Abstract
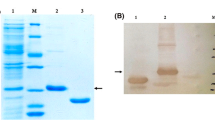
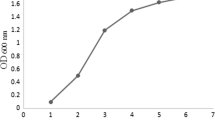
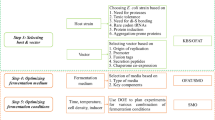
The production of recombinant anti-HIV peptide, T-20, in Escherichia coli was optimized by statistical experimental designs (successive designs with multifators) such as 24–1 fractional factorial, 23 full factorial, and 22 rotational central composite design in order. The effects of media compositions (glucose, NPK sources, MgSO4, and trace elements), induction level, induction timing (optical density at induction process), and induction duration (culture time after induction) on T-20 production were studied by using a statistical response surface method. A series of iterative experimental designs was employed to determine optimal fermentation conditions (media and process factors). Optimal ranges characterized by %T-20 (proportion of pepttide to the total cell protein) were observed, narrowed down, and further investigated to determine the optimal combination of culture conditions, which was as follows: 9, 6, 10, and 1 mL of glucose, NPK sources, MgSO4, and trace elements, respectively, in a total of 100 mL of medium inducted at an OD of 0.55–0.75 with 0.7 mM isopropyl-β-d-thiogalactopyranoside in an induction duration of 4 h. Under these conditions, up to 14% of T-20 was obtained. This statistical optimization allowed, the production of T-20 to be increased more than twofold (from 6 to 14%) within, a shorter induction duration (from 6 to 4 h) at the shake-flask scale.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Richman, D. (1998), Nat. Med. 4(11), 1232–1233.
Chan, D. C., Fass, D., Berger, J. M., and Kim, P. S. (1997), Cell 89, 263–273.
Kilby, J. M., Hopkins, S., Venetta, T. M., et al. (1998), Nat. Med. 4(11), 1302–1307.
Rice, W. G., Supko, J. G., Malspeis, L., et al. (1995), Science 270, 1194–1197.
Vanot, G., Valerie, D., Guilhem, M. C., Phan-Tan-Luu, R. and Comeau, L. C. (2002), Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 60, 417–419.
Rimsky, L. T., Shugars, D. C., and Matthews, T. (1998), J. Virol. 72, 986–992.
Wei, X., Ghosh, S. K., Taylor, M. E., et al. (1995), Nature 373, 117–122.
Lee, K.-M. and Gilmore, D. F. (2005), Appl. Biochem Biotechnol. 133, 113–148.
Lee, K.-M. and Gilmore, D. F. (2005), Process Biochem. 40, 226–249.
Montgomery, D. C. (2004), Design and Analysis of Experiments, 6th ed., John Wiley & Sons, New York.
Myers, R. H. and Montgomery, D. C. (2002), Response surface Methodology Process and Product Optimization Using Designed Experiments, 2nd ed., John Wiley & Sons, New York.
Bollag, D. M., Rozycki, M. D., and Edelstiin, S. J. (1996), Protein Methods, 2nd ed., John Wiley & Sons, New York.
Buzzini, P. (2000), J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 24, 41–45.
Coninck, J., Bouquelet, S., Dumortier, V., Duyme, F., and Verdieer-Denantes, I. (2000), J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 24, 285–290.
El-Heolw, E. R., Abdel-Fatth, Y. R., Ghanem, K. M., and Mohamad, E. A. (2000), Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 54, 515–520.
Hounsa, C. G., Aubry, J. M., Dubourguier, H. C., and Hornez, J. P. (1996), Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 45, 746–770.
Souza, M. C. O., Roberto I. C., and Milagres, A. M. F. (1999), Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 52, 768–772.
Toksoy, E., Onsan, Z. I., and Kirdar, B. (2002), World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 18, 23–27.
Tong, W. Y., Yao, S. J., Zhu, Z. Q., and Yu., J. (2001), Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 57, 674–679.
Trupkin, S., Levin, L., Forchiassin, F., and Viale, A. (2003), J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 30, 682–690.
Xie, L., Hall, D., Eiteman, M. A., and Altman, E. (2003), Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 63, 267–273.
Glick, B. R. (1995), Biotechnol. Adv. 13(2), 247–261.
Cserjan-Puschmann, M., Kramer, M., Duerrschmid, E., Striedner, G., and Bayer, K. (1999), Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 53, 43–50.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Coauthors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, KM., Rhee, CH., Kang, CK. et al. Sequential and simultaneous statistical optimization by dynamic design of experiment for peptide overexpression in recombinant Escherichia coli . Appl Biochem Biotechnol 135, 59–80 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1385/ABAB:135:1:59
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/ABAB:135:1:59