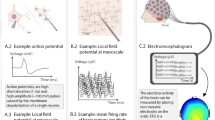
Abstract
The paper reviews mathematical and numerical aspects in EEG modelling and gives researchers new in this field an overview about the state-of-the-art results and techniques on the topic. The classical dipolar source model is presented for modelling the electrical activity of the brain and several discretization methods for solving the forward model are described. Theoretical results from the mathematical analysis of the forward and inverse problem are given and an overview of the most popular numerical methods for solving the inverse problem is presented. A specific case study for EEG modelling in neonates highlights current questions that are actually asked by the clinicians.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adde, G.: Méthodes de traitement d’images appliquées au problème inverse en Magnéto-Electro-Encéphalographie. Thèse de doctorat (2005)
Adde, G., Clerc, M., Faugeras, O., Keriven, R., Kybic, J., Papadopoulo, T.: Symmetric BEM formulation for the M/EEG forward problem. In: Information Processing in Medical Imaging, pp. 524–535. Springer, Berlin (2003)
Akalin Acar, Z., Makeig, S.: Effects of forward model errors on EEG source localization. Brain Topogr. 26, 378–396 (2013)
Azizollahi, H., Darbas, M., Diallo, M.M., El Badia, A., Lohrengel, S.: EEG in neonates: forward modelling and sensitivity analysis with respect to variations of the conductivity. Math. Biosci. Eng. 15, 905–932 (2018). https://doi.org/10.3934/mbe.2018041.
Azizollahi, H., Aarabi, A., Wallois, F.: Effects of uncertainty in head tissue conductivity and complexity on EEG forward modelling in neonates. Hum. Brain Mapp. 37(10), 3604–3622 (2016)
Baillet, S.: Toward Functional Brain Imaging of Cortical Electrophysiology Markovian Models for Magneto and Electroencephalogram Source Estimation and Experimental Assessments. Ph.D. thesis, University of Paris Orsay, France (1998)
Baillet, S., Mosher, J.C., Leahy, R.M.: Electromagnetic brain mapping. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 18(6), 14–30 (2001)
Baillet, S., Tadel, F., Leahy, R.M., Mosher, J.C., Delorme, A., Makeig, S., Oostenveld, R., Hämäläinen, M., Dalal, S.S., Zumer, J., Clerc, M., Wolters, C.H., Kiebel, S., Jensen, O.: Academic Software Toolboxes for the Analysis of MEG Data. In: IFMBE Proceedings BIOMAG2010, Dubrovnik, Croatia, vol. 28 (2010)
Baratchart, L., Leblond, J., Mandrea, F., Saff, E.B.: How can meromorphic approximation help to solve some 2D inverse problems for the Laplacian? Inverse Probl. 15, 79–90 (1999)
Baratchart, L., Ben Abda, A., Ben Hassen, F., Leblond, J.: Recovery of pointwise sources or small inclusions in 2D domains and rational approximation. Inverse Probl. 21, 51–74 (2005)
Baratchart, L., Leblond, J., Marmorat, J.-P.: Inverse source problem in a 3D ball from best meromorphic approximation on 2D slices. Electron. Trans. Numer. Anal. 25, 41–53 (2006)
Bassila, R., Clerc, M., Leblond, J., Marmorat, J.-P., Papadopoulo, T.: (2008). http://www-sop.inria.fr/apics/FindSources3D/
Berg, P., Scherg, M.: A fast method for forward computation of multiple-shell spherical head models. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 90, 58–64 (1994)
Chen, H., Halleza, F., Staelens, S.: Influence of skull conductivity perturbations on EEG dipole source analysis. Med. Phys. 37(8), 4475–4484 (2010)
Cho, J.-H., Vorweck, J., Wolters, C.H., Knösche, T.R.: Influence of the head model on EEG and MEG source connectivity analyses. NeuroImage 10, 60–77 (2015)
