Abstract
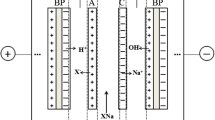
Electrodialysis (ED) shows good potential for downstream processing of acetate fermentation broths, to separate acetic acid while unreacted glucose and other nutrients are partially recycled back to the fermenter. With conventional anion- and cation-exchange membranes, higher current increased acetate flux, water flux, and energy consumption. Multiple ED stacks connected in series with unequal initial volumes for a batch process maximized acetate concentration in the concentrating stream to 134g/L calcium-magnesium acetate (CMA) in the fermentation broth at pH 6.8. Back-transport of acetate from the product into the feed stream and water transport limit the maximum concentration possible. Cost of ED is about $295/ton acetate for the CMA broth.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Parekh, S. R. and Cheryan, M. (1991), Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 36, 384–387.
Parekh, S. R. and Cheryan, M. (1994), Biotechnol. Lett. 16, 139–142.
Witjitra, K., Shah, M. M., and Cheryan, M. (1996), Enzyme Microbial Technol. 19, 322–327.
Cheryan, M. (1998), Ultrafiltration and Microfiltration Handbook, Technomic, Lancaster, PA.
Parekh, S. R. and Cheryan, M. (1994), Enzyme Microbial Technol. 16, 104–109.
Shah, M. M. and Cheryan, M. (1995), Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 51–52, 413–422.
Han, I. S. and Cheryan, M. (1995), J. Membrane Sci. 107, 107–113.
Raman, L. P., Rajagopalan, N., and Cheryan, M. (1994), Chem. Eng. Progr. 90(3), 68–74.
Han, I. S. and Cheryan, M. (1996), Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 57/58, 19–27.
Yen, Y. H. and Cheryan, M. (1991), Trans. Inst. Chemical Engrs. (UK). 69 (Part C), 200–205.
Yen, Y. H. and Cheryan, M. (1993), J. Food Eng. 20, 267–282.
Chukwu, U. N. and Chervan M. (1996), J. Food Sci. 61, 1223–1226.
Perry, R. H., Green, D. W., and Maloney, J. O. (1984), Perry's Chemical Engineering Handbook, 6th ed. McGraw-Hill, New York.
Chukwu, U. N. (1995), Ph. D. thesis, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, Urbana, IL.
Yao, P. X. and Toda, K. (1990), J. Gen. Appl. Microbiol. 36, 111–125.
Perez, A., Andres, L. J., Alvarez, R., Coca, J., and Hill, C. G., Jr. (1993). J. Food Process Eng., 17, 177–190.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chukwu, U.N., Cheryan, M. Electrodialysis of acetate fermentation broths. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 78, 485–499 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1385/ABAB:78:1-3:485
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/ABAB:78:1-3:485