Abstract
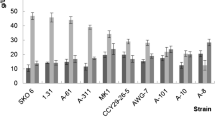
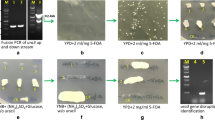
Inulin and glycerol were used as substrates for efficient erythritol and citric acid production by newly engineered Yarrowia lipolytica strains. Hydrolysis of inulin by the Y. lipolytica Wratislavia K1 strain was established by expressing the Kluyveromyces marxianus INU1 gene. Erythritol was produced in two stages: inulin was used for biomass formation, followed by erythritol biosynthesis initiated by glycerol addition. The highest titer of erythritol obtained, 120.9 g L−1 with the yield of 0.6 g g−1, was produced by the K1 INU 6 strain. Moreover, the K1 INU 6 strain in fed-batch culture produced a high amount of citric acid: 105.2 g L−1 after 235 h from 200 g L−1 of inulin. Maximum activity of inulinase during this culture was 14000 U g−1 of cell dry mass. The presented study proves the potential of new Y. lipolytica transformants for efficient erythritol and citric acid production from inexpensive raw materials such as inulin and glycerol.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akiyama, S., Suzuki, T., Sumino, Y., Nakao, Y., & Fukuda, H. (1973a). Induction and citric acid productivity of fluoroacetate- sensitive mutant strains of Candida lipolytica. Agricultural and Biological Chemistry, 37, 879–884. DOI: 10.1271/ bbb1961.37.879.
Akiyama, S., Suzuki, T., Sumino, Y., Nakao, Y., & Fukuda, H. (1973b). Relationship between aconitate hydratase activity and citric acid productivity in fluoroacetate-sensitive mutant strain of Candida lipolytica. Agricultural and Biological Chemistry, 37, 885–888. DOI: 10.1271/bbb1961.37.885.
Baldwin, T. K., Gaffoor, I., Antoniw, J., Andries, C., Guenther, J., Urban, M., Hallen-Adams, H. E., Pitkin, J., Hammond-Kosack, K. E., & Trail, F. (2010). A partial chromosomal deletion caused by random plasmid integration resulted in a reduced virulence phenotype in Fusarium graminearum. Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions, 23, 1083–1096. DOI: 10.1094/mpmi-23-8-1083.
Chi, Z., Chi, Z., Zhang, T., Liu, G., & Yue, L. (2009). Inulinaseexpressing microorganisms and applications of inulinases. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 82, 211–220. DOI: 10.1007/s00253-008-1827-1.
Chi, Z. M., Zhang, T., Cao, T. S., Liu, X. Y., Cui, W., & Zhao, C. H. (2011). Biotechnological potential of inulin for bioprocesses. Bioresource Technology, 102, 4295–4303. DOI: 10.1016/j.biortech.2010.12.086.
Crolla, A., & Kennedy, K. J. (2004). Fed-batch production of citric acid by Candida lipolytica grown on n-paraffins. Journal of Biotechnology, 110, 73–84. DOI: 10.1016/j.jbiotec. 2004.01.007.
Cui, W., Wang, Q., Zhang, F., Zhang, S. C., Chi, Z. M., & Madzak, C. (2011). Direct conversion of inulin into single cell protein by the engineered Yarrowia lipolytica carrying inulinase gene. Process Biochemistry, 46, 1442–1448. DOI: 10.1016/j.procbio.2011.03.017.
Dashtban, M., Schraft, H., Syed, T. A., & Qin, W. (2010). Fungal biodegradation and enzymatic modification of lignin. International Journal of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 1, 36–50.
Finogenova, T. V., Shishkanova, N. V., Fausek, E. A., & Eremina, S. S. (1991). Biosynthesis of isocitric acid from ethanol by yeasts. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 36, 231–235. DOI: 10.1007/bf00164426.
Finogenova, T. V., Morgunov, I. G., Kamzolova, S. V., & Chernyavskaya, O. G. (2005). Organic acid production by the yeast Yarrowia lipolytica: A review of prospects. Applied Biochemistry and Microbiology, 41, 418–425. DOI: 10.1007/s10438-005-0076-7.
F¨orster, A., Jacobs, K., Juretzek, T., Mauersberger, S., & Barth, G. (2007a). Overexpression of the ICL1 gene changes the product ratio of citric acid production by Yarrowia lipolytica. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 77,. DOI: 10.1007/s00253-007-1205-4.
F¨orster, A., Aurich, A., Mauersberger, S., & Barth, G. (2007b). Citric acid production from sucrose using a recombinant strain of the yeast Yarrowia lipolytica. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 75, 1409–1417. DOI: 10.1007/s00253-007- 0958-0.
Franck, A. (2002). Technological functionality of inulin and oligofructose. British Journal of Nutrition, 87, S287–S291. DOI: 10.1079/bjn/2002550.
