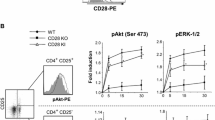
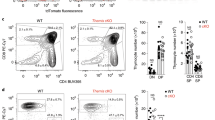
Abstract
T cell activation is central to initiating an immune response. Two signals are required: an antigen-specific signal through the T cell receptor (TCR) and an antigen-independent costimulatory signal, primarily through CD28 in naïve T cells. Although many of the molecules involved in TCR signal transduction have been identified, the signaling pathways downstream of CD28 involved in costimulation are not well-defined. Through mutagenesis, we have generated a panel of Jurkat T cell lines in which CD28 costimulation fails to upregulate the RE/AP composite element of the IL-2 promoter. Biochemical analysis and genetic rescue of the defects in these cell lines will lead to a better understanding of CD28 signal transduction.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chambers CA, Allison JP: Costimulation in T cell responses. Curr Opin Immunol 1997;9: 396–404.
Schwartz RH: T cell clomalanergy. Curr Opin Immunol 1997;9: 351–357.
Harding FA, McArthur JG, Gross JA, Raulet DH, Allison JP: CD28-mediated signaling co-stimulates murine T cells and prevents induction of anergy in T-cell clones. Nature 1992;356:607–609.
June CH, Bluestone JA, Nadler LM, Thompson CB: The B7 and CD28 receptor families. Immunology Today 1994;15:321–331.
Walts TH, DeBenedette MA: T cell co-stimulatory molecules other than CD28. Curr Opimm 1999;11: 286–293.
Borriello F, Sethna MP, Boyd SD, et al.: B7-1 and B7-2 have overlapping, critical roles for immuno globulin class switching and germinal center formation. Immunity 1997;6:303–313.
Green JM, Noel PJ, Sperling AI, Waluras TL, Gray GS, Bluestone JA, Thompson CB: Absence of B7-dependent resporses in CD 28-deficient mice. Immunity 1994;1: 501–508.
Shahinian A, Pfeffer K, Lee KP, et al.: Differential T cell costimulatory requirements in CD28-deficient mice. Science 1993; 261: 609–612.
Riegel JS, Corthesy B, Flanagan WM, Crabtree GR: Regulation of the interleukin-2 gene. Chem Immunol 1992;51:266–298.
Fraser JD, Irving BA, Crabtree GR, Weiss A: Regulation of interleukin-2 gene enhancer activity by the T cell accessory molecule CD28. Science 1991;251:313–316.
Shapiro VS, Truitt KE, Imboden JB, Weiss A: CD28 mediates transcriptional upregualtion of the interleukin-2 (IL-2) promoter through a composite element containing the CD28R Eand NF-IL-2B AP-1 sites. Mol Cell Biol 1997; 17:4051–4058.
Shapiro VS, Mollenauer MN, Weiss A: Endo genous CD28 expressed on myeloma cells upregulates interleukin-8 production: implications for multiple myeloma progression. Blood 2001;98: 187–193.
Shapiro VS, Mollenauer MN, Weiss A: Nuclear factor of activated T cells and AP-1 are insufficient for IL-2 promoter activation: requirement for CD28 up-regulation of RE/AP. J Immunol 1998;161: 4051–4058.
Holdorf AD, Kanagawa O, A.S. Shaw AS: CD28 and T cell co-stimulation. Rev Immunogen 2000;2:175–184.
Ward SG: CD28: a signaling perspective. Biochem J 1996;318:361–377.
Ruland J, Duncan GS, Elia A, et al.: Bc110 is a positive regulator of antigen receptor-induced activation of NF-kappaB and neural tube closure. Cell 2001;104:33–42.
Sun Z, Arendt CW, Ellmeier W, et al.: PKC-theta is required for TCR-induced NF-kappaB activation in mature but not immature lymphocytes. Nature 2000;404:402–407.
Bachmaier K, Krawczyk C, Kozieradzki I, et al.: Negative regulation of lymphocyte activation and autoimmunity by the molecular adaptor Cb1-b. Nature 2000; 403:211–216.
Chiang Y, Kole HK, Brown K, et al.: Cb1-b regulates the CD28 dependence of T-cell activation. Nature 2000;403:216–220.
Kane LP, Andres PG, Howland KC, Abbas AK, Weiss A: Akt provides the CD28 costimulatory signal for up-regulation of IL-2 and IFN gamma but not Th2 cytokines. Nat Immunol 2001;2:37–44.
Burr JS, Savage NDL Messah GE, Kimzey SL, Shaw AS, Green JM: Distinct motifs within CD28 regulate T cell proliferation and induction of Bcl-XL. J. Immunol. 2001; 166:5331–5335.
Harada Y, Tolishima M, Matsumoto Y, et al.: Critical requirement for the membrane-proximal cytosolic tyrosine residue for CD28-mediated costimulation in vivo. J Immunol 2001;166: 3797–3803.
Okkenhaug K, Wu L, Garza KM, et al.: A point mutation in CD28 distinguishes proliferative signals from survival signals. Nat Immunol 2001;2:325–332.
Sadra A, Cinek T, Arellano JL, Shi J, Truitt KE, Imboden JB: Identification of tyrosine phosphorylation sites in the CD28 cytoplasmic domain and their role in the costimulation of Jurkat T cells. J Immunol 1999;162:1966–1973.
Chuang E, Fisher TS, Morgan RW, et al.: The CD28 and CTLA-4 receptors associate with theserine/threonine phosphatase PP2A. Immunity 2000;13:313–322.
