Abstract
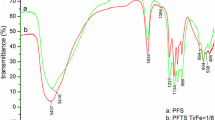
A new type of coagulant, polysilicate-ferric-zinc (PSFZn) with different Fe/Zn molar ratios, was synthesised using water glass (industrial grade, w(SiO2) = 21 mass %, ρ = 1.34 × 103 kg m−3, modulus = 3.2), FeSO4 · 7H2O, ZnSO4, and NaClO3 by way of co-polymerisation in the same (Fe + Zn)/Si molar ratio based on polysilicate-ferric (PSF). The effect of the Fe/Zn molar ratios on the morphology and structure was systematically investigated using scanning electron microscopy (SEM), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), and X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis. Three samples, namely PSFZn4, PSFZn1, and PSFZn0.25, represented Fe/Zn molar ratios of 4, 1, and 0.25, respectively, and were selected for a comparative study while a constant (Fe + Zn)/Si molar ratio equal to 1 was maintained. Accordingly, PSFZn was found to be a complex compound rather than a simple mixture of raw materials. With the decrease in Fe/Zn, a great change occurred in the surface morphology, from a tetrahedral cluster structure to a lamellar structure. The Fe—O and Fe—O—Si bonds were gradually replaced by Zn—O and Zn—O—Si. However, the crystalline peaks were more obvious with the increase in the number of zinc ions; hence the new polymer would be formed from iron, zinc, and polysilicate. In addition, the coagulation performance of PSFZn was investigated using a surface water sample. PSFZn4 exhibited a better coagulation performance than the other PSFZn coagulants. Additionally, the trends in changes in pH with different coagulation times after adding PSFZn were studied relative to PSF and FS. The replacement of zinc ions with iron ions could effectively counter the rapid decrease in pH. The effect of settling time on the coagulation efficiency was also investigated. PSFZn4 exhibited a better settlement performance than PSF and poly aluminium chloride (PAC). Hence, the partial substitution of zinc salt with iron salt not only addresses the inadequacies of iron salt but also improves the coagulation efficiency of zinc salt in water treatment.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cheng, W. P. (2001) Hydrolytic characteristics of polyferric sulfate and its application in surface water treatment. Separation Science and Technology, 36, 2265–2277.DOI: 10.1081/ss-100105917.
Du, J., Zhang, C., Wang, T., & Ding, K. (2006) Studies on property and preparation of polysilicic acid-ferric and zinc sulfate containing boron. Journal of Shanghai Chemical Industry, 2, 18–21.
Fu, Y., & Yu, S. L. (2006) Exterior shapes and coagulation performance of solid poly-ferric silicic sulfate. Environmental Chemistry, 25, 471–476.
Fu, Y., & Yu, S. L. (2007) Characterization and coagulation performance of solid poly-silicic-ferric (PSF) coagulant. Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 353, 2206–2213.DOI: 10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2007.02.038.
Fu, Y., Yu, S. L., Yu, Y. Z., Qiu, L. P., & Hui, B. (2007) Reaction mode between Si and Fe and evaluation of optimal species in poly-silicic-ferric coagulant. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 19, 678–688.DOI: 10.1016/s1001-0742(07)60114-4.
Fu, Y., & Yu, S. L. (2009) Characterization and phosphorus removal of poly-silicic-ferric coagulant. Desalination, 247, 442–455.DOI: 10.1016/j.desal.2009.02.053.
Fu, Y., Yu, S. L., & Han, C. W. (2009) Morphology and coagulation performance during preparation of poly-silicic-ferric (PSF) coagulant. Chemical Engineering Journal, 149, 1–10.DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2007.03.020.
Fu, Y., Gao, B. Y., Zhang, Y. F., Zhang, X. Y., & Shi, N. (2011) Organic modifier of poly-silicic-ferric coagulant: Characterization, treatment of dyeing wastewater and floc change during coagulation. Desalination, 277, 67–73.DOI: 10.1016/j.desal.2011.04.007.
Fan, W. Y., Qiu, X. H., Zhao, S. F., & Liu, Y. S. (2006) Study on applied properties of polymerized silicate containing aluminum sulfate and zinc sulfate (PSAZS). Journal of Shenyang Institute of Chemical Technology, 3, 16–19.
