Abstract
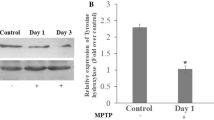
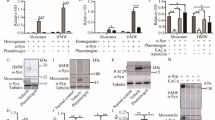
Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) are proteolytic enzymes capable of degrading components of the extracellular matrix. Recent evidence has implicated MMPs in the pathogenesis of neurodegenerative diseases as Alzheimer’s disease and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. In this study, we investigated the involvement of MMP-9 (gelatinase B) in the 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP) mouse model of Parkinson’s disease using zymography, immunohistochemistry, and Western blot analysis. The activity of MMP-9 was upregulated at 3 h after MPTP injection in the striatum and after 24 h in the substantia nigra. Although MMP-9 expression decreased in the striatum by 72 h, it remained elevated in the substantia nigra compared to controls up to 7 d after MPTP administration. Immunohistochemistry showed that neurons and microglia are the source of MMP-9 expression after MPTP administration to mice. Treatment with a hydroxamate-based MMP inhibitor, Ro 28-2653 significantly reduced dopamine depletion and loss of tyrosine hydroxylase immunoreactive neurons in the substantia nigra pars compacta. MMP-9 expression as measured via zymography in the substantia nigra was reduced by the MMP inhibitor. These results indicate that MMP-9 is induced after MPTP application in mice and that pharmacologic inhibition of MMPs protects against MPTP neurotoxicity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asahi M., Sumii T., Fini M. E., Itohara S., and Loh E. (2001) Matrix metalloproteinase 2 gene knockout has no effect on acute brain injury after focal ischemia. Neuroreport 12, 3003–3007.
Asahina M., Yoshiyama Y., and Hattori T. (2001) Expression of matrix metalloproteinase-9 and urinary-type plasminogen activator in Alzheimer’s disease brain. Clin. Neuropathol. 20, 60–63.
Beal M. F. (1995) Aging, energy, and oxidative stress in neurodegenerative diseases. Ann. Neurol. 38, 357–366.
Beal M. F. (1998) Excitotoxicity and nitric oxide in Parkinson’s disease pathogenesis. Ann. Neurol. 44(3 Suppl. 1), S110-S114.
Beuche W., Yushchenko M., Mader M., Maliszewska M., Felgenhauer K., and Weber F. (2000) Matrix metalloproteinase-9 is elevated in serum of patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neuroreport 11, 3419–3422.
Clark A., Krekoski C. A., Bou S. S., Chapman K. R., and Edwards D. R. (1997) Increased gelatinase A (MMP-2) and gelatinase B (MMP-9) activities in human brain after focal ischemia. Neurosci. Lett. 238, 53–55.
Coggeshall R. E. (1992) Aconsideration of neural counting methods. Trends Neurosci. 15, 9–13.
Date I., Felton D. L., and Felton S. Y. (1990) Long-term effect of MPTP in the mouse brain in relation to ageing: neurochemical and immunocytochemical analysis. Brain Res. 519, 266–276.
Duchenin A. M., Gudehithlu K. P., Neff N. H., and Hadjiconstantinou M. (1992) C-fos mRNA in mouse brain after MPTP treatment. Neurochem. Int. 20, 281–287.
Fini M. E., Cook J. R., Mohan R., and Brinckerhoff C. E. (1998) Regulation of matrix metalloproteinase gene expression. In Matrix Metalloproteinases. Parks W. C. and Mecham R. P. (eds.). New York: Academic Press, pp. 299–356.
Fujimura M., Gasche Y., Morita-Fujimura Y., Massengale J., Kawase M., and Chan P. H. (1999) Early appearance of activated matrix metalloproteinase-9 and blood-brain barrier disruption in mice after focal cerebral ischemia and reperfusion. Brain Res. 842, 92–100.
Gijbels K., Proost P., Masure S., Carton H., Biliau A., and Opdenakker G. (1993) Gelatinase B is present in the cerebrospinal fluid during experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis and cleaves myelin basic protein. J. Neurosci. Res. 36, 432–440.
