Abstract
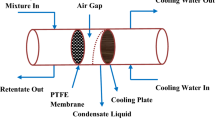
The present study investigated the impact of the driving force (Δp) on the transport properties. All the experiments and calculations were performed for air-gap membrane distillation (AGMD). In the course of the experiments, it was found that an identical value of Δp could be attained by applying different values of feed and permeate temperatures. It was highlighted that constant values of water fluxes could be achieved using the constant driving force created by different temperatures. Moreover, the relation between \({J_{{{\rm{H}}_2}{\rm{O}}}}\) and 1/Tf was shown to be linear only for the \({J_{{{\rm{H}}_2}{\rm{O}}}}\) created at ΔT = Tf − Tp > 35 K. This work’s significant finding was to highlight the limitation of the Arrhenius-type equation applied in the activation energy calculations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alkhudhiri, A., Darwish, N., & Hilal, N. (2013). Produced water treatment: Application of Air gap membrane distillation. Desalination, 309 46–51. DOI: 10.1016/j.desal.2012.09.017.
Arrhenius, S. A. (1889). Über die Dissociationswärme und den Einflusβ der Temperatur auf den Dissociationsgrad der Elektrolyte. Leipzig, Germany: Wilhelm Engelman. (in German)
Baranowski, B. (1991). Non-equilibrium thermodynamics as applied to membrane transport. Journal of Membrane Science, 57 119–159. DOI: 10.1016/s0376-7388(00)80675-4.
El-Bourawi, M. S., Ding, Z., Ma, R., & Khayet, M. (2006). A framework for better understanding membrane distillation separation process. Journal of Membrane Science, 285 4–29. DOI: 10.1016/j.memsci.2006.08.002.
Francis, L., Ghaffour, N., Alsaadi, A. A., & Amy, G. L. (2013). Material gap membrane distillation: A new design for water vapor flux enhancement. Journal of Membrane Science, 448 240–247. DOI: 10.1016/j.memsci.2013.08.013.
Godino, M. P., Barragán, V. M., Izquierdo, M. A., Villaluenga, J. P. G., Seoane, B., & Ruiz-Bauzá, C. (2009). Study of the activation energy for transport of water and methanol through a Nafion membrane. Chemical Engineering Journal, 152 20–25. DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2009.03.022.
Gryta, M. (2005). Osmotic MD and other membrane distillation variants. Journal of Membrane Science, 246 145–156. DOI: 10.1016/j.memsci.2004.07.029.
Imdakm, A. O., & Matsuura, T. (2005). Simulation of heat and mass transfer in direct contact membrane distillation (MD): The effect of membrane physical properties. Journal of Membrane Science, 262 117–128. DOI: 10.1016/j.memsci.2005.05.026.
Jönsson, A. S., Wimmerstedt, R., & Harrysson, A. C. (1985). Membrane distillation — a theoretical study of evaporation through microporous membranes. Desalination, 56 237–249. DOI: 10.1016/0011-9164(85)85028-1.
Kast, W., & Hohenthanner, C. R. (2000). Mass transfer within the gas-phase of porous media. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 43 807–823. DOI: 10.1016/s0017-9310(99)00158-1.
Khayet, M. (2011). Membranes and theoretical modeling of membrane distillation: A review. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 164 56–88. DOI: 10.1016/j.cis.2010.09.005.
Khayet, M., & Matsuura, T. (2011). Membrane distillation: Principles and applications. Amsterdam, The Netherlands: Elsevier.
Kimura, S., Nakao, S. I., & Shimatani, S. I. (1987). Transport phenomena in membrane distillation. Journal of Membrane Science, 33 285–298. DOI: 10.1016/s0376-7388(00)80286-0.
Kujawa, J., Kujawski, W., Koter, S., Jarzynka, K., Rozicka, A., Bajda, K., Cerneaux, S., Persin, M., & Larbot, A. (2013). Membrane distillation properties of TiO2 ceramic membranes modified by perfluoroalkylsilanes. Desalination and Water Treatment, 51 1352–1361. DOI: 10.1080/19443994.2012.704976.
Kujawa, J., Cerneaux, S., Koter, S., & Kujawski, W. (2014). Highly efficient hydrophobic titania ceramic membranes for water desalination. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 6 14223–14230. DOI: 10.1021/am5035297.
Kujawski, W., Krajewska, S., Kujawski, M., Gazagnes, L., Larbot, A., & Persin, M. (2007). Pervaporation properties of fluoroalkylsilane (FAS) grafted ceramic membranes. Desalination, 205 75–86. DOI: 10.1016/j.desal.2006.04.042.
Kujawski, W., Sobolewska, A., Jarzynka, K., Güell, C., Ferrando, M., & Warczok, J. (2013). Application of osmotic membrane distillation process in red grape juice concentration. Journal of Food Engineering, 116 801–808. DOI: 10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2013.01.033.
Laganà, F., Barbieri, G., & Drioli, E. (2000). Direct contact membrane distillation: Modelling and concentration experiments. Journal of Membrane Science, 166 1–11. DOI: 10.1016/s0376-7388(99)00234-3.
Lawson, K. W., & Lloyd, D. R. (1997). Membrane distillation. Journal of Membrane Science, 124 1–25. DOI: 10.1016/s0376-7388(96)00236-0.
Martínez-Díez, L., & Tejerina-García, A. F. (1986). Diffusion of MgCl2 through nuclepore membranes of polycarbonate. Il Nuovo Cimento D, 7 771–780. DOI: 10.1007/bf02453437.
Petrychkovych, R., Setnickova, K., & Uchytil, P. (2013). The influence of water on butanol isomers pervaporation transport through polyethylene membrane. Separation and Purification Technology, 107 85–90. DOI: 10.1016/j.seppur.2013.01.014.
Phattaranawik, J., Jiraratananon, R., & Fane, A. G. (2003). Heat transport and membrane distillation coefficients in direct contact membrane distillation. Journal of Membrane Science, 212 177–193. DOI: 10.1016/s0376-7388(02)00498-2.
Sartorius (2015). Polytetrafluorethylene (PTFE) membrane filter 11806–47-N. Retrieved on February 2015 from http://www.sartorius.com/en/product/product-detail/11806-47-n/
Sha, S., Kong, Y., & Yang, J. R. (2012). The pervaporation performance of C60-filled ethyl cellulose hybrid membrane for gasoline desulfurization: Effect of operating temperature. Energy & Fuels, 26 6925–6929. DOI: 10.1021/ef300986n.
Shirazi, M. M. A., Kargari, A., Tabatabaei, M., Ismail, A. F., & Matsuura, T. (2014). Concentration of glycerol from dilute glycerol wastewater using sweeping gas membrane distillation. Chemical Engineering and Processing: Process Intensification, 78 58–66. DOI: 10.1016/j.cep.2014.02.002.
Varghese, J. G., Karuppannan, R. S., & Kariduraganavar, M. Y. (2010). Development of hybrid membranes using chitosan and silica precursors for pervaporation separation of water + isopropanol mixtures. Journal of Chemical & Engineering Data, 55 2084–2092. DOI: 10.1021/je9003993.
Wynne-Jones, W. F. K., & Eyring, H. (1935). The absolute rate of reactions in condensed phases. The Journal of Chemical Physics, 3 492–502. DOI: 10.1063/1.1749713.
Zemansky, M. W. (1968). Heat and thermodynamics. New York, NY, USA: McGraw Hill.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kujawa, J., Kujawski, W. Driving force and activation energy in air-gap membrane distillation process. Chem. Pap. 69, 1438–1444 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1515/chempap-2015-0155
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1515/chempap-2015-0155