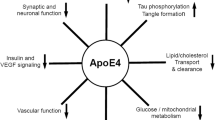
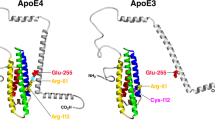
Abstract
The contribution of neuroplasticity to Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is supported by important effects of apoE on both the pathology of AD and the environmental and developmental factors influencing its etiologies. The earlier age of onset of apoE4 AD patients could be caused by defects in apoE-related compensatory repair mechanisms. The role of apoE in stimulating neuronal regeneration like neurite sprouting has received much support, with apoE4 consistently showing defects both in vitro and in vivo and in AD. In addition, growing evidence indicates that the reduced sprouting activity of apoE4 represents a gain-of-negative function; that is, apoE3-stimulated sprouting increases with increasing apoE3 dose, while any neurite sprouting with apoE4 is decreased with increasing apoE4 dose. Clearly, the dose responses for all relevant apoE activities need evaluation, as well as determination of the physiologically relevant doses in the brain. Because apoE4 plays a major role in the risk and onset of AD for ∼50% of AD cases, therapies that target the mechanism of this increased risk would greatly impact AD prevalence. Possible targets include apoE expression levels and regulation, and apoE protein structure or gene replacement. The gain-of-negative function of apoE4 in neurite sprouting, or any apoE4-specific activity, could have important clinical implications for the pharmacogenetic efficacy of therapeutic drugs that impact or target apoE expression or activity. Some therapeutic drugs, including estrogen that can regulate apoE levels, show apoE isotype-dependent efficacy in AD therapy. Other candidate drugs that could modulate apoE expression include antioxidants, anti-inflammatories, and statins. The contribution of apoE4 to drug efficacy may distinguish mechanisms of disease onset from those of progression, since the pleiotropic effects of apoE and its isotypes raise the strong possibility that the isotypes differ in the mechanism by which they contribute to AD etiology.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alvarez X. A., Muozo R., Pichel V., Perez P., Laredo M., Fernandez-Novoa L., et al. (1999) Double-blind placebo-controlled study with citicoline in APOE genotyped Alzheimer’s disease patients. Effects on cognitive performance, brain bioelectrical activity and cerebral perfusion. Methods Findings Exp. Clin. Pharmacol. 21, 633–644.
Arendt T. (2001a) Alzheimer’s disease as a disorder of mechanisms underlying structural brain self-organization. Neuroscience 102, 723–765.
Arendt T. (2001b) Disturbance of neuronal plasticity is a critical pathogenetic event in Alzheimer’s disease. Int. J. Dev. Neurosci. 19, 231–245.
Arendt T. and Zvegintseva H. (1987) Alzheimer’s disease: increase in dendritic branching of reticular neurons in basal nucleus—a sign of regeneration? in Cellular and Molecular Basis of Cholinergic Function, Dowdell, M. J., and Hawthorne, J. N., eds., VCH, Weinhem, Germany, pp. 869–873.
Arendt T., Bruckner M. K., Gertz H. J., and Marcova L. (1998a) Cortical distribution of neurofibrillary tangles in Alzheimer’s disease matches the pattern of neurons that retain their capacity of plastic remodelling in the adult brain. Neuroscience 83, 991–1002.
Arendt T., Holzer M., and Gartner U. (1998b) Neuronal expression of cycline dependent kinase inhibitors of the INK4 family in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neural Transm. 105, 949–960.
Arendt T., Schindler C., Bruckner M. K., Eschrich K., Bigl V., Zedlick D., and Marcova L. (1997) Plastic neuronal remodeling is impaired in patients with Alzheimer’s disease carrying apolipoprotein epsilon 4 allele. J. Neurosci. 17, 516–529.
Arendt T., Zvegintseva H. G., and Leontovich T. A. (1986) Dendritic changes in the basal nucleus of Meynert and in the diagonal band nucleus in Alzheimer’s disease—a quantitative Golgi investigation. Neuroscience 19, 1265–1278.
Ashford J. W. and Jarvik L. (1985) Alzheimer’s disease: does neuron plasticity predispose to axonal neurofibrillary degeneration? N. Engl. J. Med. 313, 388,389.
Ashford J. W. and Mortimer J. A. (2002) Non-familial Alzheimer’s disease is mainly due to genetic factors. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 4, 169–177.
Barres B. A. and Smith S. J. (2001) Neurobiology. Cholesterol—making or breaking the synapse. Science 294, 1296,1297.
Bassett C. N. and Montine T. J. (2003) Lipoproteins and lipid peroxidation in Alzheimers disease. J. Nutr. Health Aging 7(1), 446–451.
Bellosta S., Nathan B. P., Orth M., Dong L. M., Mahley R. W., and Pitas R. E. (1995) Stable expression and secretion of apolipoproteins E3 and E4 in mouse neuroblastoma cells produces differential effects on neurite outgrowth. J. Biol. Chem. 270, 27063–27071.
