Abstract
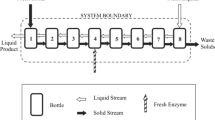
In continuous-flow enzymatic microbioreactors, enzymes on the channel walls catalyze reaction(s) among feed chemicals, resulting in the production of some desirable material or the destruction of some undesirable material. Computational models of microbioreactors were developed using the CFD-ACE+ multiphysics simulation package. These models were validated via comparison with experimental data for the destruction of urea, catalyzed by urease. Similar models were then used to assess the impact of internal features on destruction efficiency. It was found that triangular features within the channels enhanced the destruction efficiency more than could be attributed to the increase in surface area alone.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wegeng, R., Call, C., and Drost, K. (1996), Chemical System Miniaturization, PNNL-SA-27317, Pacific Northwest National Laboratory, Richland, WA.
Schuth, F. (1995), Crystallographically Defined Pore Systems: Reaction Vessels with Molecular Dimensions, Microsystem Technology for Chemical and Biological Microreactors, Max Planck Institute, Mainz, Germany.
Srinivasan, R., Hsing, I.-M., Berger, P. F., Jensen, K. F., Firebaugh, S. L., Schmidt, M. A., Harold, M. P., Lerou, J. J., and Ryley, J. (1997), AIChE J. 43(11), 3059–3069.
Zheng, A.-P., Jones, F., Fang, J., and Cui, (2000), in Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Microreaction Technology (IMRET IV), Irven Rinard (Ed.), AIChE, Atlanta, GA, pp. 284–292.
Duffy, D. C., McDonald, J. C., Schueller, O. J. A., and Whitesides, G. M. (1998), Anal. Chem. 70, 4974–4984.
Jones, F., Lu, Z., and Elmore, B. (2002), Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 98–100, 627–640.
Jones, F., Forrest, S., Palmer, J., Lu, Z., Elmore, J., and Elmore, B. (2004), Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 113–116, 261–272.
Mengeaud, V., Ferrigno, R., Josserand, J., and Girault, H. (2001), in Microreaction Technology, IMRET 5: Proceedings of the Fifth International Conference on Microreaction Technology, Springer-Verlag, New York, pp. 350–358.
Marioth, E., Loebbecke, S., Scholz, M., Schnürer, F., Türcke, T., Antes, J., and Krause, H. (2001), in Microreaction Technology, IMRET 5: Proceedings of the Fifth International Conference on Microreaction Technology, M. Matlosz, W. Ehrfeld, and J. P. Baselt (Eds.), Springer-Verlag, New York, pp. 262–274.
Heo, H., and Suh, Y. (2003), in Proceedings of the First International Conference on Microchannels and Minichannels, S. G. Kandlikar, G. P. Celata, S. Nishio, P. Stephan, B. Thonon (Eds.), American Society of Mechanical Engineers, New York, pp. 249–255.
Niklas, M., and Favre-Marinet, M. (2003), in Proceedings of the First International Conference on Microchannels and Minichannels, S. G. Kandlikar, G. P. Celata, S. Nishio, P. Stephan, B. Thonon eds., American Society of Mechanical Engineers, New York, pp. 335–342.
Barz, D. and Ehrhard, P. (2003), in Proceedings of the First International Conference on Microchannels and Minichannels, S. G. Kandlikar, G. P. Celata, S. Nishio, P. Stephan, B. Thonon eds., American Society of Mechanical Engineers, New York, pp. 365–371.
CDF Research Corporation. (2003), CFD-ACE(U) User’s Manual, Huntsville, AL.
Van Doormaal, J. and Raithby, G. (1984), Numer. Heat Transfer 7, 147–163.
Crowe, C., Roberson, J., and Elger, D. (2001), Engineering Fluid Mechanics, 7th ed., John Wiley & Sons, New York.
Sorrell, L. and Myerson, A., (1982), AIChE J. 28(5), 772–778.
DeTurck, D., Gladney, L., and Pietrovito, A. (1996), The Interactive Textbook of PFP 96, http://dept.physics.upenn.edu/courses/gladney/mathphys/subsection4_1_7.html, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bailey, R., Jones, F., Fisher, B. et al. Enhancing design of immobilized enzymatic microbioreactors using computational simulation. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 122, 639–652 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1385/ABAB:122:1-3:0639
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/ABAB:122:1-3:0639