Abstract
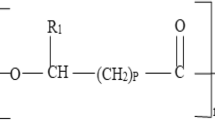
Broader usage of biodegradable plastics in packaging and disposable products as a solution to environmental problems would heavily depend on further reduction of costs and the discovery of novel biodegradable plastics with improved properties. As the first step in our pursuit of eventual usage of industrial food wastewater as nutrients for microorganisms to synthesise environmental-friendly bioplastics, we investigated the usage of soya wastes from a soya milk dairy, and malt wastes from a beer brewery plant as the carbon sources for the production of polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA) by selected strain of microorganism. Bench experiments showed that Alcaligenes latus DSM 1124 used the nutrients from malt and soya wastes to biosynthesise PHAs. The final dried cell mass and specific polymer production of A. latus DSM 1124 were 32g/L and 70% polymer/cells (g/g), 18.42 g/L and 32.57% polymer/cell (g/g), and 28 g/L and 36% polymer/cells (g/g), from malt waste, soya waste, and from sucrose, responctively. These results suggest that many types of food wastes might be used as the carbon source for the production of PHA.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Byrom, D. (1994), in Plastics from microbes: microbial synthesis of polymers and polymer precursors, Mobley, D. P., ed., Hanser, Munich, pp. 5–11.
Yu, P. and Giuliany, B. (1989), Frontiers 9 (11), 4–7.
Lee, S. Y. (1995), Biotechnol. Bioeng. 49, 1–14.
Helmut, B., Gross, R. A., Lenz, R. W., and Fuller, R. C. (1990), Adv. Biochem. Eng./Biotechnol. 41, 78–91.
Linko, S., Vaheri, H., and Seppala, J. (1993), Enzyme Microbiol. Technol. 15(5), 401–406.
Lee, S. Y. (1996), Trends Biotechnol. 14, 431–438.
Yamane, T., Fukunagga, M., and Lee, Y. W. (1996), Biotechnol. Bioeng. 50(2), 197–202.
Kim B. S. and Chang, H. S. (1995), Biotechnol. Techniques 9(5), 311–314.
Alderte, J. E., Karl, D. W., and Park, C. H. (1993), Biotechnol. Prog. 9(5), 520–525.
Shah N. N., Hanna, M. L., and Taylor, R. T. (1996), Biotechnol. Bioeng. 49(2), 161–171.
Son, H. and Lee, S. (1996), Biotechnology Lett. 18, 1217–1222.
Yu, P. H., Chua, H., and Ho, L. Y. (1996), Proceedings of the Asia-Pacific Conference on Sustainable Energy and Environ mental Technology, Singapore, pp. 623–630.
Yu, P. H., Chua, H., Huang, A. L., Lo, W., and Chen, J. C. (1998), Conversion of food industrial wastes into bioplastics. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol.
Gomez, J. G. C., Rodrigues, M. F. A., Alli, R. C. P., Torres, B. B., Bueno Netto, C. L., Oliverira, M. S., and da Silva, L. F. (1996), Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 45, 785–791.
Hahn S. K., Chang, Y. K., Kim, B. S., and Chang, H. N. (1994), Biotechnol. Bioeng. 44(2), 256–261.
Roh, K. S., Yeom, S. H., and Yoo, Y. J. (1995), Biotechnol. Techniques. 9(10), 709–771.
Greenberg, A. E., Clesceri, L. S., and Eton, A. D. (1992), TKN analysis (5310C). Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 18th ed., Apha, Washington, DC.
Jan, S., Roblot, C., Goethals, G., Courtois, J., Courtois, B., Saucedo, J. E. N., Seguin, J. P., and Barbotin, J. N. (1995), Anal. Biochem. 225, 258–263.
Jan S., Roblot, C., Courtois, J., Courtois, B., Barbotin, J. N., and Seguin, J. P. (1996), Enzyme Microbiol. Technol. 18, 195–201.
Hu, W. F., Chua, H., and Yu, P. H. F. (1997), Biotechnol. Lett. 19, 695–698.
Chua, H., Yu, P. H. F., and Ho, L. Y. (1997), Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 63, 627–635.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, P.H., Chua, H., Huang, AL. et al. Conversion of industrial food wastes by Alcaligenes latus into polyhydroxyalkanoates. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 78, 445–454 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1385/ABAB:78:1-3:445
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/ABAB:78:1-3:445