Benzing W. C., Mufson E. J., and Armstrong D. M. (1993) Alzheimer’s disease-like dystrophic neurites characteristically associated with senile plaques are not found within other neurodegenerative diseases unless amyloid beta-protein deposition is present. Brain Res. 606, 10–18.
Bertoni-Freddari C. (1988) Age-dependent deterioration of neuronal membranes and the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease: a hypothesis. Med. Hypotheses 25, 147–149.
Blacker D., Haines J. L., Rodes L., Terwedow H., Go R. C. P., Harrell L. E., et al. (1997) ApoE-4 and age at onset of Alzheimer’s disease: the NIMH genetics initiative. Neurology 48, 139–147.
Boyles J. K., Zoellner C. D., Anderson L. J., Kosik L. M., Pitas R. E., Weisgraber K. H., et al. (1989) A role for apolipoprotein E, apolipoprotein A-I, and low density lipoprotein receptors in cholesterol transport during regeneration and remyelination of the rat sciatic nerve. J. Clin. Invest. 83, 1015–1031.
Bretsky P. M., Buckwalter J. G., Seeman T. E., Miller C. A., Poirier J., Schellenberg G. D., et al. (1999) Evidence for an interaction between apolipoprotein E genotype, gender, and Alzheimer disease. Alzheimer Dis. Assoc. Disord. 13, 216–221.
Bruses J. L., Chauvet N., and Rutishauser U. (2001) Membrane lipid rafts are necessary for the maintenance of the (alpha)7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor in somatic spines of ciliary neurons. J. Neurosci. 21, 504–512.
Buttini M., Akeefe H., Lin C., Mahley R. W., Pitas R. E., Wyss-Coray T., and Mucke L. (2000) Dominant negative effects of apolipoprotein E4 revealed in transgenic models of neurodegenerative disease. Neuroscience 97, 207–210.
Buttini M., Orth M., Bellosta S., Akeefe H., Pitas R. E., Wyss-Coray T., et al. (1999) Expression of human apolipoprotein ε3 or ε4 in the brains of apoe-/- mice: isoform-specific effects on neurodegeneration. J. Neurosci. 19, 4867–4880.
Buxbaum J. D., Cullen E. I., and Friedhoff L. T. (2002) Pharmacological concentrations of the HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor lovastatin decrease the formation of the Alzheimer beta-amyloid peptide in vitro and in patients. Front. Biosci. 7, a50-a59.
Cambon K., Davies H. A., and Stewart M. G. (2000) Synaptic loss is accompanied by an increase in synaptic area in the dentate gyrus of aged human apolipoprotein E4 transgenic mice. Neuroscience 97, 685–692.
Cassell M. D. and Brown M. W. (1984) Distribution of timm’s stain in the nonsulphide-perfused human hippocampal formation. J. Comp. Neurol. 222, 461–471.
Chawen J. A., Torres-Aleman I., and Garcia-Segura L. M. (1992) Trophic effects of estradiol on fetal rat hypothalamic neurons. Neuroendocrinology 56, 895–901.
Chen Y., Lomnitski L., Michaelson D. M., and Shohami E. (1997) Motor and cognitive deficits in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice after closed head injury. Neuroscience 80(4), 1255–1262.
Corder E. H., Saunders A. M., Strittmatter W. J., Schmechel D. E., Gaskell P. C., Small G. W., et al. (1993) Gene dose of apolipoprotein E type 4 allele and the risk of Alzheimer’s disease in late onset families. Science 261, 921–923.
Cotman C. W., Cummings B. J., and Pike C. J. (1993) Molecular cascades in adaptive versus pathological plasticity. Raven Press, New York.
Cotman C. W., Cummings B. J., and Whitson J. S. (1991) The role of misdirected plasticity in plaque biogenesis and Alzheimer’s disease pathology., in Growth Factors and Alzheimer’s Disease, Hefti, F., Brachet, B., and Christen, W. Y., eds., Springer-Verlag, Berlin, pp. 222–233.
Danik M. and Poirier J. (1998) Apolipoprotein E and neuronal plasticity following experimental deafferentation and in Alzheimer’s disease. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 26, 262–266.
DeMattos R. B., Brendza R. P., Heuser J. E., Kierson M., Cirrito J. R., Fryer J., et al. (2001) Purification and characterization of astrocyte-secreted apolipoprotein E and J-containing lipoproteins from wild-type and human apoE transgenic mice. Neurochem. Int. 39, 415–425.
DeMattos R. B., Curtiss L. K. and Williams D. L. (1998) A minimally lipidated form of cell-derived apolipoprotein E exhibits isoform-specific stimulation of neurite outgrowth in the absence of exogenous lipids or lipoproteins. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 4206–4212.
Dietschy J. M. and Turley S. D. (2001) Cholesterol metabolism in the brain. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 12, 105–12.
Fagan A. M., Bu G., Sun Y., Daugherty A., and Holtzman D. M. (1996) Apolipoprotein E-containing high density lipoprotein promotes neurite outgrowth and is a ligand for the low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein. J. Biol. Chem. 271, 30121–30125.