Gong, F., Sheng, J., Chi, Z., & Li, J. (2007). Inulinase production by a marine yeast Pichia guilliermondii and inulin hydrolysis by the crude inulinase. Journal of Industrial Microbiology & Biotechnology, 34, 179–185. DOI: 10.1007/s10295- 006-0184-2.
Grand View Research (2015). Inulin market analysis by application (food & beverage, dietary supplements, pharmaceuticals) and segment forecasts to 2020. Retrieved from http://www.grandviewresearch.com/industry-analysis/inulin-market
Gritz, L., & Davies, J. (1983). Plasmid-encoded hygromycin B resistance: the sequence of hygromycin B phosphotransferase gene and its expression in Escherichia coli and Saccha romyces cerevisiae. Gene, 25, 179–188. DOI: 10.1016/0378- 1119(83)90223-8.
Holz, M., F¨orster, A., Mauersberger, S., & Barth, G. (2009). Aconitase overexpression changes the product ratio of citric acid production by Yarrowia lipolytica. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 81, 1087–1096. DOI: 10.1007/s00253-008- 1725-6.
Jeya, M., Lee, K. M., Tiwari, M. K., Kim, J. S., Gunasekaran, P., Kim, S. Y., Kim, I. W., & Lee, J. K. (2009). Isolation of a novel high erythritol-producing Pseudozyma tsukubaensis and scale-up of erythritol fermentation to industrial level. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 83, 225–231. DOI: 10.1007/s00253-009-1871-5.
Kamzolova, S. V., Morgunov, I. G., Aurich, A., Perevoznikova, O. A., Shishkanova, N. V., Stottmeister, U., & Finogenova, T. V. (2005). Lipase secretion and citric acid production in Yarrowia lipolytica yeast grown on animal and vegetable fat. Food Technology and Biotechnology, 43, 113–122.
Kamzolova, S. V., Finogenova, T. V., & Morgunov, I. G. (2008). Microbial production of citric and isocitric acids from sunflower oil. Food Technology and Biotechnology, 46, 51–59.
Kobayashi, Y., Iwata, H., Mizushima, D., Ogihara, J., & Kasumi, T. (2015). Erythritol production by Moniliella megachiliensis using nonrefined glycerol waste as carbon source. Letters in Applied Microbiology, 60, 475–480. DOI: 10.1111/lam.12391.
Lazar, Z., Walczak, E., & Robak, M. (2011). Simultaneous production of citric acid and invertase by Yarrowia lipolytica SUC+ transformants. Bioresource Technology, 102, 6982–6989. DOI: 10.1016/j.biortech.2011.04.032.
Lin, S. J., Wen, C. Y., Liau, J. C., & Chu, W. S. (2001). Screening and production of erythritol by newly isolated osmophilic yeast-like fungi. Process Biochemistry, 36, 1249–1258. DOI: 10.1016/s0032-9592(01)00169-8.
Lin, S. J., Wen, C. Y., Wang, P. M., Huang, J. C., Wei, C. L., Chang, Chu, W. S. (2010). High-level production of erythritol by mutants of osmophilic Moniliella sp. Process Biochemistry, 45, 973–979. DOI: 10.1016/j.procbio.2010.03. 003.
Liu, X. Y., Chi, Z., Liu, G. L., Wang, F., Madzak, C., & Chi, Z. M. (2010). Inulin hydrolysis and citric acid production from inulin using the surface-engineered Yarrowia lipolytica displaying inulinase. Metabolic Engineering, 12, 469–476. DOI: 10.1016/j.ymben.2010.04.004.
Liu, X. Y., Chi, Z., Liu, G. L., Madzak, C., & Chi, Z. M. (2013). Both decrease in ALC1 gene expression and increase in ICL1 gene expression in marine-derived yeast Yarrowia lipolytica expressing INU1 gene enhance citric acid production from inulin. Marine Biotechnology, 15, 26–36. DOI: 10.1007/s10126- 012-9452-5.
Mauersberger, S., Wang, H. J., Gaillardin, C., Barth, G., & Nicaud, J. M. (2001). Insertional mutagenesis in the nalkane- assimilating yeast Yarrowia lipolytica: Generation of tagged mutations in genes involved in hydrophobic substrate utilization. Journal of Bacteriology, 183, 5102–5109. DOI: 10.1128/jb.183.17.5102-5109.2001.
Miller, G. L. (1959). Use of dinitrosalicylic acid reagent for determination of reducing sugar. Analytical Chemistry, 31, 426–428. DOI: 10.1021/ac60147a030.
Pagliaro, M., & Rossi, M. (2008). The future of glycerol: New usages for a versatile raw material (RSC green chemistry series, Book 1). Cambridge, UK: The Royal Society of Chemistry. DOI: 10.1039/9781847558305.
