Abstract
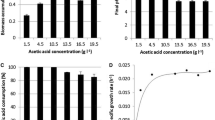
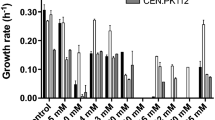
The combined effects of inhibitors present in lignocellulosic hydrolysates was studied using a multivariate statistical approach. Acetic acid (0–6 g/L), formic acid (0–4.6 g/L) and hydroquinone (0–3 g/L) were tested as model inhibitors in synthetic media containing a mixture of glucose, xylose, and arabinose simulating concentrated hemicellulosic hydrolysates. Inhibitors were consumed sequentially (acetic acid, formic acid, and hydroquinone), alongside to the monosaccharides (glucose, xylose, and arabinose). Xylitol was always the main metabolic product. Additionally, glycerol, ethanol, and arabitol were also obtained.
The inhibitory action of acetic acid on growth, on glucose consumption and on all product formation rates was found to be significant (p≤0.05), as well as formic acid inhibition on xylose consumption and biomass production. Hydroquinone negatively affected biomass productivity and yield, but it significantly increased xylose consumption and xylitol productivity. Hydroquinone interactions, either with acetic or formic acid or with both, are also statistically signficant. Hydroquinone seems to partially lessen the acetic acid and amplify formic acid effects. The results clearly indicate that the interaction effects play an important role on the xylitol bioprocess.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Roberto, I. C., Felipe, M. G. A., Lacis, L. S., Silva, S. S., and Mancilha, I. M. (1991), Bioresour. Technol. 36, 271–275.
Vandeska, E., Amartey, S., Kuzmanova, S., and Jeffries, T. W. (1995), World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 11, 213–218.
Oh, D. K., Kim, S. Y., and Kim, J. H. (1998), Biotechnol. Bioeng. 58, 440–444.
Saha, B. C., and Bothast, R. J. (1999), J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 22, 633–636.
Roseiro, J. C., Peito, M. A., Gírio, F. M., and Amaral-Collaço, M. T. (1991), Arch. Microbiol. 156, 484–490.
Domínguez, J. M. (1998), Biotechnol. Lett. 20, 53–56.
Converti, A. and Domínguez, J. M. (2001), Biotechnol. Bioeng. 75, 39–45.
Parajó, J. C., Domínguez, H., and Domínguez, J. M. (1998), Bioresour. Technol. 66, 25–40.
Zaldivar, J. and Ingram, L. O. (1999), Biotechnol. Bioeng. 66, 203–210.
Zaldivar, J., Martínez, A., and Ingram, L. O. (2000), Biotechnol. Bioeng. 68, 524–530.
Gutierrez, T., Buszko, M. L., Ingram, L. O., and Preston, J. F. (2002), Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 98–100, 327–340.
Ranatunga, T. D., Jervis, J., Helm, R. F., McMillan, J. D., and Hatzis, C. (1997), Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 67, 185–198.
Larsson, S., Palmqvist, E., Hahn-Hägerdal, B., et al. (1999), Enzyme Microbiol. Technol. 24, 151–159.
Larsson, S., Quintana-Sáinz, A., Reimann, A., Nilvebrant, N. O., and Jönsson, L. J. (2000), Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 84–6, 617–632.
Palmqvist, E., Grage, H., Meinander, N. Q., and Hahn-Hägerdal, B. (1999), Biotechnol. Bioeng. 63, 46–55.
Fenske, J. J., Griffin, D. A., and Penner, M. H. (1998), J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 20, 364–368.
Oliva, J. M., Ballesteros, I., Negro, M. J., Manzanares, P., Cabanas, A., and Ballesteros, M. (2004), Biotechnol. Prog. 20, 715–720.
Oliva, J. M. Ballesteros, I., Negro, M. J., Manzanares, P., and Ballesteros, M. (2004), In: 26th Symposium on Biotechnology for Fuels and Chemicals, Finkelstein, M. and Davison B., eds., pp. 163.
Carvalheiro, F., Duarte, L. C., Lopes, S., Parajó, J. C., Pereira, H., and Gírio, F. M. (2005), Process Biochem. 40, 1215–1223.
Mussatto, S. I. and Roberto, I. C. (2004), Bioresour. Technol. 93, 1–10.
Mussatto, S. I., Santos, J. C., and Roberto, I. C. (2004), J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 79, 590–596.
Rodrigues, R. C. L. B., Felipe, M. G. A., Silva, J. B. A. E., and Vitolo, M. (2003), Process Biochem. 38, 1231–1237.
Mancilha, I. M. and Karim, M. N. (2003), Biotechnol. Prog. 19, 1837–1841.
Felipe, M. G. A., Vieira, D. C., Vitolo, M., Silva, S. S., Roberto, I. C., and Mancilha, I. M. (1995), J. Basic Microbiol. 35, 171–177.
Lima, L. H. A., Felipe, M. G. A., Vitolo, M., and Torres, F. A. G. (2004), Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol 65, 734–738
Duarte, L. C., Carvalheiro, F., Neves, I., and Gírio, F. M. (2005), Appl. Biochem Biotechnol. 121, 413–425.
Montgomery, D. C. (1997), Design and analysis of experiments, John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York.
Amaral-Collaço, M. T., Gírio, F. M., and Peito, M. A. (1989), In: Enzyme Systems for Lignocellulosic Degradation, Coughlan, M. P., ed., Elsevier Applied Science, London, pp. 221–230.
Oh, D. K. and Kim, S. Y. (1998), Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 50, 419–425.
Tavares, J. M. Duarte, L. C., Amaral-Collaço, M. T., and Gírio, F. M. (2000) Enzyme Microbiol. Technol. 26, 743–747.
Gírio, F. M., Amaro, C., Azinheira, H., Pelica, F., and Amaral-Collaço, M. T. (2000), Bioresour. Technol. 71, 245–251.
Sánchez, S., Bravo, V., Castro, E., Moya, A. J., and Camacho, F. (2002), J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 77, 641–648.
Duarte, L. C., Carvalheiro, F., Lopes, S., Marques, S., Parajó, J. C., and Gírio, F. M. (2004), Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol., 113–116, 1041–1058.
Pampulha, M. E. and Leisola, M. (2002), Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 31, 547–550.
Granström, T. and Leisola, M. (2002), Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 58, 511–516.
Mussatto, S. I., and Roberto, I. C. (2004), Biotechnol. Prog 20, 134–139.
Heipieper, H. J. Keweloh, H., and Rehm, H. J. (1991), Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 57, 1213–1217.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Duarte, L.C., Carvalheiro, F., Tadeu, J. et al. The combined effects of acetic acid, formic acid, and hydroquinone on Debaryomyces hansenii physiology. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 130, 461–475 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1385/ABAB:130:1:461
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/ABAB:130:1:461