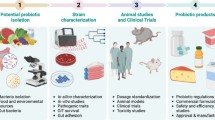
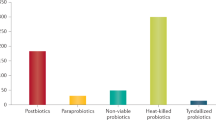
Abstract
Scientific evidence in the prevention and treatment of various disorders is accumulating regarding probiotics. The health benefits supported by adequate clinical data include increased resistance to infectious disease, decreased duration of diarrhea, management of inflammatory bowel disease, reduction of serum cholesterol, prevention of allergy, modulation of cytokine gene expression, and suppression of carcinogen production. Recent ventures in metabolic engineering and heterologous protein expression have enhanced the enzymatic and immunomodulatory effects of probiotics and, with time, may allow more active intervention among critical care patients. In addition, a number of approaches are currently being explored, including the physical and chemical protection of cells, to increase probiotic viability and its health benefits. Traditional immobilization of probiotics in gel matrices, most notably calcium alginate and κ-carrageenan, has frequently been employed, with noted improvements in viability during freezing and storage. Conflicting reports exist, however, on the protection offered by immobilization from harsh physiologic environments. An alternative approach, microencapsulation in “artificial cells,” builds on immobilization technologies by combining enhanced mechanical stability of the capsule membrane with improved mass transport, increased cell loading, and greater control of parameters. This review summarizes the current clinical status of probiotics, examines the promises and challenges of current immobilization technologies, and presents the concept of artificial cells for effective delivery of therapeutic bacterial cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Roberfroid, M. B. (2000), Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 71, 1682S-1687S.
Metchnikoff, E. (1908), The Prolongation of Life, G. P. Putnam’s Sons, New York.
Shah, N P. (2000), J. Dairy Sci. 83, 894–907.
Audet, P., Paquin, C., and Lacroix, C. (1988), Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 29, 11–18.
Chandramouli, V., Kailasapathy, K., Peiris, P., and Jones, M. (2004), J. Microbiol. Methods 56, 27–35.
Hansen, L. T., Allan-Wojtas, P. M., Jin, Y. L., and Paulson, A. T. (2002), Food Microbiol. 19, 35–45.
Park, J. K. and Chang, H. N. (2000), Biotechnol. Adv. 18, 303–319.
Chang, T. M. S. (1964), Science 146, 524–525.
Gill, H. S. and Guarner, F. (2004), Postgrad. Med. J. 80, 516–526.
Gionchetti, P., Rizzello, F., Venturi, A., and Campieri, M. (2000), J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 15, 489–493.
Huang, J. S., Bousvaros, A., Lee, J. W., Diaz, A., and Davidson, E. J. (2002), Dig. Dis. Sci. 47, 2625–2634.
Szajewska, H. and Mrukowicz, J. Z. (2001), J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 33(Suppl. 2), S17-S25.
Szajewska, H., Kotowska, M., Mrukowicz, J. Z., Armanska, M., and Mikolajczyk, W. (2001), J. Pediatr. 138, 361–365.
Aso, Y., Akaza, H., Kotake, T., Tsukamoto, T., Imai, K., and Naito, S. (1995), Eur. Urol. 27, 104–109.
McIntosh, G. H., Royle, P. J., and Playne, M. J. (1999), Nutr. Cancer 35, 153–159.
Singh, J., Rivenson, A., Tomita, M., Shimamura, S., Ishibashi, N., and Reddy, B. S. (1997), Carcinogenesis 18, 833–841.
Rayes, N., Seehofer, D., Hansen, S., et al. (2002), Transplantation 74, 123–127.
Lodinova-Zadnikova, R. and Sonnenborn, U. (1997), Biol. Neonate 71, 224–232.
Bukowska, H., PieczulMroz, J., Chelstowski, K., and Naruszewicz, M. (1997), Atherosclerosis 134, 325.
Steidler, L., Hans, W., Schotte, L., et al. (2000), Science 289, 1352–1355.
Steidler, L. (2002), Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 82, 323–331.
Gill, H. S. (1998), Int. Dairy. J. 8, 535–544.
Meydani, S. N. and Ha, W. K. (2000), Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 71, 861–872.
Gill, H. S. (2003), Best Pract. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 17, 755–773.
Guarner, F. and Malagelada, J. R. (2003), Best Pract. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 17, 793–804.
Van’t Veer, P., Dekker, J., Lamers, J., et al. (1989), Cancer Res. 49, 4020–4023.
Kirjavainen, P. V., Salminen, S. J., and Isolauri, E. (2003), J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 36, 223–227.
Matricardi, P. M., Bjorksten, B., Bonini, S., et al. (2003), Allergy 58, 461–471.
Gilliland, S. E., Nelson, C. R., and Maxwell, C. (1985), Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 49, 377–381.
Schaafsma, G., Meuling, W. J., van Dokkum, W., and Bouley, C. (1998), Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 52, 436–440.
