Abstract
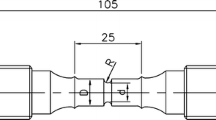
The effect of tensile prestraining-induced residual stress on the fatigue life of notched steel parts was investigated. The study was performed on AISI 4140 steel. Rotating bending fatigue tests were carried out on semicircular notched specimens with different notch radii in the as-quenched and tempered conditions. Metallography of the specimens was performed by means of light optical microscopy. The finite-element method was used to evaluate the residual stress distribution near the notch region. Fatigue tests revealed fatigue life improvement for notched specimens, which changes depending on the notch radii and applied stress. Scanning electron microscopy was used to examine the fracture surfaces of the specimens.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. Wohlfahrt, Shot Peening and Fatigue of Materials, Proc. Int. Conf. Shot Peening 1, A. Niku-Lari, Ed., Pergamon Press Oxford, 1982, p 257–262
M. Desvignes, G. Gentil, and K. Habou, Fatigue Behavior of Shot Peened Steel, Proc. Int. Conf. Shot Peening, H. Wohlfahrt, R. Kopp, and O. Vöhringer, Ed., Garmisch Partenkirchen, 1987, DGM-Informationsglsellsschoft oberursel, p 369–376
Y.H. Yu, The Effect of Shot Peening on Strain Controlled Fatigue Behaviours, Proc. Int. Conf. Shot Peening 4, K. Lida, Ed., The Japan Society of Precision Engineering, 1990, p 411–418
A. Bigonnet, Fatigue Strength of Shot-Peened Grade 35NCD15 Steel: Variation of Residual Stresses Introduced by Shot-Peening According to Type of Loading, Proc. Int. Conf. Shot Peening 3, H. Wohlfahrt, R. Kopp, and O. Vöhringer, Ed., Garmisch-Partenkirchen, 1987, DGM-Informationsglsellsschoft oberursel, p 659–666
J.K. Gregory and L. Wagner, Selective Surface Aging to Improve Fatigue Behavior in a High-Strength Beta Titanium Alloy, Proc. 5th Int. Conf. on Fatigue and Fatigue Threshold, EMAS Publishing, England, 1993, p 177–182
Z. Dingquan, X. Kewei, and H. Jiawen, Aspect of the Residual Stress Field at a Notch and Its Effect on Fatigue, Mater. Sci. Eng., A, Vol 136, 1991, p 79–83
L. Bertini and V. Fontanari, Fatigue Behavior of Induced Hardened Notched Components, Int. J. Fatigue, Vol 21, 1999, p 611–617
Z. Xu, H. Jiawen, and H. Zhou, Effect of Residual Stress on Fatigue Behavior of Notches, Fatigue, Vol 16, 1993, p 337–344
X. Kewei, H. Naisai, and Z. Huijiu, Prediction of Notch Fatigue Limits in a Compressive Residual Stress Field, Eng. Fract. Mech., Vol 25 (No. 2), 1996, p 171–176
G.E. Dieter, Mechanical Metallurgy, McGraw-Hill, New York, 1986
D.W. Hammond and S.A. Meguig, Crack Propagation in the Presence of Shot-peening Residual Stresses, Eng. Fract. Mech., Vol 37, 1990, p 387–390
R.W. Landgraf and R.A. Chernenkoff, Residual Stress Effects on Fatigue of Surface Processed Steels, STP 1004, ASTM Intl., R.A. Chernenkoff, Ed., 1996, 571–575
J.H. Underwood and J.F. Throop, “Residual Stress Effects on Fatigue Cracking of Pressurized Cylinders and Notched Bending Specimens,” Proc. SESA Spring Meeting, 1980
J.H. Underwood, Residual-stress Effects at a Notch Root in A723 Steel to Extend Fatigue Life, Exp. Mech., Vol 35, 1995, p 61–65
P.B. Aswath, S. Suresh, and D.K. Holm, Load Interaction Effects on Compression Fatigue Crack Growth in Ductile Solids, J. Eng. Mater. Technol., Vol 110, 1988, p 278–285
M. Toparli, A. Özel, and T. Aksoy, Effect of the Residual Stresses on the Fatigue Crack Growth Behavior at Fastener Holes, Mater. Sci. Eng., A, Vol 225, 1997, p 196–203
S.K. Lin, Y. Lee, and M. Lu, Evaluation of the Staircase and the Accelerated Test Methods for Fatigue Limit Distributions, Int. J. Fatigue, Vol 23, 2001, p 75–83
J.E. Campbell, “Shot Peening for Improved Fatigue Properties and Stress Corrosion Resistance,” Report MC1C-71-02, Metals and Ceramics Information Center, Columbus, OH, 1971
O.C. Zienkiewicz, S. Valliapand, and I.P. King, “Elasto-plastic Solutions of Engineering Problems ‘Initial Stress’ Finite Element Approach,” Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng., Vol 1, 1969, p 95–100
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sadeler, R., Ozel, A., Kaymaz, I. et al. The effect of residual stresses induced by prestraining on fatigue life of notched specimens. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 14, 351–355 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1361/10599490523995
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1361/10599490523995