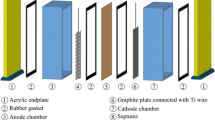
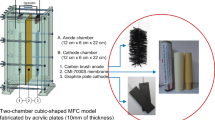
Abstract
Electro-membrane generation of Ag(II) in nitric acid was experimentally explored in a three-electrode laboratory cell with respect to various operating parameters. DSA-O2, titanium plate and saturated Ag/AgCl were employed as the anode, cathode and reference electrode, respectively. The considered process parameters included anolyte temperature and Ag(I) initial concentration, electrolysis time, current density and supporting electrolyte concentration. Parameter effect on the Ag(II) concentration, current density and energy consumption were determined by the Taguchi and ANOVA methods for test design and data analysis, respectively. The results revealed that current density, AgNO3 concentration and temperature had noticeable effect on the generation of Ag(II). On the other hand, AgNO3 concentration and current density showed the most dominant effect on the Ag(II) current efficiency: 48.5% and 30.3%, respectively. AgNO3 concentration and current density were also found to have the highest effect on the energy consumption: 72.4% and 15.9%, respectively. Validity of the Taguchi method was also assessed by collecting the actual data.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Balazs, G. B., Chiba, Z., Hsu, P., Lewis, P. R., Murguia, L., & Adamson, M. (1997). Destruction of hazardous and mixed wastes using mediated electrochemical oxidation in a Ag(II)HNO3 bench scale system. In Proceedings of the 6. International Conference on Radioactive Waste Management and Environmental Remediation, ICEM’ 97, October 12–16, 1997. Singapore, Singapore: ICEM. DOI: 10.2172/611759.
Balazs, G. B., & Lewis, P. R. (1999). U.S. Patent No. 5,919,350. Washington, D.C.: U.S. Patent and Trademark Office.
Bard, A. J., & Faulkner, L. R. (1980). Electrochemical methods: Fundamentals and applications. New York, NY, USA: Wiley.
Bringmann, J., Ebert, K., Galla, U., & Schmieder, H. (1995). Electrochemical mediators for total oxidation of chlorinated hydrocarbons: Formation kinetics of Ag(II), Co(III) and Ce(IV). Journal of Applied Electrochemistry, 25, 846–851. DOI: 10.1007/bf00772203.
Carson, R. W., & Bremer, B. W. (2004). W.O. Patent No. 2,004,012,206. Geneva, Switzerland: World Intellectual Property Organization.
Chandrasekara Pillai, K., Chung, S. J., & Moon, I. S. (2008). Studies on electrochemical recovery of silver from simulated waste water from Ag(II)/Ag(I) based mediated electrochemical oxidation process. Chemosphere, 73, 1505–1511. DOI: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2008.07.047.
Chandrasekara Pillai, K., Matheswaran, M., Chung S. J., & Moon, I. S. (2009). Studies on promising cell performance with H2SO4 as the catholyte for electrogeneration of Ag2+ from Ag+ in HNO3 anolyte in mediated electrochemical oxidation process. Journal of Applied Electrochemistry, 39, 23–30. DOI: 10.1007/s10800-008-9633-0.
Chiba, Z. (1993). Mediated electrochemical oxidation of mixed wastes. In Second International Mixed Waste Symposium, August 17–20, 1993. Baltimore, Maryland, USA: American Society of Mechanical Engineers Mixed Waste Committee.
Chung, S. J., Chandrasekara Pillai, K., & Moon, I. S. (2009). A sustainable environmentally friendly NO x removal process using Ag(II)/Ag(I)-mediated electrochemical oxidation. Separation and Purification Technology, 65, 156–163. DOI: 10.1016/j.seppur.2008.10.030.
Huang, K. L., Chen, T. S., & Yeh, K. J. C. (2009). Regeneration of Ce(IV) in simulated spent Cr-etching solutions using an undivided cell. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 171, 755–760. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.06.061.
Jalali, A. A., Mohammadi, F., & Ashrafizadeh, S. N. (2009). Effects of process conditions on cell voltage, current efficiency and voltage balance of a chlor-alkali membrane cell. Desalination, 237, 126–139. DOI: 10.1016/j.desal.2007.11.056.
Jones, C., Del Campo, J., Nevins, P., & Legg, S. (2002). Decontamination/destruction technology demonstration for organics in transuranic waste. Herndon, VA, US: AEA Technology Engineering Services. DE-BC26-01-NT 41201. DOI: 10.2172/816603.
Karimi, F., Ashrafizadeh, S. N., & Mohammadi, F. (2012). Process parameter impacts on adiponitrile current efficiency and cell voltage of an electromembrane reactor using emulsiontype catholyte. Chemical Engineering Journal, 183, 402–407. DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2011.12.031.
Kariyajjanavar, P., Narayana, J., Nayaka, Y. A., & Umanaik, M. (2010). Electrochemical degradation and cyclic voltammetric studies of textile reactive azo dye cibacron navy WB. Portugaliae Electrochimica Acta, 28, 265–277. DOI: 10.4152/pea.201004265.
Lehmani, A., Turq, P., & Simonin, J. P. (1996). Oxidation kinetics of water and organic compounds by silver(II) using a potentiometric method. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 143, 1860–1866. DOI: 10.1149/1.1836915.
Leung, P. K., Ponce de León, C., Low, C. T. J., & Walsh, F. C. (2011). Ce(III)/Ce(IV) in methanesulfonic acid as the positive half cell of a redox flow battery. Electrochimica Acta, 56, 2145–2153. DOI: 10.1016/j.electacta.2010.12.038.