Fagan A. M., Murphy B. A., Patel S. N., Kilbridge J. F., Mobley W. C., Bu G., and Holtzman D. M. (1998) Evidence for normal aging of the septo-hippocampal cholinergic system in apoE (-/-) mice but impaired clearance of axonal degeneration products following injury. Exp. Neurol. 151, 314–325.
Farlow M. R., Lahiri D. K., Poirier J., Davignon J., et al. (1998) Treatment outcome of tacrine therapy depends on apolipoprotein genotype and gender of the subjects with Alzheimer’s disease. Neurology 50(3), 669–677.
Farrer L. A., Cupples L. A., Haines J. L., Hyman B., Kukull W. A., Myers R. H., and van Duijin C. M. (1997) Effects of age, sex, and ethnicity on the association between apolipoprotein E genotype and Alzheimer disease. A meta-analysis. APOE and Alzheimer’s Disease Meta Analysis Consortium. JAMA 278, 1349–1356.
Farrer L. A., Cupples L. A., van Duijn C. M., Kurz A., Zimmer R., Muller U., et al. (1995) Apolipoprotein E genotype in patients with Alzheimer’s disease: implications for the risk of dementia among relatives. Ann. Neurol. 38, 797–808.
Fernandes M. A., Proenca M. T., Nogueira A. J., Oliveira L. M., Santiago B., Santana I., and Oliveira C. R. (1999) Effects of apolipoprotein E genotype on blood lipid composition and membrane platelet fluidity in Alzheimer’s disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1454, 89–96.
Ferrer I., Guionnet N., Cruz-Sanchez F., and Tunon T. (1990) Neuronal alterations in patients with dementia: a Golgi study on biopsy samples. Neurosci. Lett. 114, 11–16.
Feussner G., Dobmeyer J., Grone H. J., Lohmer S., and Wohlfeil S. (1996) A 10-bp deletion in the apolipoprotein epsilon gene causing apolipoprotein E deficiency and severe type III hyperlipoproteinemia. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 58, 281–291.
Fischer O. (1907) Miliare necrosen mit drusigen wucherungen der neurofibrillen, eine regelmassige veranderung der hirnrinde bei seniler demenz. Psychiatrie Neurol. 22, 361–372.
Gaarskjaer F. B. (1986) The organization and development of the hippocampal mossy fiber system. Brain Res. Rev. 11, 335–357.
Geddes J. W., Lundgren K., and Kim Y. K. (1991) Aberrant localization of MAP5 immunoreactivity in the hippocampal formation in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neurosci. Res. 30, 183–191.
Geddes J. W., Monaghan D. T., Cotman C. W., Lott I. T., Kim R. C., and Chui H. C. (1985) Plasticity of hippocampal circuitry in Alzheimer’s disease. Science 230, 1179–1181.
Gimpl G., Burger K., and Fahrenholz F. (1997) Cholesterol as modulator of receptor function. Biochemistry 36, 10959–10974.
Gonatas N. K., Anderson W., and Evangelista I. (1967) The contribution of altered synapses in the senile plaque: an electron microscopic study in Alzheimer’s dementia. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2, 25–39.
Gottfries C. G., Karlsson I., and Svennerholm L. (1996) Membrane components separate early-onset Alzheimer’s disease from senile dementia of the Alzheimer type. Int. Psychogeriatr. 8, 365–372.
Handelmann G. E., Boyles J. K., Weisgraber K. H., Mahley R. W., and Pitas R. E. (1992) Effects of apolipoprotein E, β-very low density lipoproteins, and cholesterol on the extension of neurites by rabbit dorsal root ganglion neurons in vitro. J. Lipid Res. 33, 1677–1688.
Heininger K. (2000) A unifying hypothesis of Alzheimer’s disease. IV. Causation and sequence of events. Rev. Neurosci. 11, 213–328.
Herz J. (2001) The LDL receptor gene family: (un)expected signal transducers in the brain. Neuron 29, 571–581.
Hesse C., Larsson H., Fredman P., Minthon L., Andreasen N., Davidsson P., and Blennow K. (2000) Measurement of apolipoprotein E (apoE) in cerebrospinal fluid. Neurochem. Res. 25, 511–517.
Hoffman P. W. and Chernak J. M. (1994) The rat amyloid precursor protein promoter contains two DNA regulatory elements which influence high level gene expression. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 201, 610–617.
Holtzman D. M. and Fagan A. M. (1998) Potential role of apoE in structural plasticity in the nervous system—implications for disorders of the central nervous system. Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 8, 250–255.
Holtzman D. M., Pitas R. E., Kilbridge J., Nathan B., Mahley R. W., Bu G., and Schwartz A. L. (1995) Low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein mediates apolipoprotein E-dependent neurite outgrowth in a central nervous system-derived neuronal cell line. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 92, 9480–9484.
