Abstract
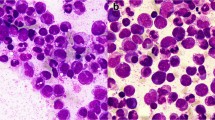
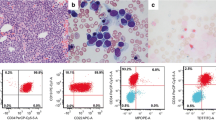
Myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) often transforms into acute leukemia, usually of a myeloid phenotype. However, the transformation of MDS into acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) is extremely rare. We present a case of refractory anemia with excess of blasts (RAEB) that transformed into ALL. MDS (RAEB) was diagnosed in a 68-year-old Japanese woman in August 2001. Two months later, MDS progressed to erythroleukemia (French-American-British [FAB]classification, acute myeloid leukemia fAML]-M6), and in December, 2001, she was treated with combined chemotherapy containing aclarubicin, cytarabine, and granulocyte colony-stimulating factor, which improved her clinical symptoms. However, 1 month after the chemotherapy, she developed ALL. The blasts at that time had a markedly basophilic cytoplasm with multiple cytoplasmic vac-uoles, and their morphology mimicked that of ALL-L3. The blasts also expressed CD13, a myeloid marker, in addition to lymphoid markers. Southern-blot analysis revealed rearrangement of the immunoglobulin heavy chain, but no additional chromosomal abnormality characteristic of ALL-L3 was detected. The patient was treated with chemotherapy, but she developed tumor lysis syndrome and died of multiple organ failure. Although the precise mechanism of lymphoid transformation is not yet fully understood, this case clinically supports the nature of MDS as a pluripotent hematopoietic stem cell disorder.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Koeffler P. Myelodysplastic syndromes (preleukemia).Semin Hemalol. 1986;23:284–299.
Janssen JWG, Buschle M, Layton M, et al. Clonal analysis of myelodysplastic syndromes: evidence of multipotential stem cell origin.Blood. 1989;73:248–254.
Mufti GJ, Galton DA. Myelodysplastic syndromes: natural history and features of prognostic importance.Clin Haematol. 1986:15:953–9711.
Ikeda T, Sato K, Yamashita T, et al. Burkitt’s acute lymphoblastic leukaemia transformation after myelodysplastic syndrome.Br J Haematol. 2001;115:69–71.
Follows GA, Owen RG, Ashcroft AJ, Parapia LA. Eosinophilic myelodysplasia transforming to acute lymphoblastic leukemia.J Clin Pathol. 1999;52:388–389.
Pajor L, Matolesy A, Vass JA, et al. Phenotypic and genotypic analysis of blastic cell population suggest that pure B-lymphoblas- tic leukemia may arise from myelodysplastic syndrome.Leukemia Res. 199822:13–17.
Lima CS, des Souza CA, Cardinalli IA, Lorand-Metze I. Lym- phoblastic transformation of myelodysplastic syndrome.Rev Paul Med. 1997;115:1508–1512.
Abruzzese E, Buss D, Rainer R, Pettenati MJ, Rao PN. Progression of a myelodysplastic syndrome to pre-B acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a case report and cell lineage study.Ann Hematol. 1996;73:35–38.
Escudicr SM, Albitar M, Robertson LE, Andreef M, Pierce S, Kan-tarijan HM. Acute lymphoblastic leukemia following preleukemic syndromes in adults.Leukemia. 1996;10:473–477.
Collides PA, Bennet JM. Transformation of chronic myelomono- cytic leukemia to acute lymphoblastic leukemia.Am J Hematol. 1995;49:157–162.
Kohno T, Amenomori T, Atogami S, et al. Progression from myelodysplastic syndrome to acute lymphoblastic leukemia with Philadelphia chromosome and p190 BCR-ABL transcript.Br J Haematol. 1996;93:389–391.
Suvajdzic N, Jankovic G, Bogdanovic A, Colovic M, Rolovic Z. Acute lymphoblastic leukemia in refractory anemia with ringed sideroblasts [in Serbian].Srp Arh Celok Lek. 1992;120:193–196.
Hernandez JM, Sanchez I, Gonzalez M, A Orfao, Gonzalez-Sarmiento R, San Miguel JF. Acute lymphoid leukemias following either a previous chronic myelogenous leukemia or myelodysplastic syndrome: phenotypic and genotypic differences.Am J Hematol. 1993:43:256–258.
San MiguelJF, Hernandez JM, Gonzalez-Sarmiento R, et al. Acute leukemia after a primary myelodysplastic syndrome: immunophe- notypic, genotypic, and clinical characteristics.Blood.1991;78:768–774.
Komatsu N, Yoshida M, Eguchi M, et al. Simultaneous expression of lymphoid and myeloid phenotypes in acute leukemia arising from myelodysplastic syndrome.Am J Hematol. 1988;28:103–106.
Ascensao JL, Kay NE, Wright JJ, et al. Lymphoblastic transformation of myelodysplastic syndrome.Am J Hematol 1986;22:431–434.
San Miguel JF, Gonzales M, Canizo MC, et al. The nature of blast cells in myelodysplastic syndromes evolving to acute leukemia.Blut. 1986;52:357–363.
