Abstract
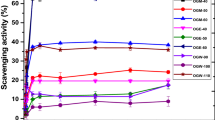
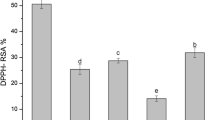
Phyllanthus amarus (P. amarus) is a herbal plant used in the treatment of various diseases such as hepatitis, diabetes, and cancer. Efficiency of its bioactive compounds extraction and therefore the biological activity of the extracts are significantly influenced by both solvent character and extraction method. This study is aimed at the determination of the influence of six various solvents (water, acetonitrile, ethanol, methanol, ethyl acetate, and dichloromethane) and nine different extraction methods (conventional, ultrasound-assisted, microwave-assisted, and six novel methods) on the extraction efficiency and antioxidant capacity of P. amarus. The results indicated that water extracted the maximal amount of phenolics from P. amarus and had the highest antioxidant capacity, while microwave-assisted extraction provided the highest yields of phenolics and saponins, and the highest antioxidant capacity with the lowest energy consumption when compared to the other extraction methods. These findings implied that water and microwave-assisted extraction are recommended as the most effective solvent and method for the extraction of bioactive compounds from P. amarus for potential application in the pharmaceutical and nutraceutical industries.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amoros, M., Fauconnier, B., & Girre, R. L. (1987). In vitro antiviral activity of a saponin from Anagallis arvensis, Primulaceae, against herpes simplex virus and poliovirus. Antiviral Research, 8, 13–25. DOI: 10.1016/0166-3542(87)90084-2.
Apak, R., Gorinstein, S., Böhm, V., Schaich, K. M., Özyürek, M., & Güçlü, K. (2013). Methods of measurement and evaluation of natural antioxidant capacity/activity (IUPAC technical report). Pure and Applied Chemistry, 85, 957–998. DOI: 10.1351/pac-rep-12-07-15.
Azmir, J., Zaidul, I. S. M., Rahman, M. M., Sharif, K. M., Mohamed, A., Sahena, F., Jahurul, M. H. A., Ghafoor, K., Norulaini, N. A. N., & Omar, A. K. M. (2013). Techniques for extraction of bioactive compounds from plant materials: A review. Journal of Food Engineering, 117, 426–436. DOI: 10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2013.01.014.
Cheok, C. Y., Salman, H. A. K., & Sulaiman, R. (2014). Extraction and quantification of saponins: A review. Food Research International, 59, 16–40. DOI: 10.1016/j.foodres.2014.01.057.
Chisté, R. C., de Toledo Benassi, M., & Mercadante, A. Z. (2014). Efficiency of different solvents on the extraction of bioactive compounds from the Amazonian fruit Caryocar villosum and the effect on its antioxidant and colour properties. Phytochemical Analysis, 25, 364–372. DOI: 10.1002/pca.2489.
Cunniff, P. (1995). Official methods of analysis of AOAC International (16th ed.). Arlington, VA, USA: Association of Analytical Communities.
Dai, J., & Mumper, R. J. (2010). Plant phenolics: Extraction, analysis and their antioxidant and anticancer properties. Molecules, 15, 7313–7352. DOI: 10.3390/molecules15107313.
Dhanani, T., Shah, S., Gajbhiye, N. A., & Kumar, S. (2013). Effect of extraction methods on yield, phytochemical constituents and antioxidant activity of Withania somnifera. Arabian Journal of Chemistry. DOI: 10.1016/j.arabjc.2013.02.015. (in press)
Doughari, J. H. (2012). Phytochemicals: Extraction methods, basic structures and mode of action as potential chemotherapeutic agents. In V. Rao (Ed.), Phytochemicals — A global perspective of their role in nutrition and health (chapter 1, pp. 1–32). Rijeka, Croatia: InTech. DOI: 10.5772/26052.
Garofulić, I. E., Dragović-Uzelac, V., Režek Jambrak, A., & Jukić, M. (2013). The effect of microwave assisted extraction on the isolation of anthocyanins and phenolic acids from sour cherry Marasca (Prunus cerasus var. Marasca). Journal of Food Engineering, 117, 437–442. DOI: 10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2012.12.043.