Huang D. Y., Weisgraber K. H., Strittmatter W. J., and Matthew W. D. (1995) Interaction of Apolipoprotein E with laminin increases neuronal adhesion and alters neurite morphology. Exp. Neurol. 136, 251–257.
Huang D. Y., Liu X. Q., and Mahley R. W. (1999) Differential effects of cytosolic apolipoprotein (APO) E3 and ApoE4 on neurite outgrowth. c. Neurosci. Abstr. 16.4.
Hyman B. T., Gomez-Isla T., Rebeck G. W., Briggs M., Chung H., West H. L., et al. (1996) Epidemiological, clinical, and neuropathological study of apolipoprotein E genotype in Alzheimer’s disease. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 802, 1–5.
Ihara Y. (1988) Massive somatodendritic sprouting of cortical neurons in Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Res. 459, 138–144.
Ji Z. S., Pitas R. E., and Mahley R. W. (1998) Differential cellular accumulation/retention of apolipoprotein E mediated by cell surface heparan sulfate proteoglycans. Apolipoproteins E3 and E2 greater than E4. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 13452–13460.
Jick H., Zornberg G. L., Jick S. S., Seshadri S., and Drachman D. A. (2000) Statins and the risk of dementia. Lancet 356, 1627–1631.
Johannsson G., Oscarsson J., Rosen T., Wiklund O., Olsson G., Wilhelmsen L., and Bengtsson B. A. (1995) Effects of growth hormone therapy on serum lipoprotein levels in growth hormone deficient adults. Influence of gender and apo(A) and apoE phenotypes. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 15(12), 2142–2150.
Jordan J., Galindo M. F., Miller R. J., Reardon C. A., Getz G. S., and LaDu M. J. (1998) Isoform-specific effect of apolipoprotein E on cell survival and beta-amyloid-induced toxicity in rat hippocampal pyramidal neuronal cultures. J. Neurosci. 18, 195–204.
Joseph J., Shukitt-Hale B., Denisova N. A., Martin A., Perry G., and Smith M. A. (2001) Copernicus revisited: amyloid beta in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol. Aging 22, 131–146.
Kerr M. E. and Kraus M. (1998) Genetics and the central nervous system: apolipoprotein E and brain injury. AACN Clin. Issues 9, 524–530.
Kivatinitz S. C., Pelsman M. A., Alonso A. C., Bagatolli L., and Quiroga S. (1997) High-density lipoprotein aggregated by oxidation induces degeneration of neuronal cells. J. Neurochem. 69, 2102–2114.
Kosik K. (1992) Alzheimer’s disease: A cell biological perspective. Science 256, 780–783.
Koudinov A. R. and Koudinova N. V. (2001) Essential role for cholesterol in synaptic plasticity and neuronal degeneration. FASEB J. 15, 1858–1860.
Kushwaha R. S., Foster D. M., Barrett P. H., Carey K. D., and Bernard M. G. (1991) Metabolic regulation of plasma apolipoprotein E by estrogen and progesterone in the baboon (Papio sp.). Metabolism 40, 93–100.
LaDu M. J., Reardon C., Van Eldik L., Fagan A. M., Bu G., Holtzman D., and Getz G. S. (2000) Lipoproteins in the central nervous system. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 903, 167–175.
Lang T., Bruns D., Wenzel D., Riedel D., Holroyd P., Thiele C., and Jahn R. (2001) SNAREs are concentrated in cholesterol-dependent clusters that define docking and fusion sites for exocytosis. EMBO J. 20, 2202–2213.
Laskowitz D. T., Horsburgh K., and Roses A. D. (1998) Apolipoprotein E and the CNS response to injury. J. Cerebr. Blood Flow Metab. 18, 465–471.
Laskowitz D. T., Sheng H., Bart R., Joyner K. A., Roses A. D., and Warner D. S. (1997) Apolipoprotein E-deficient mice have increased susceptibility to focal ischemia. J. Cerebr. Blood Flow Metab. 17, 753–758.
Le Bars P. L., Katz M. M., Berman N., Itil T. M., Freedman A. M., and Schatzberg A. F. (1997) A placebo-controlled, double-blind, randomized trial of an extract of Ginkgo biloba for dementia. JAMA 278, 1327–1332.
Locatelli S., Lutjohann D., Schmidt H. H., Otto C., Beisiegel U., and von Bergmann K. (2002) Reduction of plasma 24S-hydroxycholesterol (cerebrosterol) levels using high-dosage simvastatin in patients with hypercholesterolemia: evidence that simvastatin affects cholesterol metabolism in the human brain. Arch. Neurol. 59, 213–216.
MacGowan S. H., Wilcock G. K., and Scott M. (1998) Effect of gender and apolipoprotein E genotype on response to anticholinesterase therapy in Alzheimer’s disease. Int. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 13, 625–630.
Mahley R. W. (1988) Apolipoprotein E: cholesterol transport protein with expanding role in cell biology. Science 240, 622–630.
Mahley R. and Huang Y. (1999) Apolipoprotein E: from atherosclerosis to Alzheimer’s disease and beyond. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 10, 207–217.
