Abstract
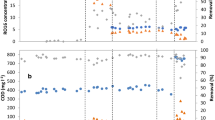
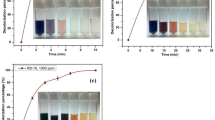
The objective of the present study was to assess the biological decolorization of an industrial, spent reactive dyebath and its three dye components (Reactive Blue 19 [RB 19], Reactive Blue 21 [RB 21], and Reactive Red 198 [RR 198]) under methanogenic conditions. Using a mixed, methanogenic culture, batch assays were performed to evaluate the rate and exten of color removal as well as any potential toxic effects. Overall, a high rate and extent of color removal (>10 mg/[L·h] and 88%, respectively) were observed in cultures amended with either RB19 (an anthraquinone dye) or spent dyebath at an initial dye concentration of 300 mg/L (expressed as RB 19 equivalent) and 30 g/L of NaCl. Inhibition of acidogenesis and, to a larger degree, of methanogenesis resulting in accumulation of volatile fatty acids was observed in both RB 19- and spent dyebath-amended cultures. RB 21 (a phthalocyanine dye) and RR 198 (an azo dye) tested at an initial concentration of 300 mg/L did not result in any significant inhibition of the mixed methanogenic culture. Based on results obtained with cultures amended with RB 19 with and without NaCl, as well as a control culture amended with 30 g/L of NaCl, salt was less inhibitory than either RB 19 or the dyebath. Therefore, the toxic effect of the spent dyebath is at least partially attributed to its major dye component RB 19 and NaCl. Further testing of the effect of RB 19 decolorization products on the methanogenic activity in the absence of NaCl demonstrated that these products are much less inhibitory than the parent dye. Although color removal occurred despite the severe culture inhibition, biological decolorization of full-strength reactive spent dyebaths using methanogenic cultures in a repetitive, closed-loop system is not deemed feasible. For this reason, a fermentative and halotolerant culture was developed and successfully used in our laboratory for the decolorization of industrial reactive dyebaths with 100 g/L of NaCl.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aspland, J. R. (1997), Textile Dyeing and Coloration, American Association of Textile Chemists and Colorists, Research Triangle Park, NC.
Phillips, D. (1996), J. Soc. Dyers Colour 112, 183–186.
Rys, P. and Zollinger, H. (1989), in The Theory of Coloration of Textiles, Johnston, A., ed., Society of Textile Dyers and Colorists, West Yorkshire, England.
Zollinger, H. (1991), Color Chemistry, 2nd ed., VCH, New York.
US Environmental Protection Agency. (1997), Notebook Project: Profile of the Textile Industry, EPA/310-R-97-009, Office of Compliance, Washington, DC.
Pagga, U. and Brown, D. (1986), Chemosphere 15, 479–491.
Seshadri, S., Bishop, P. L., and Agha, A. M. (1994), Waste Manage 14, 127–137.
Vandevivere, P. C., Bianchi, R., and Verstraete, W. (1998), J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 72, 289–302.
Beydilli, M. I., Pavlostathis, S. G., and Tincher, W. C. (2000), Water Environ. Res. 72, 698–705.
Hao, O. J., Hyunook, K., and Chiang, P. C. (2000), Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 30, 449–505.
Nigam, P., Banat, I. M., Singh, D., and Marchant, R. (1996), Proc. Biochem. 31, 435–442.
Beydilli, M. I., Pavlostathis, S. G., and Tincher, W. C. (1998), Water Sci. Technol. 38(4–5), 225–232.
Stolz, A. (2001), Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 56, 69–80.
McMullan, G., Meehan, C., Conneely, A., Kirby, N., Robinson, T., Nigam, P., Banat, I. M., Marchant, R., and Smyth, W. F. (2001), Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 56, 81–87.
van der Zee, F. P., Bouwman, R. H. M., Strik, D. P. B. T. B., Lettinga, G., and Field, J. A. (2001), Biotechnol. Bioeng. 75, 691–701.
Beydilli, M. I., Matthews, R. D., and Pavlostathis, S. G. (2001), Water Sci. Technol. 43(2), 333–340.
Fontenot, E. J., Beydilli, M. I., Lee, Y. H., and Pavlostathis, S. G. (2002), Water Sci. Technol. 45(10), 105–111.
American Public Health Association. (1998), Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 20th ed. APHA-AWWA-WEF, Washington, DC.
Panswad, T. and Luangdilok, W. (2000), Water Res. 34, 4177–4184.
Knarr, R., Velasco, M., Lynn, S., and Tobias, C. (1992), J. Electrochem. Soc. 139, 948–954.
Revenga, J., Rodriguez, F., and Tijero, J. (1994), J. Electrochem. Soc. 141, 330–333.
Itoh, K., Yatone, C., and Ogawa, T. (1993), Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 50, 522–527.
Delée, W., O'Neil, C., Hawkes, F. R., and Pinheiro, H. M. (1998), J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 73, 323–335.
Malpei, F., Andreoni, V., Daffonchio, D., and Rozzi, A. (1998), Biores. Technol. 63, 49–56.
Cooling, F. B. III, Maloney, C. L., Nagel, E., Tabinowski, J., and Odom, J. M. (1996), Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 62, 2999–3004.
Lee, Y. H. and Pavlostathis, S. G. (2001), in Proceedings of the 74th Annual Water Environment Federation Conference and Exposition (WEFTEC 2001)-Session 31: Small and Natural Systems and Water Reuse: Water Reclamation and Reuse II, Atlanta, GA, October 2001, Water Environment Federation, Alexandria, VA, p. 22.
Zhou, W. and Zimmermann, W. (1993), FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 107, 157–162.
Carliell, C. M., Barclay, S. J., Naidoo, N., Buckley, C. A., Mulholland, D. A., and Senior, E. (1995), Water SA 21, 61–69.
Heinfling, A., Bergbauer, M., and Szewzyk, U. (1997), Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 48, 261–266.
Heinfling, A., Martinez, M. J., Martinez, A. T., Bergbauer, M., and Szewzyk, U. (1998), Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 64, 2788–2793.
Heinfling, A., Martinez, M. J., Martinez, A. T., Bergbauer, M., and Szewzyk, U. (1998), FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 165, 43–50.
Conneely, A., Smyth, W. F., and McMullan, G. (1999), J. Porphyr. Phthalocyan. 3, 552–559.
Swamy, J., and Ramsay, J. A. (1999), Enzyme Microb. Technol. 24, 130–137.
Heintling-Weidtmann, A., Reemtsma, T., Storm, T., and Szewzyk, U. (2001), FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 203, 179–183.
Reemtsma, T. and Jakobs, J. (2001), Environ. Sci. Technol. 35, 4655–4659.
Rinzema, A., van Lier, J. B., and Lettinga, G. (1988), Enzyme Microb. Technol. 10, 24–32.
De Baere, L. A., Devocht, M., van Assche, P., and Verstraete, W. (1984), Water Res. 18, 543–548.
Abadulla, E., Tzanov, T., Costa, S., Robra, K.-H., Cavaco-Paulo, A., and Gübitz, G. M. (2000), Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 66, 3357–3362.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fontenot, E.J., Lee, Y.H., Matthews, R.D. et al. Reductive decolorization of a textile reactive dyebath under methanogenic conditions. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 109, 207–225 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1385/ABAB:109:1-3:207
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/ABAB:109:1-3:207