Gao, B. Y., Yue, Q. Y., Zhao, H., & Song, Y. (2000) Properties and evaluation of polyferric-silicate-sulfate (PFSS) coagulant as a coagulant for water treatment. In H. H. Hahn, E. Hofmann, & H. Ødegaard (Eds.), Chemical water and wastewater treatment VI (pp. 15–22). Berlin, Germany: Springer. DOI: 10.1007/978-3-642-59791-6_2.
Hasegawa, T., Hashimoto, T., Onitsuka, T., Goto, K., & Tambo, N. (1991) Characteristics of metal-polysilicate coagulants. Water Science & Technology, 23, 1713–1722.
Liu, H. Q., Yuan, T. Y., Tan, C. D., & Wang, F. Z. (2002) Properties and uses of the zinc polysilicate flocculant. Inorganic Chemical Industry, 2002 (2) 28–30.
Martyn, C. N., Osmond, C., Edwardson, J.A., Barker, D.J. P., Harris, E. C., & Lacey, R. F. (1989) Geographical relation between Alzheimer’s disease and aluminum in drinking water. The Lancet, 333, 61–62.DOI: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)91425-6.
Moussas, P. A., & Zouboulis, A. I. (2008) A study on the properties and coagulation behaviour of modified inorganic polymeric coagulant—Polyferric silicate sulphate (PFSiS). Separation and Purification Technology, 63, 475–483.DOI: 10.1016/j.seppur.2008.06.009.
Ohno, K., Uchiyama, M., Saito, M., Kamei, T., & Magara, Y. (2004) Practical design of flocculator for new polymeric inorganic coagulant — PSI. Water Science & Technology: Water Supply, 4, 67–75.
Santosa, S. J., Kunarti, E. S., & Karmanto (2008) Synthesis and utilization of Mg/Al hydrotalcite for removing dissolved humic acid. Applied Surface Science, 254, 7612–7617.DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2008.01.122.
Shi, Y. H., Fan, M. H., Brown, R. C., Sung, S. W., & Van Leeuwen, J. (2004) Comparison of corrosivity of polymeric sulfate ferric and ferric chloride as coagulants in water treatment. Chemical Engineering and Processing: Process Intensification, 43, 955–964.DOI: 10.1016/j.cep.2003.09.001.
Shi, J., Zhang, Y., Zou, K. Y., & Xiao, F. (2011) Speciation characterization and coagulation of poly-silica-ferric-chloride: The role of hydrolyzed Fe(III) and silica interaction. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 23, 749–756.DOI: 10.1016/s1001-0742(10)60471-8.
Tan, C. D., Liu, H. Q., Yuan, T. Y., & Li, H. Q. (2001) Study on the coefficient of resistance in process of sugarcane’s clarification by PSAZ-sulfitation process. Journal of Guang Xi University: Natural Science Edition, 26 (1) 44–47. (in Chinese)
Wang, D. S., & Tang, H. X. (2001) Modified inorganic polymer flocculant-PFSi: Its preparation, characterization and coagulation behavior. Water Research, 35, 3418–3428.DOI: 10.1016/s0043-1354(01)00034-3.
Xu, X., Yu, S. L., Shi, W. X., Jiang, Z. Q., & Wu, C. (2009) Effect of acid medium on the coagulation efficiency of polysilicate-ferric (PSF)—A new kind of inorganic polymer coagulant. Separation and Purification Technology, 66, 486–491.DOI: 10.1016/j.seppur.2009.02.006.
Zouboulis, A. I., & Moussas, P. A. (2008) Polyferric silicate sulphate (PFSiS): Preparation, characterisation and coagulation behaviour. Desalination, 224, 307–316.DOI: 10.1016/j.desal.2007.06.012.
Zouboulis, A. I., Moussas, P. A., & Vasilakou, F. (2008) Polyferric sulphate: preparation, characterization and application in coagulation experiments. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 155, 459–468.DOI: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.11.108.
Zeng, Y. B., & Park, J. B. (2009) Characterization and coagulation performance of a novel inorganic polymer coagulant-Poly-zinc-silicate-sulfate. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 334, 147–154.DOI: 10.1016/j.colsurfa.2008.10.009.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, X., Shen, RY., Liang, YT. et al. Characterisation and coagulation performance of polysilicate-ferric-zinc. Chem. Pap. 69, 864–871 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1515/chempap-2015-0022
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1515/chempap-2015-0022