Nagler A, Brenner B, Tatarsky I. Secondary refractory anemia with excess of blasts in transformation terminating as acute lymphoblastic leukemia.Acta Haematol. 1986;76:164–165.
Bonati A, Delia D, Starcich R. Progression of a myelodysplastic syndrome to pre-B acute lymphoblastic leukaemia with unusual phenotype.Br J Haematol. 1986;64:487–491.
Neame PB, Soamboonsrup P, Browman G, et al. Simultaneous or sequential expression of lymphoid and myeloid phenotypes in acute leukemia.Blood. 1985;65:142–148.
Eridani S, Chan LC, Halil O, Pearson TC. Acute biphenotypic leukemia (myeloid and null-ALL type) supervening in a myelodysplastic syndrome.Br J Haematol 1985;61:525–529.
Inoshita T. Acute lymphoblastic leukemia following myelodysplastic syndrome.Am.J Clin Pathol. 1985;84:233–237.
Pereira AM, De Castro JT, Santos EG, Perloiro MC, Catovsky D. T lymphoblastic transformation of refractory anemia with excess of blasts.Clin Lab Haematol. 1985;7:89–95.
Bereneman ZN, Bockstaele DV, DeMeyerP et al. A myelodysplastic syndrome preceding acute lymphoblastic leukemia.Br J Haematol. 1985;60:353–354.
Hehlmann R, Zonnchen B, Thiel E, Walther B. Idiopathic refractory sideroachrestic anemia progressing to acute mixed lymphoblastic- myelomonocytic leukemia.Blut. 1983;46:11–21.
Hussein KK, Salem Z, Bottomley SS, Livingston RB. Acute leukemia in idiopathic sideroblastic anemia: response to combination chemotherapy.Blood. 1982;59:652–657.
Barton JC, Conrad ME, Parmley RT. Acute lymphoblastic leukemia in idiopathic refractory sideroblastic anemia: evidence for a common lymphoid and myeloid progenitor cell.Am J Hematol. 1980;9:109–115.
Culligan DJ, Cacha P, Whittaker J, Jacobs A, Padua RA. Clonal lymphocytes are detectable in only some cases of MDS.Br J Haematol. 1992;81:346–352.
Van KampH, Fibbe WE, Jansen RP, et al. Clonal involvement of granulocytes and monocytes, but not of T and B lymphocytes and natural killer cells in patients with myelodysplasia: analysis by X-linked restriction fragment length polymorphisms and poly-merase chain reaction of the phosphoglycerate kinase gene.Blood. 1992;80:1774–1780.
Tricot G, Boogaerts MA, De Wolf-PeelersC, Van denBergheH, Verwilghen RL. The myelodysplastic syndromes: different evolution patterns based on sequential morphological and cytogenetic investigations.Br J Haematol. 1985;59:659–670.
Tricot G, Vlietnick R, Boogaerts MA, et al. Prognostic factors in the myelodysplastic syndromes: importance of initial data on peripheral blood counts, bone marrow cytology, trephine biopsy and chromosomal analysis.Br J Haematol. 1985;60:19–32.
Sham RL, Bennett JM. Burkitt cell leukemia with myelodysplasia as a presentation of HIV infection.Hematol Pathol. 1992;6:95–98.
Raimondi SC, Shurtleff SA, Downing JR, et al. 12p abnormalities and the TEL gene (ETV6) in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia.Blood. 1997;90:4559–4566.
Bain BJ. Acute leukemia: immunophenotyping, cytogenetics and molecular genetics—the MIC and MIC-M classifications. In: Bain BJ, ed.Leukemia Diagnosis. 2nd ed. Blackwell Science; 1999:53–112.
Stark AN, Scott CS, Bhatt B, Roberts BE. Myelodysplastic syndrome coexisting with acute lymphoblastic leukemia.J Clin Pathol. 1986;39:728–730.
Johansson B, Moorman AV, Hass OA, et al. Hematologic malignancies with t(4:11)(q21: q23)—a cytogenetic, morphologic, immuno- phenotypic, and clinical study of 183 cases.Leukemia. 1998;12:779–7788.
Harris NL, Jaffe ES, Stein H, et al. A revised European-American classification of lymphoid neoplasms: a proposal from the International Lymphoma Study Group.Blood. 1994;84:1361–1392.
Shiramizu B, Barriga F, Neequaye J, et al. Patterns of chromosomal break point location in Burkitt’s lymphoma: relevance to geography and EBV association.Blood. 1991;77:1516–1526.
Adams JM, Harris AW, Pinkert CA, et al. The c-myc oncogene driven by immunoglobulin enhancer induces lymphoid malignancy in transgenic mice.Nature. 1985;318:533–538.
Magrath IT, Bhatia K. Pathogenesis of small non-cleaved cell lymphoma (Burkitt’s lymphoma). In: Magrath IT, ed.The Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma. 2nd ed. London: Arnold; 1997:385–410.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Sato, N., Nakazato, T., Kizaki, M. et al. Transformation of myelodysplastic syndrome to acute lymphoblastic leukemia: A case report and review of the literature. Int J Hematol 79, 147–151 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1532/IJH97.03137
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1532/IJH97.03137