Gu Z., Kaul M., Yab B., Kridel S. J., Cui J., Strongin A., et al. (2002) S-Nitrosylation of matrix metalloproteinases: signaling pathway to neuronal cell death. Science 297, 1186–1190.
Hirsch E. C., Breidert T., Rousselet E., Hunot S., Hartmann A., and Michel P.P. (2003) The role of glial reaction and inflammation in Parkinson’s disease. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 991, 214–228.
Ihara M., Tomimoto H., Kinoshita M., Oh J., Noda M., Wakita H., et al. (2001) Chronic cerebral hypoperfusion induces MMP-2 but not MMP-9 expression in the microglia and vascular endothelium of white matter. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 21, 828–834.
Jung K., Krell H. W., Ortel B., Hasan T., Romer A., Schnorr D., et al. (2003) Plasma matrix metalloproteinase 9 as biomarker of prostate cancer progression in Dunning (Copenhagen) rats. Prostate 54, 206–211.
Kaur D., Yantiri F., Rajagopalan S., Kumar J., Mo J. Q., Boonplueang R., et al. (2003) Genetic or pharmacological iron chelation prevents MPTP-induced neurotoxicity in vivo: a novel therapy for Parkinson’s disease. Neuron 37, 899–909.
Kim G. W., Gasche Y., Grzeschik S., Copin J. C., Maier C. M., and Chan P. H. (2003) Neurodegeneration in striatum induced by the mitochondrial toxin 3-nitropropionic acid: role of matrix metalloproteinase-9 in early blood brain barrier disruption? J. Neurosci. 23, 8733–8742.
Kleiner D. E. and Stetler-Stevenson W. G. (1994) Quantitative zymography: detection of picogram quantities of gelatinases. Anal. Biochem. 218, 325–329.
Kurkowska-Jastrzebska I., Wronska A., Kohutnicka M., Czlonkowski A., and Czlonkowska A. (1999) The inflammatory reaction following 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine intoxication in mouse. Exp. Neurol. 156, 50–61.
Kurlan R, Kim M. H., and Gash D. M. (1991) The time course and magnitude of spontaneus recovery of parkinsonism produced by intracarotid administration of 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine to monkeys. Ann. Neurol. 29, 677–679.
Langston J. W., Ballard P., Tetrud J. W., and Irwin I. (1983) Chronic parkinsonism in humans due to produce of meperidine-analog synthesis. Science 219, 979–980.
Leake A., Morris C. M., and Whateley J. (2000) Brain matrix metalloproteinase 1 levels are elevated in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurosci. Lett. 291, 201–203.
Lim G., Backstrom J. R., Cullen M. J., et al. (1996) Matrix metalloproteinases in the neocortex and spinal cord of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis patients. J. Neurochem. 67, 251–259.
Lorenzl S., Albers D. S., Narr S., Chirichigno J., and Beal M. F. (2002) Expression of MMP-2, MMP-9, and MMP-1 and their endogenous counterregulators TIMP-1 and TIMP-2 in postmortem brain tissue of Parkinson’s disease. Exp. Neurol. 178, 13–20.
Lorenzl S., Albers D. S., Relkin N., Ngyuen T., Hilgenberg S. L., Chirichigno J., et al. (2003) Increased plasma levels of matrix metalloproteinase-9 in patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Neurochem. Int. 43, 191–196.
Maeda A. and Sobel R. A. (1996) Matrix metalloproteinases in the normal human central nervous system, microglia nodules, and multiple sclerosis lesions. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 55, 300–309.
Miyazaki K., Hasegawa M., Funahashi K., and Umeda M. (1993) A metallopreoteinase inhibitor domain in Alzheimer amyloid protein precursor. Nature 362, 839–841.
Nagase H. and Woessner J. F. (1999) matrix metalloproteinases: a minireview. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 21,491–21,494.
