Abstract
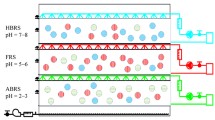
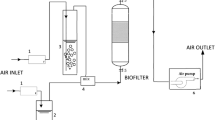
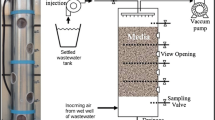
Biofiltration is a biological process which is considered to be one of the more successful examples of biotechnological applications to environmental engineering, and is most commonly used in the removal of odoriferous compounds. In this study, we have attempted to assess the efficiency with which both single and complex odoriferous compounds could be removed, using one- or two-stage biofiltration systems. The tested single odor gases, limonene, α-pinene, and iso-butyl alcohol, were separately evaluated in the biofilters. Both limonene and α-pinene were removed by 90% or more EC (elimination capacity), 364 g/m3/h and 321 g/m3/h, respectively, at an input concentration of 50 ppm and a retention time of 30 s. The iso-butyl alcohol was maintained with an effective removal yield of more than 90% (EC 375 g/m3/h) at an input concentration of 100 ppm. The complex gas removal scheme was applied with a 200 ppm inlet concentration of ethanol, 70 ppm of acetaldehyde, and 70 ppm of toluene with residence time of 45 s in a one- or two-stage biofiltration system. The removal yield of toluene was determined to be lower than that of the other gases in the one-stage biofilter. Otherwise, the complex gases were sufficiently eliminated by the two-stage biofiltration system.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ruokojärvi, A., Ruuskanen, J., and Martikainen, P. J. (1995), J. Air Waste Manage. Assoc. 51(1), 11–16.
Auria, R., Aycaguer, A. C., and Devinny, J. S. (1998), J. Air Waste Manage. Assoc. 48, 65–70.
Mohseni, M. and Allen, D. G. (1999), J. Air Waste Manage. Assoc. 49(12), 1434–1441.
McNevin, D. and Barford, J. (2000), Biochem. Eng. J. 5(3), 231–242.
Shinabe, K., Oketani, S., Ochi, T., et al. (2000), Biochem. Eng. J. 5(3), 209–217.
Park, D. H., Cha, J. M., et al. (2002), Biochem. Eng. J. 11, 167–173.
Morales, M., Perez, F., Auria, R., and Revah, S. (1994), in Advances in Bioprocess Engineering (Galindo, E. and Ramirez, O. T., eds.), Kluwer Academic, Dordrecht, The Netherlands, pp. 405–411.
Shareefdeen, Z., Baltzis, B., Oh, Y.-S., and Bartha, R. (1993), Biotech. Bioeng. 41, 512–524.
Deshusses, M. A., Hamer, G., and Dunn, I. J. (1995), Environ. Sci. Technol. 29, 1059–1068.
Williams, T. O. and Miller, F. C. (1992), Biocycle Magazine 33(10), 72–77.
Lee, G. Y. (2004), PhD Thesis, Chonnam National University, Gwangju, Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jeong, GT., Park, DH., Lee, GY. et al. Application of two-stage biofilter system for the removal of odorous compounds. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 132, 1077–1088 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1385/ABAB:132:1:1077
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/ABAB:132:1:1077