaki and K. Fujimoto: The reaction performances and characterization of Fischer-Tropsch synthesis Co/SiO2 catalysts prepared from mixed cobalt salts. Appl. Catal., A 202, 121 (2000).
J. Panpranot, S. Kaewkun, P. Praserthdam, J.G. Goodwin Jr.: Effect of cobalt precursors on the dispersion of cobalt on MCM-41. Catal. Lett. 91, 95 (2003).
R. Riva, H. Miessner, R. Vitali and G. Piero Del: Metal-support interactionin Co/SiO2 and Co/TiO2. Appl. Catal., A 196, 111 (2000).
N. Tsubaki, S. Sun and K. Fujimoto: Different functions of the noble metals added to cobalt catalysts for Fischer–Tropsch synthesis. J. Catal. 199, 236 (2001).
A.Y. Khodakov, J. Lunch, D. Bazin, B. Rebours, N. Zanier, B. Moisson and P. Chaumette: Reducibility of cobalt species in silica-supported Fischer–Tropsch catalysts. J. Catal. 168, 16 (1997).
J. Panpranot, J.G. Goodwin Jr. and A. Sayari: CO hydrogenation on Ru-promoted Co/MCM-41 catalysts. J. Catal. 211, 530 (2002).
A. Barbier, A. Hanif, J. Dalmon and G.A. Martin: Preparation and characterization of well-dispersed and stable Co/SiO2 catalysts using the ammonia method. Appl. Catal., A 168, 333 (1998).
C.M. Lok, G. Gray, and G.J. Kelly: Catalysts with high cobalt surface area. International Patent Publication Number, WO 01/87480 A1 (2001).
E. Iglesia: Natural Gas Conversion IV, Studies in Surface Science and Catalysis, (Elsevier Science B.V, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1997), p. 153, 107.
W.K. Jozwiak, E. Szubiakiewicz, J. Goralski, A. Klonkowski and T. Paryjczak: Physico-chemical and catalytic study of the Co/SiO2 catalysts. Kinetics Catal. 45, 247 (2004).
E.J.C. Dawnay, M.A. Fardad, M. Green and E.M. Yeatman: Growth and characterization of semiconductor nanoparticles in porous sol-gel films. J. Mater. Res. 12, 3115 (1997).
P. Yang, C.F. Song, M.K. Lu, X. Yin, G.J. Zhou, D. Xu and D.R. Yuan: The luminescence of PbS nanoparticles embedded in sol-gel silica glass. Chem. Phys. Lett. 345, 429 (2001).
A. Martucci, J. Fick, J. Schell, G. Battaglin and M. Guglielmi: Microstructural and nonlinear optical properties of silica–titania sol-gel film doped with PbS quantum dots. J. Appl. Phys. 86, 79 (1999).
Potoczna-D. Petru and L. Krajczyk: Spreading of cobalt phase and silicate formation in Co/SiO2 model catalyst. Catal. Lett. 87, 51 (2003).
P. Hudon and D.R. Baker: The nature of phase separation in binary oxide melts and glasses. I. Silicate systems. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 303, 299 (2002).
I. Alstrup, I. Chorkendorff, R. Candia, B.S. Clausen and H. Topsøe: A combined x-ray photoelectron and Mössbauer emission spectroscopy study of the state of cobalt in sulfided, supported and unsupported Co–Mo catalysts. J. Catal. 77, 397 (1982).
Z.P. Xu and H.C. Zeng: Thermal evolution of cobalt hydroxides: A comparative study of their various structural phases. J. Mater. Chem. 8, 2499 (1998).
M. Oku and Y. Sato: In-situ x-ray photoelection spectroscopic study of the reversible phase transition between CoO and Co3O4 in oxygen of 10-3 Pa. Appl. Surf. Sci. 55, 37 (1992).
A.M. Saib, M. Claeys and E. van Steen: Silica supported cobalt Fischer–Tropsch catalysts: Effect of pore diameter of support. Catal. Today 71, 395 (2002).
D.G. Castner, P.R. Watson and I.Y. Chan: X-ray absorption spectroscopy, x-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, and analytical electron microscopy studies of cobalt catalysts. 2. Hydrogen reduction properties. J. Phys. Chem. 94, 819 (1990).
A.C. Soares Sabioni and B.J. Wuensch: Grain-boundary diffusion of Co2+ in ZnO (http://web.mit.edu/cmse/www/Wuensch97.pdf, 1997).
V.B. Prokpenko, V.S. Gurin, A.A. Alexeenko, V.S. Kulikauskas and D.L. Kovalenko: Surface segregation of transition metals in sol-gel silica films. J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 33, 3152 (2000).
A. Ramos-Mendoza, H. Tototzintle-Huitle, A. Mendoza-Galvan and J. Gonzalez-Hernandez: Optical and structural properties of sol-gel SiO2 layers containing cobalt. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 19, 1600 (2001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Park, S.M., Ki, W., Yu, J. et al. Sol-gel synthesis of highly dispersed cobalt nanoparticles on silica thin films. Journal of Materials Research 20, 3094–3101 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1557/JMR.2005.0390
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/JMR.2005.0390