Hamrouni-Sellami, I., Rahali, F. Z., Rebey, I. B., Bourgou, S., Limam, F., & Marzouk, B. (2013). Total phenolics, flavonoids, and antioxidant activity of Sage (Salvia officinalis L.) plants as affected by different drying methods. Food and Bioprocess Technology, 6, 806–817. DOI 10.1007/s11947-012-0877-7.
Hari Kuma, K. B., & Kuttan, R. (2004). Protective effect of an extract of Phyllanthus amarus against radiation-induced damage in mice. Journal of Radiation Research, 45, 133–139. DOI: 10.1269/jrr.45.133.
Jin, J., Ma, H., Wang, W., Luo, M., Wang, B., Qu, W., He, R., Owusu, J., & Li, Y. (2015). Effects and mechanism of ultrasound pretreatment on rapeseed protein enzymolysis. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture. DOI: 10.1002/jsfa.7198. (in press)
Kalia, K., Sharma, K., Singh, H. P., & Singh, B. (2008). Effects of extraction methods on phenolic contents and antioxidant activity in aerial parts of Potentilla atrosanguinea Lodd. and quantification of its phenolic constituents by RPHPLC. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 56, 10129–10134. DOI: 10.1021/jf802188b.
Kamonwannasit, S., Nantapong, N., Kumkrai, P., Luecha, P., Kupittayanant, S., & Chudapongse, N. (2013). Antibacterial activity of Aquilaria crassna leaf extract against Staphylococcus epidermidis by disruption of cell wall. Annals of Clinical Microbiology and Antimicrobials, 12, art. no. 20. DOI: 10.1186/1476-0711-12-20.
Kha, T. C., & Nguyen, M. H. (2014). Extraction and isolation of plant bioactives. In C. J. Scarlett, & Q. V. Vuong (Eds.), Plant bioactive compounds for pancreatic cancer prevention and treatment (Series: Cancer etiology, diagnosis and treatments, chapter 6, pp. 117–144). Hauppauge, NY, USA: Nova Science Publishers.
Lacaille-Dubois, M. A. (2005). Bioactive saponins with cancer related and immunomodulatory activity: Recent developments. In Atta-ur-Rahman (Ed.), Bioactive natural products (Series: Studies in natural products chemistry, Vol. 32, Part L, pp. 209–246). Amsterdam, The Netherlands: Elsevier. DOI: 10.1016/s1572-5995(05)80057-2.
Lim, Y. Y., & Murtijaya, J. (2007). Antioxidant properties of Phyllanthus amarus extracts as affected by different drying methods. LWT — Food Science and Technology, 40, 1664–1669. DOI: 10.1016/j.lwt.2006.12.013.
Londhe, J. S., Devasagayam, T. P. A., Foo, L. Y., & Ghaskadbi, S. S. (2008). Antioxidant activity of some polyphenol constituents of the medicinal plant Phyllanthus amarus Linn. Redox Report, 13, 199–207. DOI: 10.1179/135100008x308984.
Londhe, J. S., Devasagayam, T. P. A., Foo, L. Y., Shastry, P., & Ghaskadbi, S. S. (2012). Geraniin and amariin, ellagitannins from Phyllanthus amarus, protect liver cells against ethanol induced cytotoxicity. Fitoterapia, 83, 1562–1568. DOI: 10.1016/j.fitote.2012.09.003.
Mahomoodally, M. F., & Muthoora, D. D. (2014). Kinetic of inhibition of carbohydrate-hydrolysing enzymes, antioxidant activity and polyphenolic content of Phyllanthus amarus Schum. & Thonn. (Phyllanthaceae). Journal of Herbal Medicine, 4, 208–223. DOI: 10.1016/j.hermed.2014.09.003.
Maity, S., Chatterjee, S., Variyar, P. S., Sharma, A., Adhikari, S., & Mazumder, S. (2013). Evaluation of antioxidant activity and characterization of phenolic constituents of Phyllanthus amarus root.Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 61, 3443–3450. DOI: 10.1021/jf3046686.
Mandal, P., Sinha Babu, S. P., & Mandal, N. C. (2005). Antimicrobial activity of saponins from Acacia auriculiformis. Fitoterapia, 76, 462–465. DOI: 10.1016/j.fitote.2005.03.004.
