Abstract
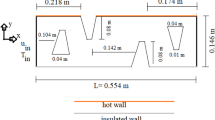
Liquid flow in a tubular reactor with flat internal baffles of various widths was investigated. On the basis of the laser Doppler anemometry (LDA) measurements, the main flow parameters, i.e. the mean and fluctuating velocity components and turbulent kinetic energy (TKE) were determined. The investigations demonstrated that the insertion of baffles into a pipe and a change in their width caused a generation of liquid stream whirls, induced liquid recirculation loops and intensified the flow considerably. The results can be useful in describing turbulent flow in tubular reactors with baffles and in optimising their design.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Atabi, M., Chin, S. B., & Luo, X. Y. (2005a). Flow structure in circular tubes with segmental baffles. Journal of Flow Visualization and Image Processing, 12, 301–311. DOI: 10.1615/JFlowVisImageProc.v12.i3.60.
Al-Atabi, M. T., Chin, S. B., & Luo, X. Y. (2005b). Visualization of mixing of flow in circular tubes with segmental baffles. Journal of Visualization, 8, 89. DOI: 10.1007/bf03181649.
Al-Atabi, M. (2011). Design and assessment of a novel static mixer. The Canadian Journal of Chemical Engineering, 89, 550–554. DOI: 10.1002/cjce.20412.
Albrecht, H. E., Damaschke, N., Borys, M., & Tropea, C. (2003). Laser Doppler and phase Doppler measurement techniques. Berlin, Germany: Springer. DOI: 10.1007/978-3-662-05165-8.
Craig, T. O. (1987). Heat transfer during polymerization in motionless mixers. Polymer Engineering & Science, 27, 13861389. DOI: 10.1002/pen.760271806.
Dantec Dynamics (2005). Installation & user’s guide (BSA flow software, version 4). Skovlunde, Denmark: Dantec Dynamics.
DeGraaff, D. B., & Eaton, J. K. (2001). A high-resolution laser Doppler anemometer: design, qualification, and uncertainty. Experiments in Fluids, 30, 522–530. DOI: 10.1007/s00348000 0231.
Durst, F., Melling, A., & Whitelaw, J. H. (1987). Theorie und Praxis der Laser-Doppler-Anemometrie. Karlsruhe, Germany: G. Braun. DOI: 10.1007/978-3-642-52132-4.
Furling, O., Tanguy, P. A., Choplin, L., & Li, H. Z. (2000). Solid liquid mixing at high concentrations with SMX static mixers. In Proceedings of the 10th European Conference on Mixing, July 2–5, 2000 (pp. 93–100). Delft, The Netherlands: Elsevier. DOI: 10.1016/b978-044450476-0/50013-3.
Grace, H. P. (1982). Dispersion phenomena in high viscosity immiscible fluid systems and application of static mixers as dispersion devices in such systems. Chemical Engineering Communications, 14, 225–277. DOI: 10.1080/00986448208911 047.
Mehdi, Q. S., & Mushatet, K. S. (2008). Simulation of turbulent flow and heat transfer through a duct with baffle plates. Journal of Engineering and Development, 12(3), 142–157.
Mendoza Marin, F. L., Ferrareso Lona, L. M., Wolf Maciel, M. R., & Maciel Filho, R. (2006). New emulsion polymerization tubular reactor with internal angular baffles: Reaction temperature effect. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 100, 2572–2581. DOI 10.1002/app.22638.
Murasiewicz, H., & Jaworski, Z. (2013). Investigation of turbulent flow field in a Kenics static mixer by Laser Doppler Anemometry. Chemical Papers, 67, 1188–1200. DOI: 10.2478/s11696-013-0375-z.
Olivieri, G., Salatino, P., & Marzocchella, A. (2014). Advances in photobioreactors for intensive microalgal production: configurations, operating strategies and applications. Journal of Chemical Technology and Biotechnology, 89, 178–195. DOI: 10.1002/jctb.4218.
Paul, E. L., Atiemo-Obeng, V. A., & Kresta, S. M. (Eds.) (2004). Handbook of industrial mixing: Science and practice. Hoboken, NJ, USA: Wiley.
Strěk, F. (1981). Mixing and agitated vessels. Warsaw, Poland: WNT. (in Polish)
Szoplik, J., & Karcz, J. (2005). An efficiency of the liquid homogenization in agitated vessels equipped with off-centred impeller. Chemical Papers, 59, 373–379.
Tandiroglu, A. (2006). Effect of flow geometry parameters on transient heat transfer for turbulent flow in a circular tube with baffle inserts. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 49, 1559–1567. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2006.01.018.
Tandiroglu, A. (2007). Effect of flow geometry parameters on transient entropy generation for turbulent flow in circular tube with baffle inserts. Energy Conversion and Management, 48, 898–906. DOI: 10.1016/j.enconman.2006.08.022.
Venneker, B. C. H., Derksen, J. J., & Van den Akker, H. E. A. (2010). Turbulent flow of shear-thinning liquids in stirred tanks-The effects of Reynolds number and flow index. Chemical Engineering Research and Design, 88, 827–843. DOI: 10.1016/j.cherd.2010.01.002.
Wang, L. L., Tao, Y., & Mao, X. Z. (2014). A novel flat plate algal bioreactor with horizontal baffles: Structural optimization and cultivation performance. Bioresource Technology, 164, 20–27. DOI: 10.1016/j.biortech.2014.04.100.
Wojtowicz, R., & Talaga, J. (2014). Identification of turbulent liquid flow in a tubular reactor with different width baffles. Chemical Engineering Communications. DOI: 10.1080/00986445.2014.978449. (in press)
Yang, Y. T., & Hwang, C. Z. (2003). Calculation of turbulent flow and heat transfer in a porous-baffled channel. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 46, 771–780. DOI: 10.1016/s0017-9310(02)00360-5.
Zakrzewska, B. (2003). Numerical modeling of heat transport in stirred vessels. Ph.D. Thesis, West Pomeranien University of Technology Szczecin, Szczecin, Poland. (in Polish)
Zakrzewska, B., & Jaworski, Z. (2004). CFD modeling of transient flow in a stirred vessel equipped with Rushton turbine. InZynieria Chemiczna i Procesowa, 25, 1825–1830. (in Polish)
Zhang, Z. (2002). Velocity bias in LDA measurements and its dependence on the flow turbulence. Flow Measurement and Instrumentation, 13, 63–68. DOI: 10.1016/s09555986(02)00029-8.
Zlokarnik, M. (2001). Stirring: Theory and practice. Weinheim, Germeny: Wiley-VCH. DOI: 10.1002/9783527612703.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Talaga, J., Wójtowicz, R. Experimental investigations of liquid flow in pipe with flat internal baffles. Chem. Pap. 70, 477–487 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1515/chempap-2015-0236
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1515/chempap-2015-0236