Christiansen, S., Nédélec, J.C.: A preconditioner for the electric field integral equation based on Calderon formulas. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 40, 1100–1135 (2002)
Clerc, M., Kybic, J.: Cortical mapping by Laplace?Cauchy transmission using a boundary element method. Inverse Probl. 23, 2589–2601 (2007)
Clerc, M., Leblond, J., Marmorat, J.-P., Papadopoulo, T.: Source localization in EEG using rational approximation on plane sections. Inverse Probl. 28, 055018 (2012)
Colton, D.L., Kress, R.: Integral Equation Methods in Scattering Theory. Pure and Applied Mathematics. Wiley, New York (1983)
Dannhauer, M., Lanfer, B., Wolters, C.H., Knösche, T.R.: Modelling of the human skull in EEG source analysis. Hum. Brain Mapp. 32(9), 1383–1399 (2011)
Darbas, M., Diallo, M.M., El Badia, A., Lohrengel, S.: An inverse dipole source problem in inhomogeneous media: application to the EEG source localization in neonates. Submitted
Diallo, M.M.: Problème inverse de sources en Electro-Encéphalo-Graphie chez le nouveau-né. Ph.D. thesis, Université de Picardie Jules Verne, Amiens, France (2017)
El Badia, A., El Hajj, A.: Hölder stability estimates for some inverse pointwise source problems. C. R. Math. Acad. Sci. (Paris) 350(23–24), 1031–1035 (2012)
El Badia, A., Farah, M.: Identification of dipole sources in an elliptic equation from boundary measurements: application to the inverse EEG problem. J. Inverse Ill-Posed Probl. 14, 331–353 (2006)
El Badia, A., Farah, M.: A stable recovering of dipole sources from partial boundary measurements. Inverse Probl. 26, 115006 (2010)
El Badia, A., Ha-Duong, T.: An inverse source problem in potential analysis. Inverse Probl. 16, 651–663 (2000)
Engwer, C., Vorwerk, J., Ludewig, J., Wolters, C.H.: A discontinuous Galerkin method for the EEG forward problem. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 39(1), B138–B164 (2017)
Farah, M.: Problèmes inverses de sources et lien avec l’Electro-encéphalo-graphie. Ph.D. thesis, Université de Technologie de Compiègne, France (2007)
Gargiulo, P., Belfiore, P., Friogeirsson, E.A., Vanhalato, S., Ramon, C.: The effect of fontanel on scalp EEG potentials in the neonate. Clin. Neurophysiol. 126, 1703–1710 (2015)
Geddes, L.A., Baker, L.E.: The specific resistance of biological material - a compendium of data for the biomedical engineer and physiologist. Med. Bio. Eng 5(3), 271–293 (1967)
Geselowitz, D.B.: On bioelectric potentials in an homogeneous volume conductor. Biophys. J. 7, 1–11 (1967)
Gramfort, A., Papadopoulo, T., Olivi, E., Clerc, M.: OpenMEEG: opensource software for quasistatic bioelectromagnetics. Biomed. Eng. Online 9, 45 (2010)
Grech, R., Cassar, T., Muscat, J., Camilleri, K.P., Fabri, S.G., Zervakis, M., Xanthopoulos, P., Sakkalis, V., Vanrumste, B.: Review on solving the inverse problem in EEG source analysis. J. Neuro. Rehabil. 5(25), 1–33 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1186/1743-0003-5-25
Hallez, H., Vanrumste, B., Van Hese, P., D’Asseler, Y., Lemahieu, I., Van de Walle, R.: A finite difference method with reciprocity used to incorporate anisotropy in electroencephalogram dipole source localization. Phys. Med. Biol. 50, 3787–3806 (2005)
Hallez, H., Vanrumste, B., Grech, R., Muscat, J., De Clercq, W., Vergult, A., D’Asseler, Y., Camilleri, K.P., Fabri, S.G., Van Huffel, S.: Review on solving the forward problem in EEG source analysis. J. NeuroEng. Rehabil. 4(1), 46 (2007)
Hämäläinen, M.S., Hari, R., Ilmoniemi, R.J., Knuutila, J., Lounasamaa, O.V.: Magnetoencephalography—theory, instrumentation, and applications to noninvasive studies of the working human brain. Rev. Mod. Phys. 65(2), 413–497 (1993)
