Abstract
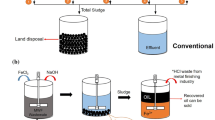
The zero-valent iron (ZVI)/H2O2 Fenton system can be considered as an effective solution for the removal of many of the organic pollutants present in the waste waters generated by the drug manufacturing industry. The hydrogen peroxide concentration and dosage rate were studied in order to improve the efficiency of the oxidant in the TOC reduction and, thereby enhance the overall catalytic performance of the ZVI/H2O2 Fenton system. TOC reductions of up to 80 % and BOD5/COD ratios of up to 0.6 were achieved in the waste water as received without dilution (TOCO approximately 5 g L−1) using hydrogen peroxide dose-staggering. This showed that the ZVI/H2O2 process led not only to a decrease in TOC removal but also to an increase in the biodegradability of the by-products formed. The hydrogen peroxide was consumed more efficiently and very low concentrations of iron dissolved (7 mg L−1) were obtained in the final effluents. The final values of COD, BOD5, the suspended solids’ content and the conductivity of the treated waste water met the limits of the Spanish legal industrial discharge, Decree 57/2005 (Ministry of Environment, Local Government and Planning, Community of Madrid, 2005). In addition, the composite thus formed, consisting of zero-valent iron and iron oxide-oxyhydroxides, can be readily removed from the treated effluent, avoiding any post-treatment step.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
APHA, AWWA, WEF (2005). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater (21st ed.). Washington, DC, USA: APHA.
Blanco, J., Torrades, F., De la Varga, M., García-Montaño, J. (2012). Fenton and biological-Fenton coupled processes for textile wastewater treatment and reuse. Desalination, 286, 394–399. DOI: 10.1016/j.desal.2011.11.055.
Chamarro, E., Marco, A., & Esplugas, S. (2001). Use of Fenton reagent to improve organic chemical biodegradability. Water Research, 35, 1047–1051. DOI: 10.1016/s0043-1354(00)00342-0.
Chen, C. Y., Kuo, J. T., Yang, H. A., Chung, Y. C. (2013). A coupled biological and photocatalysis pretreatment system for the removal of crystal violet from wastewater. Chemo-sphere, 92, 695–701. DOI: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.04. 040.
Chen, R. Z., Pignatello, J. J. (1997). Role of quinone intermediates as electron shuttles in Fenton and photoassisted Fen-ton oxidations of aromatic compounds. Environmental Science & Technology, 31, 2399–2406. DOI: 10.1021/es9610646.
Deng, Y., Englehardt, J. D. (2008). Hydrogen peroxide-enhanced iron-mediated aeration for the treatment of mature landfill leachate. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 153, 293–299. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.08.049.
EPA (1991). Guides to pollution prevention: The pharmaceutical industry (pp. 5–9). Cincinnati, OH, USA: US Environmental Protection Agency.
Farrè, M. J., Maldonado, M. I., Gernjak, W., Oller, I., Malato, S., Domènech, X., Peral, J. (2008). Coupled solar photo-Fenton and biological treatment for the degradation of diuron and linuron herbicides at pilot scale. Chemosphere, 72, 622–629. DOI: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2008.02.043.
Feitz, A. J., Joo, S. H., Guan, J., Sun, Q., Sedlak, D. L., Waite, T. D. (2005). Oxidative transformation of contaminants using colloidal zero-valentiron. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 265, 88–94. DOI: 10.1016/j.colsurfa.2005.01.038.
Ferrari, B., Paxéus, N., Lo Giudice, R., Pollio, A., Garric, J. (2003). Ecotoxicological impact of pharmaceuticals found in treated wastewaters: study of carbamazepine, clofibric acid, and diclofenac. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 55, 359–370. DOI: 10.1016/s0147-6513(02)00082-9.
Guisasola, A., Baeza, J. A., Carrera, J., Casas, C., La-fuente, J. (2003). An off-line respirometric procedure to determine inhibition and toxicity of biodegradable compounds in biomass from an industrial WWTP. Water Science & Technology, 48, 267–275.
He, C., Yang, J. N., Zhu, L. F., Zhang, Q., Liao, W. C., Liu, S. K., Liao, Y., Asi, M. A., Shu, D. (2013). pH-dependent degradation of acid orange II by zero-valent iron in presence of oxygen. Separation and Purification Technology, 117, 59–68. DOI: 10.1016/j.seppur.2013.04.028.
Joo, S. H., Feitz, A. J., Waite, T. D. (2004). Oxidative degradation of the carbothioate herbicide, molinate, using nanoscale zero-valent iron. Environmental Science &Technology, 38, 2242–2247. DOI: 10.1021/es035157g.
Joo, S. H., Feitz, A. J., Sedlak, D. L., Waite, T. D. (2005). Quantification of the oxidizing capacity of nanoparticulate zero-valent iron. Environmental Science & Technology, 39, 1263–1268. DOI: 10.1021/es048983d.
