Abstract
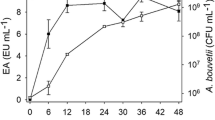
The yeast Candida lipolytica IA 1055 produced an inducible extracellular emulsification activity while utilizing glucose at different concentrations as carbon source during batch fermentation at 27°C. In all glucose concentrations studied, maximum production of emulsification activity was detected in the stationary phase of growth, after pH reached minimal values. The bioemulsifier isolated was a complex biopolymer constituting proteins, carbohydrates, and lipids. The results obtained in this work show that the biosynthesis of a bioemulsifier is not simply a prerequisite for the degradation of extracellular hydrocarbon.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fiechter, A. (1992), Trends Biotechnol. 10, 208–217.
Cooper, D. G. and Zajic, J. E. (1980), Adv. Appl. Biotechnol. 26, 229–253.
Koch, A. K., Kappeli, O., Fiechter, A., and Reiser, J. (1991), J. Bacteriol. 173, 4212–4219.
Ramana, K. V. and Zaranth, N. G. (1989), Biotechnol. Lett. 11, 437–442.
Iqbal, S., Khalid, Z. M., and Malik, K. A. (1995), Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 21, 176–179.
Guerra-Santos, L., Kappeli, O., and Fiechter, A. (1984), Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 48, 301–305.
Cirigliano, M. C. and Carman, G. M. (1984), Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 48, 747–750.
Cirigliano, M. C. and Carman, G. M. (1985), Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 50, 846–850.
Pareilleux, A. (1979), Eur. J. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 8, 91–101.
O.A.A.C. (1984), Official Methods of Analysis, Association of Analytical Chemists, Washington, DC.
Dubois, M., Gilles, K. A., Hamilton, K. J., Rebers, P. A., and Smith, F. (1956), Anal. Chem. 28, 350–356.
Robert, M., Mercadé, E., Andrés, C., Espuny, M. J., Manresa, M. A., and Guinea, J. (1991), Grasas Aceites. 42, 1–7.
Johnson, V., Singh, M., Saini, V. S., Adhikari, D. K., Sista, V., and Yadav, N. K. (1992), Biotechnol. Lett. 14, 487–490.
Hommel, R. K. and Huse, K. (1993), Biotechnol. Lett. 15, 853–858.
Rocha, C., San-Blas, F., San-Blas, G., and Vierma, L. (1992), World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 8, 125–128.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sarubbo, L.A., Marçal, M.d.C., Neves, M.L.C. et al. Bioemulsifier production in batch culture using glucose as carbon source by Candida lipolytica . Appl Biochem Biotechnol 95, 59–67 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1385/ABAB:95:1:59
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/ABAB:95:1:59