Godward, G. and Kailasapathy, K. (2003), Milchwissenschaft-Milk Sci. Int. 58, 396–399.
Wang, Y. C., Yu, R. C., and Chou, C. C. (2004), Int. J. Food Microbiol. 93, 209–217.
Holzapfel, W. H., Haberer, P., Snel, J., Schillinger, U., and Huis in’t Veld, J. H. J. (1998), Int. J. Food Microbiol. 41, 85–101.
Huang, Y. and Adams, M. C. (2004), Int. J. Food Microbiol. 91, 253–260.
Salminen, S., von Wright, A., Morelli, L., et al. (1998), Int. J. Food Microbiol. 44, 93–106.
Lu, L. and Walker, W. A. (2001), Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 73, 1124S-1130S.
Saavedra, J. M. and Tschernia, A. (2002), Br. J. Nutr. 87, S241-S246.
Vitini, E., Alvarez, S., Medina, M., Medici, M., de Budeguer, M. V., and Perdigon, G. (2000), Biocell 24, 223–232.
Chin, J., Turner, B., Barchia, I., and Mullbacher, A. (2000), Immunol. Cell Biol. 78, 55–66.
Karel, S. F., Libicki, S. B., and Robertson, C. R. (1985), Chem. Eng. Sci. 40, 1321–1354.
Witter, L. (1996), in Physical Chemistry of Food Processes, van Nostrand Reinhold, New York, pp. 475–486.
Babu, P. S., Panda, T., and Babu, M. K. M. (1991), Enzyme Microb. Technol. 13, 676–682.
Adhikari, K., Mustapha, A., Grun, I. U., and Fernando, L. (2000), J. Dairy Sci. 83, 1946–1951.
Sheu, T. Y. and Marshall, R. T. (1993), J. Food Sci. 58, 557–561.
Kebary, K. M. K., Hussein, S. A., and Badawi, R. M. (1998), Egypt. J. Dairy Sci. 26, 319–337.
Sultana, K., Godward, G., Reynolds, N., Arumugaswamy, R., Peiris, P., and Kailasapathy, K. (2000), Int. J. Food Microbiol. 62, 47–55.
Kim, Y. D., Morr, C. V., and Schenz, T. W. (1996), J. Agric. Food Chem. 44, 1308–1313.
Shah, N. P. and Ravula, R. R. (2000), Aust. J. Dairy Technol. 55, 139–144.
Lee, K. Y. and Heo, T. R. (2000), Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 66, 869–873.
Audet, P., Paquin, C., and Lacroix, C. (1990), Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 32, 662–668.
Audet, P., Paquin, C., and Lacroix, C. (1991), Biotechnol. Techniques 5, 307–312.
Sun, W. and Griffiths, M. W. (2000), Int. J. Food Microbiol. 61, 17–25.
Narayani, R. and Rao, K. P. (1993), Int. J. Pharmaceutics 95, 85–91.
Narayani, R. and Rao, K. P. (1995), J. Biomater. Sci.-Polym. Ed. 7, 39–48.
Crittenden, R., Laitila, A., Forssell P., et al. (2001), Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 67, 3469–3475.
Wang, X., Brown, I. L., Evans, A. J., and Conway, P. L. (1999), J. Appl. Microbiol. 87, 631–639.
Prevost, H. and Divies, C. (1992), Biotechnol. Lett. 14, 583–588.
Favoro-Trindade, C. S. and Grosso, C. R. (2002), J. Microencapsul., 19, 485–494.
Rao, A. V., Shiwrarain, N., and Maharaj, I. (1989), Can. Inst. Food Sci. Technol. J. 22, 345–349.
Sanderson, G. R. (1990), in Food Gels, Elsevier, New York, pp. 201–233.
Esquisabel, A., Hernandez, R. M., Igartua, M., Gascon, A. R., Calvo, B., and Pedraz, J. L. (2002), J. Microencapsul. 19, 237–244.
Losgen, H., Brunner, G., Holloway, C. J., et al. (1978), Biomater. Med. Devices Artif. Organs 6, 151–173.
Hou, R. C., Lin, M. Y., Wang, M. M., and Tzen, J. T. (2003), J. Dairy Sci. 86, 424–428.
O’Riordan, K., Andrews, D., Buckle, K., and Conway, P. (2001), J. Appl. Microbiol. 91, 1059–1066.
Chang, T. M. S., MacIntosh, F. C., and Mason, S. G. (1966), Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 44, 115–128.
Chang, T. M. S. and Prakash, S. (1998), Mol. Med. Today 4, 221–227.
Lim, F. and Sun, A. M. (1980), Science 210, 908–910.
Prakash, S. and Chang, T. M. S. (1996), Nat. Med. 2, 883–887.
Prakash, S. and Chang, T. M. S. (1999), Artif. Cells Blood Substitutes Immobilization Biotechnol. 27, 475–481.