Martínez-Huitle, C. A., & Ferro, S. (2006). Electrochemical oxidation of organic pollutants for the wastewater treatment: Direct and indirect processes. Chemical Society Reviews, 35, 1324–1340. DOI: 10.1039/b517632h.
Matheswaran, M., Balaji, S., Chung, S. J., & Moon, I. S. (2007). Silver-mediated electrochemical oxidation: Production of silver(II) in nitric acid medium and in situ destruction of phenol in semi-batch process. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 13, 231–236.
Matheswaran, M., Balaji, S., Chung, S. J., & Moon, I. S. (2008). Mediated electrochemical oxidation of phenol in continuous feeding mode using Ag(II) and Ce (IV) mediator ions in nitric acid: A comparative study. Chemical Engineering Journal, 144, 28–34. DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2008.01.005.
Mohammadi, T., Moheb, A., Sadrzadeh, M., & Razmi, A. (2004). Separation of copper ions by electrodialysis using Taguchi experimental design. Desalination, 169, 21–31. DOI: 10.1016/j.desal.2004.08.004.
Mohammadi, F., Ashrafizadeh, S. N., & Sattari, A. (2009). Aqueous HCl electrolysis utilizing an oxygen reducing cathode. Chemical Engineering Journal, 155, 757–762. DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2009.08.030.
Mokhtari, S., Mohammadi, F., & Nekoomanesh, M. (2013). Mediated electrochemical degradation of polystyrene by silver(II): Optimization and kinetic studies. International Journal of ChemTech Research, 5, 2656–2671.
Muthuraman, G., Chung, S. J., & Moon, I. S. (2011). The combined removal of methyl mercaptan and hydrogen sulfide via an electro-reactor process using a low concentration of continuously regenerable Ag(II) active catalyst. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 193, 257–263. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.07.054.
Muthuraman, G., & Moon, I. S. (2012). A review on an electrochemically assisted-scrubbing process for environmental harmful pollutant’s destruction. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 18, 1540–1550. DOI: 10.1016/j.jiec.2012.03.021.
Muthuraman, G., Chung, S. J., & Moon, I. S. (2012). Simple technical approach for perpetual use of electrogenerated Ag(II) at semipilot scale: Removal of NO and SO2 as a model system. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 51, 2697–2703. DOI: 10.1021/ie2015813.
Noyes, A. A., & Kossiakoff, A. (1935). Argentic salts in acid solution. III. Oxidation potential of argentous-argentic salts in nitric acid solution. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 57, 1238–1242. DOI: 10.1021/ja01310a020.
Otto, K., & Wood, K. (2001). Product design: Techniques in reverse engineering and new product development. Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA: Prentice Hall.
Panizza, M., Duo, I., Michaud, P. A., Cerisola, G., & Comnellis, C. (2000). Electrochemical generation of silver(II) at boron-doped diamond electrodes. Electrochemical and Solid-State Letters, 3, 550–551. DOI: 10.1149/1.1391205.
Panizza, M., & Cerisola, G. (2009). Direct and mediated anodic oxidation of organic pollutants. Chemical Reviews, 109, 6541–6569. DOI: 10.1021/cr9001319.
Prabhakaran, D., Kannadasan, T., & Ahmed Basha, C. (2009). Treatability of resin effluents by electrochemical oxidation using batch recirculation reactor. International Journal of Environmental Science & Technology, 6, 491–498. DOI: 10.1007/bf03326088.
Raju, T., Chung, S. J., & Moon, I. S. (2009). Electrochemical recovery of silver from waste aqueous Ag(I)/Ag(II) redox mediator solution used in mediated electro oxidation process. Korean Journal of Chemical Engineering, 26, 1053–1057. DOI: 10.1007/s11814-009-0175-x.
Sequeira, C. A. C., Santos, D. M. F., & Brito, P. S. D. (2006). Mediated and non-mediated electrochemical oxidation of isopropanol. Applied Surface Science, 252, 6093–6096. DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2005.11.028.
Smith, W. H., Purdy, G. M., & McKee, S. D. (1997). Comparison of silver(II), cobalt(III) and cerium(IV) as electron transfer mediators in the MEO mixed waste treatment process. In I&EC Symposium American Chemical Society, September 15–17, 1997. Pittsburgh, PA, USA: American Chemical Society.
Taguchi, G. (1990). Introduction to quality engineering: Designing quality into products and processes. New York, NY, USA: McGraw-Hill.
Taguchi, G., Chowdhury, S., & Wu, Y. (2005). Taguchi’s quality engineering handbook. New York, NY, USA: Wiley. DOI: 10.1002/9780470258354.
Vlachogiannis, J. G., & Vlachonis, G. V. (2005). Taguchi’s method in a marine sediment’s heavy-metal determination. International Journal of Environmental Analytical Chemistry, 85, 553–565. DOI: 10.1080/03067310500107245.
Zhang, H. Y., & Park, S. M. (1995). Kinetic studies on the oxidation of cellulose and its model compounds by Mn(III). Carbohydrate Research, 266, 129–142. DOI: 10.1016/0008-6215(94)00259-i.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mokhtari, S., Mohammadi, F. & Nekoomanesh, M. Effect of process parameters on the concentration, current efficiency and energy consumption of electro-generated silver(II). Chem. Pap. 69, 1219–1230 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1515/chempap-2015-0129
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1515/chempap-2015-0129