Hämäläinen, M.S., Ilmoniemi, R.J.: Interpreting Measured Magnetic of the Brain: Estimates of Current Distributions. Technical Report TKK-F-A559, Helsinki University of Technology, Espoo (1984)
Hämäläinen, M.S., Sarvas, J.: Realistic conductivity geometry model of the human head for interpretation of neuromagnetic data. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 36(2), 165–171 (1989)
Haueisen, J., Tuch, D., Ramon, C., Schimpf, P., Wedeen, V., George, J., Belliveau, J.: The influence of brain tissue anisotropy on human EEG and MEG. NeuroImage 15, 159–166 (2002)
Hecht, F., Pironneau, O., Le Hyaric, A., Ohtsuka, K.: FreeFem++ Manual (2014)
Hédou, V.: A finite difference method to solve the forward problem in electroencephalography (EEG). J. Comput. Appl. Math. 167, 35–58 (2004)
Kellogg, O.D.: Foundations of Potential Theory. Dover, New York (1953)
Kohn, R.V., Vogelius, M.: Relaxation of a variational method of impedance computed tomography. Commun. Pure Appl. Math. 40, 745–777 (1987)
Kozlov, V.A., Maz’ya, V.G., Fomin, A.V.: An iterative method for solving the Cauchy problem for elliptic equations. Comput. Math. Phys. 31, 45–52 (1991)
Kress, R.: Linear Integral Equations. Applied Mathematical Sciences, vol. 82. Springer, Berlin (1999)
Kybic, J., Clerc, M., Abboud, T., Faugeras, O., Keriven, R., Papadopoulo, T.: A common formalism for the integral formulations of the forward EEG problem. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 24(1), 12–28 (2005)
Kybic, J., Clerc, M., Faugeras, O., Keriven, R., Papadopoulo, T.: Fast multipole acceleration of the MEG/EEG boundary element method. Phys. Med. Biol. 50, 4695–4710 (2005)
Kybic, J., Clerc, M., Faugeras, O., Keriven, R., Papadopoulo, T.: Generalized head models for MEG/EEG: boundary element method beyond nested volumes. Phys. Med. Biol. 51, 1333–1346 (2006)
Lanfer, B., Scherg, M., Dannhauer, M., Knösche, T.R., Burger, M., Wolters, C.H.: Influences of skull segmentation inaccuracies on EEG source analysis. NeuroImage 62(1), 418–431 (2014)
Lew, S., Wolters, C.H., Dierkes, T., Röer, C., MacLeod, R.S.: Accuracy and run-time comparison for different potential approaches and iterative solvers in finite element method based EEG source analysis. Appl. Numer. Math. 59(8), 1970–1988 (2009)
Mordecai, A.: Nonlinear Programming: Analysis and Methods. Dover, New York (2003)
Lew, S., Silva, D.D., Choe, M., Ellen Grant, P., Okada, Y., Wolters, C.H., Hämäläinen, M.S.: Effects of sutures and fontanels on MEG and EEG source analysis in a realistic infant head model. NeuroImage 76, 282–293 (2013)
Love, A.E.H.: A Treatise of Mathematical Theory of Elasticity. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (1927)
Meijs, J.W.H., Weier, O.W., Peters, M.J., van Oosterom, A.: On the numerical accuracy of the boundary element method. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 36(10), 1038–1049 (1989)
Montes-Restrepo, V., van Mierlo, P., Strobbe, G., Staelens, S., Vandenberghe, S., Hallez, H.: Influence of skull modeling approaches on EEG source localization. Brain Topogr. 27(1), 95–111 (2014)
Mosher, J.C., Lewis, P.S., Leahy, R.M.: Multiple dipole modeling and localization from spatio-temporal MEG data. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 39(6), 541–557 (1992)
de Munck, J.C., Peters, M.J.: A fast method to compute the potential in the multisphere model. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 40, 1166–1174 (1993)