Rymowicz, W., Rywin´ska, A., Z˙ arowska, B., & Juszczyk, P. (2006). Citric acid production from raw glycerol by acetate mutants of Yarrowia lipolytica. Chemical Papers, 60, 391–394. DOI: 10.2478/s11696-006-0071-3.
Rymowicz, W., Rywi´nska, A., & Marcinkiewicz, M. (2009). High-yield production of erythritol from raw glycerol in fedbatch cultures of Yarrowia lipolytica. Biotechnology Letters, 31, 377–380. DOI: 10.1007/s10529-008-9884-1.
Rywi´nska, A., Skrzypi´nski, A., Juszczyk, P., Boruczkowski, T., & Rymowicz, W. (2008). Characteristics of citric acid and some polyols biosynthesis from glycerol and glucose by Yarrowia lipolytica yeast. Acta Scientiarum Polonorum, Biotechnologia, 7, 27–38. (in Polish)
Rywin´ska, A., Rymowicz, W., Z˙ arowska, B., & Wojtatowicz, M. (2009). Biosynthesis of citric acid from glycerol by acetate mutants of Yarrowia lipolytica in fed-batch fermentation. Food Technology and Biotechnology, 47, 1–6.
Rywi´nska, A., Juszczyk, P., Wojtatowicz, M., Robak, M., Lazar, Z., Tomaszewska, L., & Rymowicz, W. (2013a). Glycerol as a promising substrate for Yarrowia lipolytica biotechnological applications. Biomass and Bioenergy, 48, 148–166. DOI: 10.1016/j.biombioe.2012.11.021.
Rywi´nska, A., Tomaszewska, L., & Rymowicz, W. (2013b). Erythritol biosynthesis by Yarrowia lipolytica yeast under various culture conditions. African Journal of Microbiology Research, 7, 3511–3516. DOI: 10.5897/ajmr12.2272.
Schmid-Berger, N., Schmid, B., & Barth, G. (1994). Ylt1, a highly repetitive retrotransposon in the genome of the dimorphic fungus Yarrowia lipolytica. Journal of Bacteriology, 2477–2482.
Shigechi, H., Koh, J., Fujita, Y., Matsumoto, T., Bito, Y., Ueda, M., Satoh, E., Fukuda, H., & Kondo, A. (2004). Direct production of ethanol from raw corn starch via fermentation by use of a novel surface-engineered yeast strain codisplaying glucoamylase and α-amylase. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 70, 5037–5040. DOI: 10.1128/aem.70.8.5037- 5040.2004.
Tomaszewska, L., Rywi´nska, A., & G´ladkowski, W. (2012). Production of erythritol and mannitol by Yarrowia lipolytica yeast in media containing glycerol. Journal of Industrial Microbioliology & Biotechnology, 39, 1333–1343. DOI: 10.1007/s10295-012-1145-6.
Tomaszewska, L., Rakicka, M., Rymowicz, W., & Rywi´nska, A. (2014). A comparative study on glycerol metabolism to erythritol and citric acid in Yarrowia lipolytica yeast cells. FEMS Yeast Research, 14, 966–976. DOI: 10.1111/1567- 1364.12184.
Tréton, B., Le Dall, M. T., & Heslot, H. (1978). Excretion of citric and isocitric acids by the yeast Saccharomycopsis lipolytica. European Journal of Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 6, 67–77. DOI: 10.1007/bf00500857.
Xuan, J. W., Fournier, P., Declerck, N., Chasles, M., & Gaillardin, C. (1990). Overlapping reading frames at the LYS5 locus in the yeast Yarrowia lipolytica. Molecular and Cellular Biology, 10, 4795–4806. DOI: 10.1128/mcb.10.9.4795.
Yang, L. B., Zhan, X. B., Zheng, Z. Y., Wu, J. R., Gao, M. J., & Lin, C. C. (2014). A novel osmotic pressure control fed-batch fermentation strategy for improvement of erythritol production by Yarrowia lipolytica from glycerol. Bioresource Technology, 151, 120–127. DOI: 10.1016/j.biortech.2013.10.031.
Yu, J. H., Lee, D. H., Oh, Y. J., Han, K. C., Ryu, Y. W., & Seo, J. H. (2006). Selective utilization of fructose to glucose by Candida magnoliae, an erythritol producer. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 131, 870–879. DOI: 10.1385/abab:131:1:870.
Zhao, C. H., Cui, W., Liu, X. Y., Chi, Z. M., & Madzak, C. (2010). Expression of inulinase gene in the oleaginous yeast Yarrowia lipolytica and single cell oil production from inulincontaining materials. Metabolic Engineering, 12, 510–517. DOI: 10.1016/j.ymben.2010.09.001.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rakicka, M., Lazar, Z., Rywińska, A. et al. Efficient utilization of inulin and glycerol as fermentation substrates in erythritol and citric acid production using Yarrowia lipolytica expressing inulinase. Chem. Pap. 70, 1452–1459 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1515/chempap-2016-0085
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1515/chempap-2016-0085