Kallel, M., Belaid, C., Mechichi, T., Ksibi, M., Elleuch, B. (2009). Removal of organic load and phenolic compounds from olive mill wastewater by Fenton oxidation with zero-valent iron. Chemical Engineering Journal, 150, 391–395. DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2009.01.017.
Kilroy, A. C., Gray, N. F. (1992). The toxicity of four organic solvents commonly used in the pharmaceutical industry to activated sludge. Water Research, 26, 887–892. DOI: 10.1016/0043-1354(92)90193-8.
Li, Y. C., Bachas, L. G., Bhattacharyya, D. (2007). Selected chloro-organic detoxifications by polychelate (poly(acrylic acid)) and citrate-based Fenton reaction at neutral pH environment. Industrial &Engineering Chemistry Research, 46, 7984–7992. DOI: 10.1021/ie070393b.
Liu, H., Wang, Q., Wang, C., Li, X. Z. (2013). Electron efficiency of zero-valent iron for groundwater remediation and wastewater treatment. Chemical Engineering Journal, 215–216, 90–95. DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2012.11.010.
Mazille, F., Schoettl, T., Pulgarin, C. (2009). Synergistic effect of TiO2 and iron oxide supported on fluorocarbon films. Part 1: Effect of preparation parameters on photo-catalytic degradation of organic pollutant at neutral pH. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 89, 635–644. DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2009.01.027.
Ministry of Environment, Local Government and Planning, Community of Madrid (2005). Decreto 57/2005, de 30 de ju-nio, por el que se revisan los Anexos de la Ley 10/1993, de 26 de octubre, sobre Vertidos Líquidos Industriales al Sistema Integral de Saneamiento. Boletín Oficial de la Comunidad de Madrid, 2005(159), 11–14. (in Spanish)
Neyens, E., Baeyens, J. (2003). A review of classic Fen-ton’s peroxidation as an advanced oxidation technique. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 98, 33–50. DOI: 10.1016/s0304-3894(02)00282-0.
Parra, S., Henao, L., Mielczarski, E., Mielczarski, J., Albers, P., Suvorova, E., Guindet, J., Kiwi, J. (2004). Synthesis, testing, and characterization of a novel Nafion membrane with superior performance in photoassisted immobilized Fenton catalysis. Langmuir, 20, 5621–5629. DOI: 10.1021/la049768d.
Raj, D. S. S., Anjaneyulu, Y. (2005). Evaluation of biokinetic parameters for pharmaceutical wastewaters using aerobic oxidation integrated with chemical treatment. Process Biochemistry, 40, 165–175. DOI: 10.1016/j.procbio.2003.11.056.
Seif, H. A. A., Joshi, S. G., Gupta, S. K. (1992). Effect of organic load and reactor height on the performance of anaerobic mesophilic and thermophilic fixed film reactors in the treatment of pharmaceutical wastewater. Environmental Technology, 13, 1161–1168. DOI: 10.1080/09593339209385 255.
Segura, Y., Molina, R., Martínez, F., Melero, J. A. (2009). Integrated heterogeneous sono–photo Fenton processes for the degradation of phenolic aqueous solutions. Ultrasonics Sono-chemistry, 16, 417–424. DOI: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2008.10.004.
Segura, Y., Martínez, F., Melero, J. A. (2013). Effective pharmaceutical wastewater degradation by Fenton oxidation with zero-valent iron. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 136–137, 64–69. DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2013.01.036.
Segura, Y., Martínez, F., Melero, J. A., Fierro, J. L. G. (2015). Zero valent iron (ZVI) mediated Fenton degradation of industrial wastewater: Treatment performance and characterization of final composites. Chemical Engineering Journal, 269, 298–305. DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2015.01.102.
Shimizu, A., Tokumura, M., Nakajima, K., & Kawase, Y. (2012). Phenol removal using zero-valent iron powder in the presence of dissolved oxygen: Roles of decomposition by the Fenton reaction and adsorption/precipitation. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 201–202, 60–67. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.11.009.
Soon, A. N., Hameed, B. H. (2011). Heterogeneous catalytic treatment of synthetic dyes in aqueous media using Fenton and photo-assisted Fenton process. Desalination, 269, 1–16. DOI: 10.1016/j.desal.2010.11.002.
Xu, H. Y., Prasad, M., Liu, Y. (2009). Schorl: A novel catalyst in mineral-catalyzed Fenton-like system for dyeing wastewa-ter discoloration. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 165, 1186–1192. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.10.108.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Segura, Y., Martínez, F. & Melero, J.A. Simple and efficient treatment of high-strength industrial waste water using commercial zero-valent iron. Chem. Pap. 70, 1059–1065 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1515/chempap-2016-0045
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1515/chempap-2016-0045