Prakash, S. and Chang, T. M. S. (2000), Int. J. Artif. Organs 23, 429–435.
Uludag, H., de Vos, P., and Tresco, P. A. (2000), Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 42, 29–64.
Strand, B. L., Ryan, L., Veld, P. I., et al., (2001), Cell Transplant. 10, 263–275.
Gugerli, R., Cantana, E., Heinzen, C., von Stockar, U., and Marison, I. W. (2002), J. Microencapsul. 19, 571–590.
Ma, X. J., Vacek, I., and Sun, A. (1994), Artif. Cells Blood Substitutes Immobilization Biotechnol. 22, 43–69.
Quong, D., Yeo, J. N., and Neufeld, R. J. (1999), J. Microencapsul. 16, 73–82.
Petruzzo, P., Cappai, A., Ruiu, G., Dessy, E., Rescigno, A., and Brotzu, G. (1997), Transplant. Proc. 29, 2129–2130.
Bartkowiak, A. and Hunkeler, D. (1999), Bioartif. Organs Technol., Med., Mater. 875, 219–232.
Calafiore, R., Basta, G., Luca, G., et al. (1999), Ann. NY Acad Sci. 875, 219–232.
Wang, T., Lacik, I., Brissova, M., et al. (1997), Nat. Biotechnol. 15, 358–362.
Ouyang, W., Chen, H., Jones, M. L., et al. (2004), J. Pharm. Pharmaceut. Sci. 7, 315–324.
Tse, M., Uludag, H., Sefton, M. V., and Chang, P. L. (1996), Biotechnol. Bioeng. 51, 271–280.
Awrey, D. E., Tse, M., Hortelano, G., and Chang, P. L. (1996), Biotechnol. Bioeng. 52, 472–484.
Strand, B. L., Gaserod, O., Kulseng, B., Espevik, T., and Skjak-Baek, G. (2002), J. Microencapsul 19, 615–630.
Bartkowiak, A. and Hunkeler, D. (2000), Chem. Mater. 12, 206–212.
Bartkowiak, A. (2001), Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 944, 120–134.
Haque, T., Chen, H., Ouyang, W., et al. (2005), Mol. Pharm. 2, 29–36.
Lacik, I., Brissova, M., Anilkumar, A. V., Powers, A. C., and Wang, T. (1998), J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 39, 52–60.
Rehor, A., Canaple, L., Zhang, Z., and Hunkeler, D. (2001), J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 12, 157–170.
Crooks, C. A., Douglas, J. A., Broughton, R. L., and Sefton, M. V. (1990), J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 24, 1241–1262.
Wong, H. and Chang, T. M. S. (1991), Biomater. Artif. Cells Immobilization Biotechnol. 19, 687–697.
Siuta-Cruce, P. and Goulet, J. (2001), Food Technol. 55, 36–42.
Institut Rosell-Lallemand (2002), Newsletter Number 2, Institut Rosell-Lallemand, Montreal, QC, Canada.
Steidler, L. (2003), Best Pract. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 17, 861–876.
Federici, F., Vitali, B., Gotti, R., et al. (2004), Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 70, 5066–5073.
Rodby, R. A., Tyszka, T. S., and Williams, J. W. (1991), Am. J. Med. 90, 498–504.
Williams, H. E. and Smith, L. H., Jr. (1968), Am. J. Med. 45, 715–735.
Goldkin, L., Cave, D., Jaffin, B., Robinson, W., and Bliss, C. (1985), Am. J. Gastroenterol 80, 860–865.
Chow, K. M., Liu, Z. C., Prakash, S., and Chang, T. M. S. (2003), Artif. Cells Blood Substitutes Immobilization Biotechnol. 31, 425–434.
Prakash, S. and Chang, T. M. S. (1995), Biotechnol. Bioeng. 46, 621–626.
Duncan, S. H., Richardson, A. J., Kaul, P., Holmes, R. P., Allison, M. J., and Stewart, C. S. (2002), Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 68, 3841–3847.
De Smet, I., Vanhoorde, L., Desaeyer, N., Vandewoestyne, M., and Verstraete, W. (1994), Microbiol. Ecol. Health Dis. 7, 315–329.
Jones, M., Chen, H., Ouyang, W., Metz, T., and Prakash, S. (2004), J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 1, 61–69.
De Boever, P., Wouters, R., Verschaeve, L., Berckmans, P., Schoeters, G., and Verstraete, W. (2000), Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 53, 709–714.
De Smet, I., Vanhoorde, L., Woestyne, M. V., Christiaens, H., and Verstraete, W. (1995), J. Appl. Bacteriol. 79, 292–301.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Prakash, S., Martoni, C. Toward a new generation of therapeutics. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 128, 1–21 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1385/ABAB:128:1:001
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/ABAB:128:1:001