Abstract
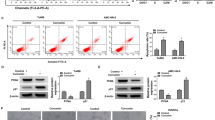
Resveratrol (trans-3,4N,-5-trihydroxystilbene), a phytoalexin present in grapes and red wine, is emerging as a natural compound with potential anticancer properties. Here we show that resveratrol affects the growth of human breast cancer cell lines MCF7, MDA-MB-231, SK-BR-3, and Bcap-37 in a dose-dependent manner and that MCF7 is the most sensitive among the four cell lines. MCF7 cells treated with resveratrol showed typical characteristics of apoptosis including the poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase cleavage, TdT-mediated dUTP nick end labeling-positive staining, and morphologic changes. Phosphorylation of the oncogene product Akt was significantly reduced followed by decreased phosphorylation and increased processing of pro-caspase-9 on resveratrol treatment. These results indicate that resveratrol seems to exert its growth-inhibitory/apoptotic effect on the breast cancer cell line MCF7 via the Akt-caspase-9 pathway.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dercks, W. and Creasy, L. L. (1989), Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 34, 203–213.
Jeandet, P., Bessis, R., and Gautheron, B. (1991), Am. J. Enol. Vitic. 42, 41–46.
Goldberg, D. M., Yan, J., Ng, E., Diamandis, E. P., Karumanchiri, A., Soleas, G., and Waterhouse, A. L. (1995), Am. J. Enol. Vitic. 46, 159–165.
Mahyar-Roemer, M., Katsen, A., Mestres, P., and Roemer, K. (2001), Int. J. Cancer. 94, 615–622.
Tinhofer, I., Bernhard, D., Senfter, M., et al. (2001), FASEB J. 15, 1613–1615.
Jang, M., Cai, L., Udeani, G. O., et al. (1997), Science 275, 218–220.
Clement, M. V., Hirpara, J. L., Chawdhury, S. H., and Pervaiz, S. (1998), Blood 92, 996–1002.
Ragione, F. D., Cucciolla, V., Borriello, A., et al., (1998), Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 250, 53–58.
Huang, C., Ma, W. Y., Goranson, A., and Dong, Z. (1999), Carcinogenesis 20, 237–242.
Schneider, Y., Vincent, F., Duranton, B., et al. (2000), Cancer Lett. 158, 85–91.
Ahmad, N., Adhami, V. M., Afaq, F., Feyes, D. K., and Mukhtar, H. (2001), Clin. Cancer Res. 7, 1466–1473.
Tessitore, L., Davit, A., Sarotto, I., and Caderni, G. (2000), Carcinogenesis 21, 1619–1622.
Carbo, N., Costelli, P., Baccino, F. M., Lopez-Soriano, F. J., and Argiles, J. M. (1999), Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 254, 739–743.
Mgbonyebi, O. P., Russo, J., and Russo, I. H. (1998), Int. J. Oncol. 12, 865–869.
Nakagawa, H., Kiyozuka, Y., Uemura, Y., Senzaki, H., Shikata, N., Hioki, K., and Tsubura, A. (2001), J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 127, 258–264.
Gehm, B. D., McAndrews, J. M., Chien, P. Y., and Jameson, J. L. (1997), Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 94, 14,138–14,143.
Basly, J. P., Marre-Fournier, F., Le Bail, J. C., Habrioux, G., and Chulia, A. J. (2000), Life Sci. 66, 769–777.
Freyberger, A., Hartmann, E., Hildebrand, H., and Krotlinger, F. (2001), Arch. Toxicol. 74, 709–715.
Gusman, J., Malonne, H., and Atassi, G. (2001), Carcinogenesis 22, 1111–1117.
Johnson, C. R., and Jarvis, W. D. (2004), Apoptosis 9, 423–427.
Cardone, M. H., Roy, N., Stennicke, H. R., et al. (1998), Science 282, 1318–1321.
Selvapandiyan, A., Debrabant, A., Duncan, R., et al. (2004), J. Biol. Chem. 279, 25,703–25,710.
James, N. H., and Roberts, R. A., (1996), Carcinogenesis 17, 1623–1632.
Tsan, M. F., White, J. E., Maheshwari, J. G., Bremner, T. A., and Sacco, J. (2000), Br. J. Haematol. 109, 405–412.
Alnemri, E. S., Livingston, D. J., Nicholson, D. W., Salvesen, G., Thornberry, N. A., Wong, W. W., and Yuan, J. (1996), Cell 87, 171.
Nicholson, D. W., and Thornberry, N. A. (1997), Trends Biochem. Sci. 22, 299–306.
Nicholson, D. W., Ali, A., Thornberry, N. A., et al. (1995), Nature 376, 37–43.
Tewari, M., Quan, L. T., O'Rourke, K., et al. (1995), Cell 81, 801–809.
Li, P., Nijhawan, D., Budihardjo, I., Srinivasula, S. M., Ahmad, M., Alnemri, E. S., and Wang, X. (1997), Cell 91, 479–489.
Dorrie, J., Gerauer, H., Wachter, Y., and Zunino, S. J. (2001), Cancer Res. 61, 4731–4739.
Bernhard, D., Tinhofer, I., Tonko, M., et al. (2000), Cell Death Differ. 7, 834–842.
Gerber, H. P., McMurtrey, A., Kowalski, J., Yan, M., Keyt, B. A., Dixit, V., and Ferrara, N. (1998), J. Biol. Chem. 273, 30,336–30,343.
Calabrese, E. J. (2005), Environ. Pollut. 138, 379–411.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Liu, J., Liu, X. et al. Resveratrol-induced cell inhibition of growth and apoptosis in MCF7 human breast cancer cells are associated with modulation of phosphorylated akt and caspase-9. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 135, 181–192 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1385/ABAB:135:3:181
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/ABAB:135:3:181