Abstract
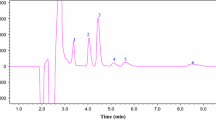
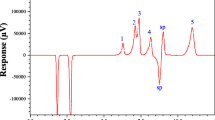
An investigation was carried out into the fast determination of five homologue imidazolium cations in ionic liquids by ion chromatography using a cation-exchange column and direct conductivity detection. Ethylenediamine, complex organic acid (citric acid, oxalic acid and tartaric acid) and organic modifiers (acetonitrile) were used as mobile phase. The influences of the eluent types, eluent concentration, eluent pH and column temperature on separation of the cations were discussed. Simultaneous separation and determination of the five homologue imidazolium cations in ionic liquids were achieved under an optimum condition. The optimized mobile phase was consisted of 0.25 mmol L−1 ethylenediamine + 0.5 mmol L−1 citric acid + 3% acetonitrile (v/v) (pH 4.1), set at a flow rate of 1.0 mL min−1. The column temperature was 40 °C and detection limits were obtained in the range of 1.1–45.6 mg L−1. The relative standard deviations of the chromatographic peak areas for the cations were <3.0% (n = 5). This method was successfully applied to separate imidazolium cations in ionic liquids produced by organic synthesis. The recoveries of spiked components were 92.5–101.9%.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Greaves TL, Drummond CJ (2008) Chem Rev 108:206–237. doi:10.1021/cr068040u
Buszewski B, Studzinska S (2008) Chromatographia 68:1–10. doi:10.1365/s10337-008-0662-y
Berthod A, Ruiz-Ángel MJ, Carda-Broch S (2008) J Chromatogr A 1184:6–18. doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2007.11.109
Liu R, Liu JF, Yin YG, Hu XL, Jiang GB (2009) Anal Bioanal Chem 393:871–883. doi:10.1007/s00216-008-2445-6
Villagran C, Deetlefs M, Pitner WR, Hardacre C (2004) Anal Chem 76:2118–2123. doi:10.1021/ac035157z
Hao FP, Haddad PR, Ruther T (2008) Chromatographia 67:495–498. doi:10.1365/s10337-008-0527-4
Li XH, Duan HL, Pan JT, Wang LF (2006) Chin J Anal Chem 34:S192–S194
Zhou S, Yu H, Ai HJ (2008) Chin J Anal Chem 36:1521–1525
Zhou S, Yu H, Yang L, Ai HJ (2008) J Chromatogr A 1206:200–203. doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2008.08.048
Stepnowski P, Muller A, Behrend P, Ranke J, Hoffmann J, Jastorff B (2003) J Chromatogr A 993:173–178. doi:10.1016/S0021-9673(03)00322-4
Stepnowski P, Mrozik W (2005) J Sep Sci 28:149–154. doi:10.1002/jssc.200400019
Ruiz-Angel MJ, Berthod A (2006) J Chromatogr A 1113:101–108. doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2006.01.124
Ruiz-Angel MJ, Berthod A (2008) J Chromatogr A 1189:476–482. doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2007.10.046
Buszewski B, Kowalska S, Stepnowski P (2006) J Sep Sci 29:1116–1125. doi:10.1002/jssc.200500358
Kowalska S, Buszewski B (2006) J Sep Sci 29:2625–2634. doi:10.1002/jssc.200600200
Qin WD, Wei HP, Li SFY (2002) Analyst 127:490–493. doi:10.1039/b110306g
Markuszewski MJ, Stepnowski P, Marszall MP (2004) Electrophoresis 25:3450–3454. doi:10.1002/elps.200406074
Gao W, Yu H, Zhou S (2010) Chromatographia 71:475–479. doi:10.1365/s10337-010-1478-0
Gjerde DT, Schmuckler G, Fritz JS (1980) J Chromatogr A 187:35–45. doi:10.1016/S0021-9673(00)87871-1
Haddad PR, Foley RC (1990) J Chromatogr A 500:301–312. doi:10.1016/S0021-9673(00)96073-4
Yu H, Mou SF (2006) J Chromatogr A 1118:118–124. doi:10.1016/j.chroma.2005.12.051
Yu H, Li RS (2008) Chromatographia 68:611–616. doi:10.1365/s10337-008-0774-4
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Heilongjiang Province (Grant No. B200909) and the Ministry of Education of Heilongjiang Province (Grant No. 11541088).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, H., Zhou, S., Gao, W. et al. A Simple Method for Determination of Homologue Imidazolium Cations in Ionic Liquids Using IC with Direct Conductivity Detection. Chroma 72, 225–230 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1365/s10337-010-1644-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1365/s10337-010-1644-4