Mahley R. W. and Rall S. C., Jr. (2000) Apolipoprotein E: far more than a lipid transport protein. Annu. Rev. Genomics Hum. Genet. 1, 507–537.
Majocha R. E., Jungalwala F. B., Rodenrys A., and Marotta C. A. (1989) Monoclonal antibody to embryonic CNS antigen A2B5 provides evidence for the involvement of membrane components at sites of Alzheimer degeneration and detects sulfatides as well as gangliosides. J. Neurochem. 53, 953–961.
Marques M. A., Harmony J. A., and Crutcher K. A. (1996) A thrombin cleavage fragment of apolipoprotein E and related synthetic peptides is receptor-mediated. Neuroreport 7, 2529–2532.
Martens J. R., Navarro-Polanco R., Coppock E. A., Nishiyama A., Parshley L., Grobaski T. D., and Tamkun M. M. (2000) Differential targeting of Shaker-like potassium channels to lipid rafts. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 7443–7446.
Masliah E., Mallory M., De Teresa R., Alford M., and Hansen L. (1993a) Differing patterns of aberrant neuronal sprouting in Alzheimer’s disease with and without Lewy bodies. Brain Res. 617, 258–266.
Masliah E., Miller A., and Terry R. D. (1993b) The synaptic organization of the neocortex in Alzheimer’s disease. Med. Hypotheses 41, 334–340.
Masliah E., Mallory M., Alford M., Ge N., and Mucke L. (1995a) Abnormal synaptic regeneration in hAPP695 transgenic and ApoE knockout mice, in Research Advances in Alzheimer’s Disease and Related Disorders, Iqbal, K., Mortimer, J., Winblad, B., and Wisniewski, H. M., eds., Wiley, Chichester, UK, pp. 405–414.
Masliah E., Mallory M., Alford M., Veinbergs I., and Roses A. D. (1995b) Apolipoprotein E role in maintaining the integrity of the aging central nervous system. Apolipoprotein E and Alzheimer’s Disease, Christian Y. and Roses A.D., eds.), Springer, New York.
Masliah E., Mallory M., Ge N., Alford M., Veinbergs I., and Roses A. D. (1995c) Neurodegeneration in the central nervous system of ApoE-deficient mice. Exp. Neurol. 136, 107–122.
Masliah E., Mallory M., Ge N., and Mucke L. (1995d) Synaptic regeneration in hAPP695 transgenic and APOE knockout mice. Neuropathology 44, 405–414.
Masliah E., Mallory M., Veinbergs I., Miller A., and Samuel W, (1996) Alterations in apolipoprotein E expression during aging and neurodegeneration. Prog. Neurobiol. 50, 493–503.
Masliah E., Samuel W., Veinbergs I., Mallory M., Mante M., and Saitoh T. (1997) Neurodegeneration and cognitive impairment in apoE-deficient mice is ameliorated by infusion of recombinant apoE. Brain Res. 751, 307–314.
Masliah E., Armasolo F., Veinbergs I., Mallory M., and Samuel W. (1999) Cerebrolysin ameliorates performance deficits, and neuronal damage in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 62, 239–245.
Mason R. P., Shoemaker W. J., Shajenko L., Chambers T. E., and Herbette L. G. (1992) Evidence for changes in the Alzheimer’s disease brain cortical membrane struture mediated by cholesterol. Neurobiol. Aging 13, 413–419.
Mauch D. H., Nagler K., Schumacher S., Gorits C., Muller E.-C., Otto A., and Pfrieger F. W. (2001) CNS synaptogenesis promoted by glial-derived cholesterol. Science 294, 1354–1357.
McKee A. C., Kowall N. W., and Kosik K. S. (1989) Microtubular reorganization and dendritic growth response in Alzheimer’s disease. Ann. Neurol. 26, 652–659.
Mesulam M. M. (1999) Neuroplasticity failure in Alzheimer’s disease: bridging the gap between plaques and tangles. Neuron 24, 521–529.
Mesulam M. M. (2000) A plasticity-based theory of the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 924, 42–52.
Meyer M. R. (1998) APOE genotype predicts when—not whether—one is predisposed to develop Alzheimer disease. Nat. Genet. 19, 321–322.
Miranda P., Williams C. L., and Einstein G. (1999) Granule cells are sexually dimorphic in their response to estradiol. J. Neurosci. 19, 3316–3325.
Muesing R. A., Miller V. T., LaRosa J. C., Stoy D. B., and Phillips E. A, (1992) Effects of unopposed conjugated equine estrogen on lipoprotein composition and apolipoprotein-E distribution. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 75, 1250–1254.
Mulder M., Ravid R., Swaab D. F., de Kloet E. R., Haasdijk E. D., Julk J., et al. (1998) Reduced levels of cholesterol, phospholipids, and fatty acids in cerebrospinal fluid of Alzheimer disease patients are not related to apolipoprotein E4. Alzheimer Dis. Assoc. Disord. 12, 198–203.