Maryott, A. A., & Smith, E. R. (1951). Table of dielectric constants of pure liquids. National Bureau of Standards Circular 514. Washington, D.C., USA: U.S. Government Printing Office.
Naumovski, N. (2014). Bioactive composition of plants and plant foods. In C. J. Scarlett, & Q. V. Vuong (Eds.), Plant bioactive compounds for pancreatic cancer prevention and treatment (Series: Cancer etiology, diagnosis and treatments, chapter 5, pp. 81–115). Hauppauge, NY, USA: Nova Science Publishers.
Nguyen, V. T., Ueng, J. P., & Tsai, G. J. (2011). Proximate composition, total phenolic content, and antioxidant activity of seagrape (Caulerpa lentillifera). Journal of Food Science, 76, C950–C958. DOI: 10.1111/j.1750-3841.2011.02289.x.
Nguyen, V. T., Vuong, Q. V., Bowyer, M. C., Van Altena, I. A., & Scarlett, C. J. (2015a). Effects of different drying methods on bioactive compound yield and antioxidant capacity of Phyllanthus amarus. Drying Technology, 33, 1006–1017.DOI: 10.1080/07373937.2015.1013197.
Nguyen, V. T., Bowyer, M. C., Vuong, Q. V., Van Altena, I. A., & Scarlett, C. J. (2015b). Phytochemicals and antioxidant capacity of Xao tam phan (Paramignya trimera) root as affected by various solvents and extraction methods. Industrial Crops and Products, 67, 192–200. DOI: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2015.01.051.
Nguyen, V. T., Pham, N. M. Q., Vuong, Q. V., Bowyer, M. C., van Altena, I. A., & Scarlett, C. J. (2015c). Phytochemical retention and antioxidant capacity of Xao Tam Phan (Paramignya trimera) root as prepared by different drying methods. Drying Technology. DOI: 10.1080/07373937.2015.1053566. (in press)
O’Brien, W. D., Jr. (2007). Ultrasound—biophysics mechanisms. Progress in Biophysics and Molecular Biology, 93, 212–255. DOI: 10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2006.07.010.
Osbourn, A., Goss, R. J. M., & Field, R. A. (2011). The saponins — polar isoprenoids with important and diverse biological activities. Natural Product Reports, 28, 1261–1268. DOI: 10.1039/c1np00015b.
Patel, J. R., Tripathi, P., Sharma, V., Chauhan, N. S., & Dixit, V. K. (2011). Phyllanthus amarus: Ethnomedicinal uses, phytochemistry and pharmacology: A review. Journal of Ethnopharmarcology, 138, 286–313. DOI: 10.1016/j.jep.2011.09.040.
Podolak, I., Galanty, A., & Sobolewska, D. (2010). Saponins as cytotoxic agents: a review. Phytochemistry Reviews, 9, 425–474. DOI: 10.1007/s11101-010-9183-z.
Poh-Hwa, T., Yoke-Kqueen, C., Indu Bala, J., & Son, R. (2011). Bioprotective properties of three Malaysia Phyllanthus species: An investigation of the antioxidant and antimicrobial activities. International Food Research Journal, 18, 887–893.
Rahman, M., Hossain, S., Rahaman, A., Fatima, N., Nahar, T., Uddin, B., & Basunia, M. A. (2013). Antioxidant activity of Centella asiatica (Linn.) urban: Impact of extraction solvent polarity. Journal of Pharmacognosy and Phytochemistry, 1, 27–32.
Roengrit, T., Wannanon, P., Prasertsri, P., Kanpetta, Y., Sripanidkulchai, B. O., & Leelayuwat, N. (2014). Antioxidant and anti-nociceptive effects of Phyllanthus amarus on improving exercise recovery in sedentary men: a randomized crossover (double-blind) design. Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition, 11, article no. 9. DOI: 10.1186/1550-2783-11-9.
Sarin, B., Verma, N., Martín, J. P., & Mohanty, A. (2014). An overview of important ethnomedicinal herbs of Phyllanthus species: Present status and future prospects. The Scientific World Journal, article ID 839172. DOI: 10.1155/2014/839172.