Nédélec, J.-C.: Acoustic and Electromagnetic Equations. Applied Mathematical Sciences, vol. 144. Springer, New York (2001)
Odabaee, M., Tokariev, A., Layeghy, S., Mesbah, M., Colditz, P.B., Ramon, C., Vanhatalo, S.: Neonatal EEG at scalp is focal and implies high skull conductivity in realistic neonatal head models. NeuroImage 96, 73–80 (2014)
Ortiz G, J.E., Pillain, A., Rahmouni, L., Andriulli, F.P.: A Calderon regularized symmetric formulation for the electroencephalography forward problem. J. Comput. Phys., 1–21 (2018)
Papageorgakis, C.: Modèles de conductivité patient-spécifiques: caractérisation de l’os du crâne. Ph.D. thesis, INRIA Sophia, Université Côte d’Azur (2017)
Pascual-Marqui, R.D.: Review of methods for solving the EEG inverse problem. Int. J. Bioelectromagn. 1, 75–86 (1999)
Pascual-Marqui, R.D.: Standardized low resolution brain electromagnetic tomography (sLORETA): technical details. Methods Find. Exp. Clin. Pharmacol. 24D, 5–12 (2002). (Author’s version)
Pursiainen, S., Lew, S., Wolters, C.H.: Forward and inverse effects of the complete electrode model in neonatal EEG. J. Neurophysiol. 117(3), 876–884 (2017)
Roche-Labarbe, N., Aarabi, A., Kongolo, G., Gondry-Jouet, C., Dümpelmann, M., Grebe, R., Wallois, F.: High-resolution electroencephalography and source localization in neonates. Hum. Brain Mapp. 29, 167–176 (2008)
Rush, S., Driscoll, D.A.: Current distribution in the brain from surface electrodes. Anesth. Analg. 47, 717–723 (1967)
Saad, Y.: Iterative Methods for Sparse Linear Systems. PWS-Kent, Boston (1996)
de Saint-Venant, A.J.C.B.: Mémoire sur la torsion des prismes. Mem. Divers Savants 14, 233–560 (1855)
Salo, M.: Unique continuation for elliptic equations Notes Fall (2014)
SimBio: A generic environment for bio-numerical simulations. https://www.mrt.uni-jena.de/simbio
Steinbach, O., Wendland, W.L.: The construction of some efficient preconditioners in the boundary element method. Adv. Comput. Math. 9, 191–216 (1998)
Vorwerk, J.: Comparison of Numerical Approaches to the EEG Forward Problem. Master’s thesis, University of Münster, Germany (2011)
Vorwerk, J.: New Finite Element Methods to Solve the EEG/MEG Forward Problem. Ph.D. thesis, University of Münster, Münster, Germany (2016)
Wolters, C.H., Köstler, H., Möller, C., Härdtlein, J., Grasedyck, L., Hackbusch, W.: Numerical mathematics of the subtraction method for the modelling of a current dipole in EEG source reconstruction using finite element head models. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 30, 24–45 (2007)
Wolters, C.H., Anwander, A., Tricoche, X., Weinstein, D., Koch, M.A., MacLeod, R.S.: Influence of tissue conductivity anisotropy on EEG/MEG field and return current computation in a realistic head model: a simulation and visualization study using high-resolution finite element modelling. NeuroImage 30(3), 818–826 (2006)
Xu, X., Xu, B., He, B.: An alternative subspace approach to EEG dipole source localization. Phys. Med. Biol. 49, 327–343 (2004)
Yitembe, B.R.: Reduction of Conductivity Uncertainty Propagations in the Inverse Problem of EEG Source Analysis. Ph.D. thesis, University of Gent (2011)
Zhang, S.: A fast method to compute surface potentials generated by dipoles within multilayer anisotropic spheres. Phys. Med. Biol. 40, 335–349 (1995)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Darbas, M., Lohrengel, S. Review on Mathematical Modelling of Electroencephalography (EEG). Jahresber. Dtsch. Math. Ver. 121, 3–39 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1365/s13291-018-0183-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1365/s13291-018-0183-z