Muller H. W., Gebicke-Harter P. J., Hangen D. H., and Shooter E. M. (1997) A specific 37,000-Dalton protein that accumulates in regenerating but not in nongenerating mammalian nerves. Science 228, 499–501.
Nathan B. P., Bellosta S., Sanan D. A., Weisgraber K. H., Mahley R. W., and Pitas R. E. (1994) Differential effects of apolipoproteins E3 and E4 on neuronal growth in vitro. Science 264, 850–852.
Nathan B. P., Chang K., Bellosta S., Brisch E., Ge N., Mahley R. W., and Pitas R. E. (1995) The inhibitory effect of apolipoprotein E4 on neurite outgrowth is associated with microtubule depolymerization. J. Biol. Chem. 270(34), 19791–19799.
Nathan B. P., Jiang Y., Wong G. K., Shen F., Brewer G., and Struble R. G. (2002) Apolipoprotein E4 inhibits, and apolipoprotein E3 promotes neurite sprouting in cultured adult mouse cortical neurons through a low-density lipoprotin receptor-related protein. Brain Res. 928, 96–105.
Neely M. D. and Montine T. J. (2002) CSF lipoproteins and Alzheimer’s disease. J. Nutr. Health Aging 6(6), 383–391.
Neely M. D., Sidell K. R., Graham D. G., and Montine T. J. (1999) The lipid peroxidation product 4-hydroxynonenal inhibits neurite outgrowth, disrupts neuronal microtubules and modifies cellular tubulin. J. Neurochem. 72, 2323–2333.
Neill D. (1995) Alzheimer’s disease: maladaptive synaptoplasticity hypothesis. Neurodegeneration 4, 217–232.
Pfrieger F. W. and Barres B. A. (1997) Synaptic efficacy enhanced by glial cells in vitro. Science 277, 1684–1687.
Phinney A. L., Deller T., Stalder M., Calhoun M. E., Frotscher M., Sommer B., et al. (1999) Cerebral amyloid induces aberrant axonal sprouting and ectopic terminal formation in amyloid precursor protein transgenic mice. J. Neurosci. 19, 8552–8559.
Pitas R. E. (1996) Microtubule formation and neurite extension are blocked by apolipoprotein E4. Semin. Cell Biol. 7, 725–731.
Pitas R. E., Ji Z. S., Weisgraber K. H., and Mahley R. W. (1998) Role of apolipoprotein E in modulating neurite outgrowth: potential effect of intracellular apolipoprotein E. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 26, 257–262.
Poirier J. (1994) Apolipoprotein E in animal models of CNS injury and in Alzheimer’s disease. Trends Neurosci. 17, 525–530.
Poirier J. (1999) Apolipoprotein E: a pharmacogenetic target for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Mol. Diagn. 4, 335–341.
Poirier J., Baccichet D. D., and Gauthier S. (1993a) Cholesterol synthesis and lipoprotein reuptake during synaptic remodeling in hippocampus in adult rats. Neuroscience 55, 81–90.
Poirier J., Davignon J., Bouthillier D., Kogan S., Bertrand P., and Gauthier S. (1993b) Apolipoprotein E polymorphism and Alzheimer’s disease. Lancet 342, 697–699.
Poirier J., Delisle M.-C., Quirion R., Aubert I., Farlow M., Lahiri D., et al. (1995a) Apolipoprotein E4 allele as a predictor of cholinergic deficits and treatment outcome in Alzheimer disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 92, 12260–12264.
Poirier J., Minnich A., and Davignon J. (1995b) Apolipoprotein E, synaptic plasticity and Alzheimer’s disease. Ann. Med. 27, 663–670.
Popko B., Goodrum J. F., Bouldin T. W., Zhang S. H., and Maeda N. (1993) Nerve regeneration occurs in the absence of apolipoprotein E in mice. J. Neurochem. 60, 1155–1158.
Posse de Chaves E. I., Rusinol A. E., Vance D. E., Campenot R. B., and Vance J. E. (1997) Role of lipoproteins in the delivery of lipids to axons during axonal regeneration. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 30766–30773.
Probst A., Basler V., Bron B., and Ulrich J. (1983) Neuritic plaques in senile dementia of Alzheimer type: a Golgi analysis in the hippocampal region. Brain Res. 268, 249–254.
Puttfarcken P. S., Manelli A. M., Falduto M. T., Getz G. S., and LaDu M,-J. (1997) Effect of apolipoprotein E on neurite outgrowth and β-amyloid-induced toxicity in developing rat primary hippocampal cultures. J. Neurochem. 68, 760–769.
Raber J., Bongers G., LeFevour A., Buttini M., and Mucke L. (2002) Androgens protect against apolipoprotein E4-induced cognitive deficits. J. Neurosci. 22, 5204–5209.
Raber J., Wong D., Buttini M., Orth M., Bellosta S., Pitas R. E., et al. (1998) Isoform-specific effects of human apolipoprotein E on brain function revealed in apoe knockout mice: increased susceptibility of females. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95, 10914–10919.