Marengere LE, Okkenhaug K, Clavreul A, Couez D, Gibson S, Mills GB, Rottapel R: The SH3 domain of Itk/Emt binds to proline-rich sequences in the cytoplasmic domain of the T cell costimulatory receptor CD28. J Immunol 1997;159:3220–3229.
Raab M, Cai YC, Bunnell SC, Heyeck SD, Berg LJ, Rudd CE: p56lck and p59fyn regulate CD28 binding to phosphatidy linositol 3-kinase, growth factor receptor-bound protein GRB-2 and T cell-specific ptoein-tyrosine kinase ITK: implications for T cell costimulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1995;92:8891–8895.
Holdorf AD, Green JM, Levin SD, et al.: Proline residues in CD28 and the Src Homology (SH) 3 domain of Lck are required for T cell costimulation. J. Exp Med 1999;190: 375–384.
Goldsmith MA, Weiss A: Isolation and characterization of a T-lymphocyte somatic mutant with altered signal transduction by the antigen receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1987;84:6879–6883.
Finco TS, Kadlecek T, Zhang W, Samelson LE, Weiss A: LAT is required for TCR-mediated activation of PLC gammal and the Ras pathway. Immunity 1998;9: 617–626.
Irvin BJ, Williams BL, Nilson AE, Maynor HO, Abraham RT: Pleitropic contributions of phospholipase C-gamma 1 (PLC-gammal) to T-cell antigen receptor-mediated signaling: reconstitution studies of a PLC-gammal-deficient Jurkat T-cell line. Mol Cell Biol 2000;20: 9149–9161.
Straus DB, Weiss A: Genetic evidence for the involvement of the ick tyrosine kinase in signal transduction through the T cell antigen receptor. Cell 1992;70:585–593.
Williams BL, Schreiher KL, Zhang W, Wange RL, Samelson LE, Leibson PJ, Abraham RT: Genetic evidence for differential coupling of Syk family kinases to the T-cell receptor, reconstitution studies in a ZAP-70 deficient Jurkat T-cell line. Mol Cell Biol 1998;18: 1388–1399.
Yablorski D, Kuhne MR, Kadlecek T, Weiss A: Uncoupling of nonreceptor kinases from PLC-gammal in an SLP-76-deficient T cell. Science 1998;281:413–416.
Iwashima M, Takamatsu M, Yamagishi H, et al.: Genetic evidence for She requirement in TCR-induced c-Rel nuclear translocation and IL-2 expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2002;99: 4544–4549.
Clements JL, Yang B, Ross-Barta SE, Eliason SL, Hrstka RF, Williamson RA, Koretzky GA: Requirement for the leukocyte-specificadapter protein SLP-76 for normal T cell development. Science 1998;281:416–419.
Molina TJ, Kishihara K, Siderovski DP, et al.: Profound block in thymocyte development in mice lacking p56 lck. Nature 1992;357: 161–164.
Negishi I, Motoyama N, Nakavama K, et al.: Essential role for ZAP-70 in both positive and negative selection of thymocytes. Nature 1995;376:435–438.
Pivniouk V, Tsitsikov E, Swinton P, Rathbun G, Alt FW, Geha RS: Impaired viability and profound block in thymocyte development in mice lacking the adaptor protein SLP-76. Cell 1998;94:229–238.
Zhang W, Sommers CL, Burshtyn DN, et al.: Essential role of LAT in T cell development. Immunity 1999;10:323–332.
Stark GR, Gudkov AV: Forward genetic analysis in mammalian cells: functional approaches to gene discovery. Hum Mol Gen 1999;8:1925–1938.
Kontgen F, Grumont RJ, Strasser A, Metcalf D, Li R, Tarlinton D, Gerondakis S: Mice lacking the c-rel proto-oncogene exhibit defects in lymphocyte proliferation, humoral immunity, and interleukin-2 expression. Genes Dev 1995;9:1965–1977.
Butscher WG, Powers C, Olive M, Virson C, Gardner K: Coordinate transactivation of the interleukin-2 CD28 response element by c-Rel and ATF-1/CREB:2. J Biol Chem 1998;273:552–560.
McGuire KL, Iacobelli M: Involvement of Rel, Fos and Jun proteins in binding activity to the IL-2 promoter CD28 response element/AP-1 sequence in human T cells. J Immunol 1997;159: 1319–1327.
Sun P, Dong P, Dai K, Hannon GJ, Beach D: p53-independent role of MDM2 in TGF-betal resistance. Science 1998;282:2270–2272.
Holland SJ, Liao XC, Mendenhall MK, et al.: Functional cloning of Srelike adaptor prote in-2 (SLAP-2), a novel inhibitor of antigen receptor signaling. J Exp Med 2001;194: 1263–1276.
Mahlmann S, McLaughlin J, Afar DE, Mohn R, Kay RJ, Witte ON: Dissection of signaling pathways and cloning of new signal transducers in tyrosine kinase-induced pathways by genetic selection. Leukemia 1998;12:1858–1865.
Velazquez L, Fellous M, Stark GR, Pellegrini S: A protein tyrosine kinase in the interferon alpha/beta signaling pathway. Cell 1992;70: 313–322.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Greene, T.A., Shapiro, V.S. Genetic analysis of CD28 signaling. Immunol Res 27, 513–520 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1385/IR:27:2-3:513
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/IR:27:2-3:513