Abstract
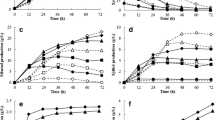
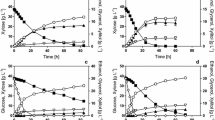
Fermentation kinetics of ethanol production from glucose, xylose, and their mixtures using a recombinant Saccharomyces 1400 (pLNH33) are reported. Single-substrate kinetics indicate that the specific growth rate of the yeast and the specific ethanol productivity on glucose as the substrate was greater than on xylose as a substrate. Ethanol yields from glucose and xylose fermentation were typically 95 and 80% of the theoretical yield, respectively. The effect of ethanol inhibition is more pronounced for xylose fermentation than for glucose fermentation. Studies on glucose-xylose mixtures indicate that the recombinant yeast co-ferments glucose and xylose. Fermentation of a 52.8 g/L glucose and 56.3 g/L xylose mixture gave an ethanol concentration of 47.9 g/L after 36 h. Based on a theoretical yield of 0.51 g ethanol/g sugars, the ethanol yield from this experiment (for data up to 24 h) was calculated to be 0.46 g ethanol/g sugar or 90% of the theoretical yield. The specific growth rate of the yeast on glucose-xylose mixtures was found to lie between the specific growth rate on glucose and the specific growth rate on xylose. Kinetic studies were used to develop a fermentation model incorporating the effects of substrate inhibition, product inhibition, and inoculum size. Good agreements were obtained between model predictions and experimental data from batch fermentation of glucose, xylose, and their mixtures.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- K s :
-
Monod constant, for growth on glucose or xylose (g/L)
- K′ s :
-
Monod constant, for product formation from glucose or xylose (g/L)
- K f :
-
Inhibition constant, for growth on glucose or xylose (g/L)
- K′ i :
-
Inhibition constant for product formation from glucose or xylose (g/L)
- m :
-
maintenance coefficient (/h)
- P :
-
ethanol concentration (g/L)
- P w :
-
ethanol concentration above which cells do not grow (g/L)
- P 2N :
-
ethanol concentration above which cells do not produce ethanol (g/L)
- S :
-
substrate concentration (g/L)
- X :
-
cell dry weight (g/L)
- Yp/s :
-
product yield constant (g-product/g-substrate)
- Y X/xyl :
-
cell yield constant from glucose (g-cells/g-substrate)
- Y X/xyl :
-
cell yield constant from xylose (g-cells/g-substrate)
- μ:
-
specific growth rate (/h)
- v:
-
specific rate of product formation (/h)
- μ m :
-
maximum specific growth rate (/h)
- VIN :
-
maximum specific rate of product formation (/h)
- μ0 :
-
specific growth rate when no initial ethanol is present (/h)
- V 0 :
-
specific rate of product formation when no initial ethanol is present (/h)
- β/f:
-
constants in product inhibition model (dimensionless)
- g :
-
glucose
- x :
-
xylose
References
Lynd, L.R., Cushman, J.H., Nichols, R.J., and Wyman, C.E. (1991), Science 51, 1318–1323.
Schneider, H. (1989), Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 9, 1–40.
Ladisch, M. R., Lin, K. W., Voloch, M., and Tsao, G. T. (1983), Enzyme Microb. Technol. 5, 82–102.
Burchhardt, G. and Ingram, L. O. (1992), Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 58, 1128–1133.
Ingram, L.O., Conway, T., Clark, D.P., Sewell, G.W., and Preston, J.F. (1987), Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 53, 2420–2425.
Ohta, K., Beall, D.S., Mejia, J.P., Shanmugam, K.T., and Ingram, L.O. (1991), Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 57, 893–900.
Doran, J.B., Aldrich, H.C., and Ingram, L.O. (1994), Biotechnol. Bioeng. 44, 240–247.
Ohta, K., Beall, D.S., Mejia, J.P., Shanmugam, K.T., and Ingram, L.O. (1991), Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 57, 2810–2815.
Zhang, M., Eddy, C., Deanda, K., Finkelstein, M., and Picataggio, S. (1995), Science 267, 240–243.
Kotter, P., Amore, R., Hollenberg, C.P., and Ciriacy, M. (1993), Curr. Genet. 38, 776–783.
Tantirungkij, M., Nakashima, N., Seki, T., and Yoshida, T. (1993), J. Ferm. Bioeng., 75, 83–88.
Ho, N.W.Y., Chen, Z., and Brainard, A. (1998), Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 64(3), 1852–1859.
Stewart, G.G., Panchal, C.J., and Rusell, I. (1982), Brew. Distill. Int. 12, 33.
Ho, N.W.Y. and Chen, Z.D. (1996), Patent pending.
Toon, S.T., Philippidis, G.P., Ho, N.W.Y., Chen, Z.D., Brainard, A., Lumpkin, R.E., and Riley, C.J. (1997), Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 63/65, 243–255.
Mulchandani, A. and Loung, J.H.T. (1989), Enzyme Microb. Technol. 11, 66–73.
van Uden, N. (1989), Alcohol Toxicity in Yeasts and Bacteria: CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL.
Luong, J.H.T. (1985), Biotechnol. Bioeng. 22, 1671–1687.
Krishnan, M.S., Xia, Y., Ho, N.W.Y., and Tsao, G.T. (1997), ACS Symposium Series: Fuels and Chemicals from Biomass vol. 666, pp. 74–92.
Krishnan, M.S., Xia, Y., Tsao, G.T., Kasthurikrishnan, N., Srinivasan, N., and Cooks, R.G. (1995), Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 51/52, 479–493.
Krishnan, M.S., Du, J.X., Cao, N.J., Gong, C.S., and Tsao, G.T. (1997), Poster 239-BIOT at the 213th ACS National Meeting, April 13–17, San Francisco, CA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Krishnan, M.S., Ho, N.W.Y. & Tsao, G.T. Fermentation kinetics of ethanol production from glucose and xylose by recombinant Saccharomyces 1400(pLNH33). Appl Biochem Biotechnol 78, 373–388 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1385/ABAB:78:1-3:373
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/ABAB:78:1-3:373