Raber J., Wong D., Yu G.-Q., Buttini M., Mahley R. W., Pitas R. E., and Mucke L. (2000) Apolipoprotein E and cognitive performance. Nature 404, 352–384.
Ramassamy C., Averill D., Beffert U., Theroux L., Lussier-Cacan S., and Cohn J. S. (2000) Oxidative insults are associated with apolipoprotein E genotype in Alzheimer’s disease brain. Neurobiol. Dis. 7, 23–37.
Rapoport S. I. (2001) In vivo fatty acid incorporation into brain phosholipids in relation to plasma availability, signal transduction and membrane remodeling. J. Mol. Neurosci. 16, 243–261; (Discussion) 279–284.
Rice D. S., Nusinowitz S., Azimi A. M., Martinez A., Soriano E., and Curran T. (2001) The reelin pathway modulates the structure and function of retinal synaptic circuitry. Neuron 313, 929–941.
Richard F., Helbecque N., Neuman E., Guez D., Levy R., and Amouyel P. (1997) ApoE genotyping and response to drug treatment in Alzheimer’s disease. Lancet 349, 539.
Rockwood K., Kirkland S., Hogan D. B., MacKnight C., Merry H., Verreault R., et al. (2002) Use of lipid-lowering agents, indication bias, and the risk of dementia in community-dwelling elderly people. Arch. Neurol. 59, 223–227.
Roses A. D. and Saunders A. M. (1997) Lipid metabolism in the brain: a truly undeveloped science, in Cerebrovascular Pathology in Alzheimer’s Disease, de la Torre, J. C., and Hachinski, V., eds., New York Academy of Sciences, New York, p. 208.
Roses A. D., Einstein G., Gilbert J., Goedert M., Han S. H., Huang D., et al. (1996) Morphological, biochemical, and genetic support for an apolipoprotein E effect on microtubular metabolism. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 777, 147–157.
Sano M., Ernesto C., Thomas R. G., Klauber M. R., Schafer K., Grundman M., et al. (1997) A controlled trial of selegiline, alpha-tocopherol, or both as treatment for Alzheimer’s disease. The Alzheimer’s Disease Cooperative Study. N. Engl. J. Med. 336, 1216–1222.
Saunders A. M., Trowers M. K., Shimkets R. A., Blakemore S., Crowther D. J., Mansfield T. A., et al. (2000) The role of apolipoprotein E in Alzheimer’s disease: pharmacogenomic target selection. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1502, 85–94.
Scheibel A. B. and Tomiyasu U. (1978) Dendritic sprouting in Alzheimer’s presentile dementia. Exp. Neurol. 60, 1–8.
Schneider L. S. and Farlow M. (1997) Combined tacrine and estrogen replacement therapy in patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 826, 317–322.
Scott R. B., Collins J. M., and Hunt P. A. (1994) Alzheimer’s disease and Down syndrome: leukocyte membrane fluidity alterations. Mech. Ageing Dev. 75, 1–10.
Sekiguchi M., Abe H., Nagato Y., Tanaka O., Guo H., and Nowakowski R. S. (1996) The abnormal distribution of mossy fiber bundles and morphological abnormalities in hippocampal formation of dreher-J (dr-J/dr-J) mouse. Dev. Brain Res. 92, 31–38.
Simchowicz T. (1911) Histologic studien uber die senile demenz, in Histologische und Histopathologische arbeiten uber die grosshirnrinde mit besonderer berucksichtigung der pathologischen anatomie der geistekrankheiten, Nissl, F. and Alzheimer, A., eds., Fischer, Jena, Germany, pp. 267–444.
Sjoberg A., Oscarsson J., Eden S., and Olofsson S. O. (1994) Continuous but not intermittent administration of growth hormone to hypophysectomized rats increases apolipoprotein-E secretion from cultured hepatocytes. Endocrinology 134, 790–798.
Slomianka L. and Geneser F. A. (1997) Postnatal development of zinc-containing cells and neuropil in the hippocampal region of the mouse. Hippocampus 7(3), 321–340.
Smith J. D., Miyata M., Poulin S. E., Neveux L. M., and Craig W. Y. (1998) The relationship between apolipoprotein E and serum oxidation-related variables is apolipoprotein E phenotype dependent. Int. J. Clin. Lab. Res. 28(2), 116–121.
Stone D. J., Rozovsky I, Morgan T. E., Anderson C. P., and Finch C. E. (1998) Increased synaptic sprouting in response to estrogen via an apolipoprotein E-dependent mechanism: implications for Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neurosci. 18(9), 3180–3185.
Stone D. J., Rozovsky I., Morgan T. E., Anderson C. P., Hajian H., and Finch C. E. (1997) Astrocytes and microglia respond to estrogen with increased apoE mRNA in vivo and in vitro. Exp. Neurol. 143, 313–318.