Nishi K. (1997) Expression of c-Jun in dopaminergic neurons of the substantia nigra in 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP)-treated mice. Brain Res. 771, 133–141.
O’Callaghan J. P., Martin P. M., and Mass M. J. (1998) The MAP kinase cascade is activated prior to the induction of gliosis in the 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP) model of dopaminergic neurotoxicity. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 844, 40–49.
Paul R., Lorenzl S., Koedel U., Sporer B., Vogel U., Frosch M., et al. (1998) Matrix metalloproteinases contribute to the blood-brain barrier disruption during bacterial meningitis. Ann. Neurol. 44, 592–600.
Peres N., Perillo E., and Zucker S. (1995) Localization of tissue inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinases in Alzheimer’s disease and normal brain. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 54, 16–22.
Saporito M. S., Thomas B. A., and Scott R. W. (2000) MPTP activates c-Jun NH(2)-terminal kinase (JNK) and its upstream regulatory kinase MKK4 in nigrostriatal neurons in vivo. J. Neurochem. 75, 1200–1208.
Sugama S., Yang L., Cho B. P., DeGiorgio L. A., Lorenzl S., Albers D. A., et al. (2003) Age-related microglial activation in 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP)-induced dopaminergic neurodegeneration in C57Bl mice. Brain Res. 964, 288–294.
Szklarczyk A., Lapinska J., Rylski M., McKay R. D. G., and Kaczmarek L. (2002) Matrix metalloproteinase-9 undergoes expression and activation during dendritic remodeling in adult hippocampus. J. Neurosci. 22, 920–930.
Tipton K. F. and Singer T. P. (1993). Advances in our understanding of the mechnisms of the neurotoxicity of MPTP and related compounds. J. Neurochem. 61, 1191–1206.
Turmel H., Hartmann A., Parain K., Douhou A., Srinivasan A., Agid Y., et al. (2001) Caspase-3 activation in 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP) treated mice. Mov. Disord. 16, 185–189.
Viswanth V., Wu Y., Boonplueang R., Chen S., Stevenson F. F., Yantri F., et al. (2001) Caspase-9 activation results in downstream caspase-8 activation and bid cleavage in 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine-induced Parkinson’s disease. J. Neurosci. 21, 9519–9528.
Wang X., Mori T., Jung J. C., Fini M. E., and Lo E. H. (2002) Secretion of matrix metalloproteinase-2 and -9 after mechanical trauma injury in rat cortical cultures and involvement of MAP kinase. J. Neurotrauma 19, 615–625.
Yang L., Schulz J. B., Klockgether T., Liao A. W., Martinou J. C., Penney J. B. Jr., et al. (1998) 1-Methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine neurotoxicity is attenuated in mice overexpressing Bcl-2. J. Neurosci. 18, 8145–8152.
Yoshiyama Y., Ashina M., and Hattori T. (2000) Selective distribution of matrix metalloproteinase-3 (MMP-3) in Alzheimer’s disease brain. Acta Neuropathol. 99, 91–95.
Zhang J. W. and Gottschall P. E. (1997) Zymographic measurement of gelatinase activity in brain tissue after detergent extraction and affinity-support purification. J. Neurosci. Methods 76, 15–20.
Zhang J. W., Deb S., and Gottschall P. E. (1998) Regional and differential expression of gelatinases in rat brain after systemic kainic acid or bicuculline administration. Eur. J. Neurosci. 10, 3358–3368.
Zhang W. J., Deb S., and Gottschall P. E. (2000) Regional and age-related expression of gelatinases in the brains of young and old rats after treatment with kainic acid. Neurosci. Lett. 295, 9–12.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lorenzl, S., Calingasan, N., Yang, L. et al. Matrix metalloproteinase-9 is elevated in 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine-induced parkinsonism in mice. Neuromol Med 5, 119–131 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1385/NMM:5:2:119
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/NMM:5:2:119