Sen, A., & Batra, A. (2013). The study of in vitro and in vivo antioxidant activity and total phenolic content of Phyllanthus amarus Schum. & Thonn.: A medicinally important plant. International Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences, 5, 942–947.
Shahriar, M., Hossain, M. I., Sharmin, F. A., Akhter, S., Haque, M. A., & Bhuiyan, M. A. (2013). In vitro antioxidant and free radical scavenging activity of Withania somnifera root. IOSR Journal of Pharmacy, 3, 38–47. DOI: 10.9790/3013-32203847.
Shokunbi, O. S., & Odetola, A. A. (2008). Gastroprotective and antioxidant activities of Phyllanthus amarus extracts on absolute ethanol-induced ulcer in albino rats. Journal of Medicinal Plants Research, 2, 261–267.
Tang, Y. Q., & Sekaran, S. D. (2011). Evaluation of Phyllanthus for its anti-cancer properties. In P. E. Spiess (Ed.), Prostate cancer — from bench to bedside (chapter 14, pp. 305–320). Rijeka, Croatia: InTech. DOI: 10.5772/27296.
Tang, Y. Q., Jaganath, I., Manikam, R., & Sekaran, S. D. (2013). Phyllanthus suppresses prostate cancer cell, PC-3, proliferation and induces apoptosis through multiple signalling pathways (MAPKs, PI3K/Akt, NFκB, and hypoxia). Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine, 2013, article ID 609581. DOI: 10.1155/2013/609581.
Tiwari, P., Kumar, B., Kaur, M., Kaur, G., & Kaur, H. (2011). Phytochemical screening and extraction: A review. Internationale Pharmaceutica Sciencia, 1, 98–106.
Vijayakumar, A., Kumar, P. P., & Jeyaraj, B. (2013). Antioxidant activity of Illicium griffithi Hook. f. & Thoms seeds — in vitro. Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical and Clinical Research, 6, 269–273.
Vuong, Q. V., Hirun, S., Roach, P. D., Bowyer, M. C., Phillips, P. A., & Scarlett, C. J. (2013). Effect of extraction conditions on total phenolic compounds and antioxidant activities of Carica papaya leaf aqueous extracts. Journal of Herbal Medicine, 3, 104–111. DOI: 10.1016/j.hermed.2013.04.004.
Vuong, Q. V., Hirun, S., Chuen, T. L. K., Goldsmith, C. D., Bowyer, M. C., Chalmers, A. C., Phillips, P. A., & Scarlett, C. J. (2014). Physicochemical composition, antioxidant and anti-proliferative capacity of a lilly pilly (Syzygium paniculatum) extract. Journal of Herbal Medicine, 4, 134–140. DOI: 10.1016/j.hermed.2014.04.003.
Weng, Y., Yu, L., Cui, J., Zhu, Y. R., Guo, C., Wei, G., Duan, J. L., Yin, Y., Guan, Y., Wang, Y. H., Yang, Z. F., Xi, M. M., & Wen, A. D. (2014). Antihyperglycemic, hypolipidemic and antioxidant activities of total saponins extracted from Aralia taibaiensis in experimental type 2 diabetic rats. Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 152, 553–560. DOI: 10.1016/j.jep.2014.02.001.
Yao, K., Dong, Y. Y., Bian, J., Ma, M. G., & Li, J. F. (2015). Understanding the mechanism of ultrasound on the synthesis of cellulose/Cu(OH)2/CuO hybrids. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 24, 27–35. DOI: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2014.12.002.
Yoshikawa, M., Morikawa, T., Kashima, Y., Ninomiya, K., & Matsuda, H. (2003). Structures of new dammarane-type triterpene saponins from the flower buds of Panax noto-ginseng and hepatoprotective effects of principal ginseng saponins. Journal of Natural Products, 66, 922–927. DOI: 10.1021/np030015l.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nguyen, V.T., Thuy Pham, H.N., Bowyer, M.C. et al. Influence of solvents and novel extraction methods on bioactive compounds and antioxidant capacity of Phyllanthus amarus. Chem. Pap. 70, 556–566 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1515/chempap-2015-0240
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1515/chempap-2015-0240