Su J. H., Cummings B. J., and Cotman C. W. (1993) Identification and distribution of axonal dystrophic neurites in Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Res. 625, 228–237.
Sun Y., Wu S., Bu G., Onifade M. K., Patel S. N., LaDu M. J., Fagan A. M., and Holtzman D. M. (1998) Glial fibrillary acidic protein-apolipoprotein E transgenic mice: astrocyte-specific expression and differing biological effects of astrocyte-secreted apoE3 and apoE4 lipoproteins. J. Neurosci. 18, 3261–3272.
Svennerholm L. and Gottfries C. G. (1994) Membrane lipids, selectively diminished in Alzheimer brains, suggest synapse loss as a primary event in early-onset form (type I) and demyelination in late-onset form (type II). J. Neurochem. 62, 1039–1047.
Teter B., Harris-White M., Frautschy S. A., and Cole G. M. (1999) Role of Apolipoprotein E and estrogen in mossy fiber sprouting in hippocampal slice cultures. Neuroscience 91, 1009–1016.
Teter B., Xu P.-T., Gilbert J. R., Roses A. D., Galasko D., and Cole G. M. (1999) Human apolipoprotein E isoform-specific differences in neuronal sprouting in organotypic hippocampal culture. J. Neurochem. 73, 2613–2616.
Teter B. (2000) Apolipoprotein E isotype-specific effects in neurodegeneration. Alzheimer Rep. 3, 199–212.
Teter B. and Ashford J. W. (2002) Neuroplasticity in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neurosci. Res. 70(3), 402–437.
Teter B., Raber J., Nathan B., and Crutcher K. A. (2002a) The presence of apoE4, not the absence of apoE3, contributes to AD pathology. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 4, 155–163.
Teter B., Xu P.-T., Gilbert J. R., Roses A. D., Galasko D., and Cole G. M. (2002b) Defective neuronal sprouting supported by human Apolipoprotein E4 represents again-of-deleterious function. J. Neurosci. Res. 68, 331–336.
Therond P., Bonnefont-Rousselot D., Laureaux C., Vasson M. P., Motta C., Legrand A., and Delattre J. (1999) Copper oxidation of in vitro dioleolylphosphatidyl-choline-enriched high-density lipoproteins: physicochemical features and cholesterol effluxing capacity. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 362(1), 139–147.
Thiele C., Hannah M. J., Fahrenholz F., and Huttner W. B. (2000) Cholesterol binds to synaptophysin and is required for biogenesis of synaptic vesicles. Nat. Cell Biol. 2, 42–49.
Ullian E. M., Sapperstein S. K., Christopherson K. S., and Barres B. A. (2001) Control of synapse number by glia. Science 291, 657–660.
Vance J. E., Campenot R. B., and Vance D. E. (2000) The synthesis and transport of lipids for axonal growth and nerve regeneration. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1486, 84–96.
Veinbergs I., Mallory M., Mante M., Rockenstein E., Gilbert J. R., and Masliah E. (1999) Differential neurotrophic effects of apolipoprotein E in aged transgenic mice. Neurosci. Lett. 265, 218–222.
Weisgraber K. H. (2001) Apolipoprotein E: Structure-function relationships. Adv. Protein Chem. 45, 249–302.
White F., Nicoll J. A., Roses A. D., and Horsburgh K. (2001) Impaired neuronal plasticity in transgenic mice expressing human apolipoprotein E4 compared to E3 in a model of entorhinal cortex lesion. Neurobiol. Dis. 8, 611–625.
Wolozin B., Kellman W., Ruosseau P., Celesia G. G., and Siegel G. (2000) Decreased prevalence of Alzheimer disease associated with 3-hydroxy-3-methyglutaryl coenzyme A reductase inhibitors. Arch. Neurol. 57, 1439–1443.
Woolley C. S. and McEwen B. S. (1993) Roles of estradiol and progesterone in regulation of hippocampal dendritic spine density during the estrous cycle in the rat. J. Comp. Neurol. 336, 293–306.
Yaffe K., Barrett-Connor E., Lin F., and Grady D. (2002) Serum lipoprotein levels, statin use, and cognitive function in older women. Arch. Neurol 59, 378–384.
Yaffe K., Cauley J., Sands L., and Browner W. (1997) Apolipoprotein E phenotype and cognitive decline in a prospective study of elderly community women. Arch. Neurol. 54, 1110–1114.
Yaffe K., Haan M., Byers A., and Tangen C. (2000) Estrogen use, APOE, and cognitive decline—evidence of gene-environment interaction. Neurology 54, 1949–1953.
Zubenko G. S., Kopp U., Seto T., and Firestone L. L. (1999) Platelet membrane fluidity individuals at risk for Alzheimer’s disease: a comparison of results from fluorescence spectroscopy and electron spin resonance spectroscopy. Psychopharmacology (Berl.) 145, 175–180.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Teter, B. ApoE-dependent plasticity in Alzheimer’s disease. J Mol Neurosci 23, 167–179 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1385/JMN:23:3:167
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/JMN:23:3:167