Abstract
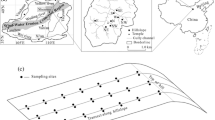
Due to its inert reaction in soil system and distinctive vertical distribution in soil profile, caesium-137 (137Cs) has been used as a tracer to assess wind erosion. In this study, 62 soil samples were collected from 4 sampling sites in Taipusi County, Inner Mongolia; Caesium-137 activities for those soil samples were measured using a gamma-ray spectrometry in Sichuan University, Chengdu. Distribution pattern of 137Cs in vertical soil profile was different for different land use and land cover types. Caesium-137 was distributed homogeneously in plow layer of cropland, and negatively exponential in low to medium cover grassland. Distribution pattern in high covered grassland was represented by a peak at 2–4 cm soil depth followed by a negative exponential curve. Based on those findings, simplified mass balance model was chosen to estimate the rate of wind erosion for cropland, while profile distribution model was used for grassland. Estimated wind erosion rates were 7990, 4270 and 1808 Mg·km−2·a−1 for cropland, low cover grassland and medium cover grassland, respectively. Wind erosion intensity correlated negatively with plant cover.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tamura, T., Jacobs, D. G., Structural implications in cesium sorption, Health Physics, 1960, 6(2): 391–398.
Rogowshi, A. S., Tamura, T., Movement of 137Cs by runoff, erosion and infiltration on the alluvial captina silt loam, Health Physics, 1965, 11(12): 1333–3340.
Owens, P. N., Walling, D. E., He, Q. P., The behaviour of bomb-derived caesium-137 fallout in catchment soils, Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 1996, 32(3): 169–191.
Ritchie, J. C., McHenry, J. R., Application of radioactive fallout cesium-137 for measuring soil erosion and sediment accumulation rates and patterns: A review, Journal of Environmental Quality, 1990, 19(2): 215–233.
Zapata, F., The use of environmental radionuclides as tracers in soil erosion and sedimentation investigations: recent advances and future developments, Soil and Tillage Research, 2003, 69(1-2): 3–13.
Sutherland, R. A., Kowalchuk, T., de Jong, E., Cesuim-137 estimates of sediment redistribution by wind, Soil Science, 1991, 151(5): 387–396.
Zhang, C. L., Dong, G. R., Zou, X. Y. et al., Deposit characteristics of Cs-137 on a semi-fixed san dune, Journal of Desert Research (in Chinese), 2002, 22(2): 154–158.
Zhang, C. L., Zou, X. Y., Dong G. R. et al., Characteristics of 137Cs deposition in steppe area, Chinese Science Bulletin, 2002, 47(10): 848–953.
Pu, L. J., Bao, H. S., Peng, B. Z. et al., Preliminary study on the potential of using 137Cs to estimate soil erosion rates in wind eroded area, China: case study on the Korla Area, Xinjiang Autonomous Region, Acta Pedologica Sinica (in Chinese), 1998, 35(4): 441–449.
Yan, P., Dong, G. R., Zhang, X. B. et al., Application of caesium-137 technique on wind erosion in Gonghe Basin, Qinghai province (II): 137Cs Reference Inventory and 137Cs model for wind erosion estimation, Journal of Desert Research (in Chinese), 2003, 23(4): 391–397.
Yan, P., Dong, G. R., Zhang X. B. et al., Preliminary results of the study on wind erosion in the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau using 137Cs technique, Chinese Science Bulletin, 2000, 45(11): 199–204.
Chappell, A., Warren, A., Spatial scales of 137Cs-derived soil flux by wind in a 25 km2 arable area of eastern England, Catena, 2003, 52(3–4): 209–234.
Ye, D. Z., Chou, J. F., Liu, J. Y. et al., Causes of sand-stormy weather in Northern China and control measures, Acta Geographica Sinica (in Chinese), 2000, 55(5): 513–521.
Zhuang, G. S., Guo, J. H., Yuan H. et al., The compositions, sources, and size distribution of the dust storm from China in spring of 2000 and its impact on the global environment, Chinese Science Bulletin, 46(11): 895–901.
Liu, J. Y., Liu, M. L., Zhuang D. F. et al., Study on spatial pattern of land-use change in China during 1995–2000, Science in China (Series D), 2003, 46(4): 373–384.
Hu, Y. F., Liu, J. Y., Zhuang D. F. et al., Study on the relationship between land-use dynamics and wind erosion dynamics in Inner Mongolia during late 1990s, Progress in Geography (in Chinese), 2003, 22(6): 541–550.
Liu, J. Y., Zhuang D. F., Zhang Z. X. et al., The establishment of land-use spatial-temporal database and its relative studies in China, Geo-Information Science (in Chinese), 2002, 4(3): 3–7.
Liu, J. Y., Buheaosier, Study on spatial-temporal feature of modern land-use change in China—using remote sensing techniques, Quaternary Sciences (in Chinese), 2000, 20(3): 229–239.
Owens, P. N., Walling, D. E., Spatial variability of caesium-137 inventories at reference sites: An example from two contrasting sites in England and Zimbabwe, Applied Radiation and Isotopes, 1996, 47(7): 699–707.
Chappell, A., The limitations of using 137Cs for estimating soil redistribution in semi-arid environments, Geomorphology, 1999, 29(1–2): 135–152.
Kachanoski, R. G., de Jong, E., Predicting the temporal relationship between soil cesium-137 and erosion rate, Journal of Environmental Quality, 1984, 13(2): 301–304.
Fredericks, D. J., Perrens, S. J., Estimating erosion using caesium-137: II. Estimating rates of soil loss, in Sediment Budgets (eds. Bordas, M. P., Walling, D. E.), Wallingford: IAHS Press, 1988, 225–231.
Zhang, X. B., Higgitt, D. L., Walling D. E., A preliminary assessment of the potential for using cesium-137 to estimate rates of soil-erosion in the Loess Plateau of China, Hydrological Sciences Journal, 1990, 35(3): 243–252.
Zhang, X. B., Wen A. B., A study of soil erosion on a steep cultivated in the Mt. Gongga region near Luding, Sichuan, China, using the 137Cs technique, Acta Geological Hispanica, 2000, 35(3–4): 229–238.
Quine, T. A., Navas, A., Walling, D. E. et al., Soil-erosion and redistribution on cultivated and uncultivated land near Las-Bardenas in the central Ebro River Basin, Spain, Land Degradation and Rehabilitation, 1994, 5(1): 41–55.
Sutherland, R. A., de Jong, E., Estimation of sediment redistribution within agricultural fields using caesium-137, Crystal Springs, Saskatchewan, Canada, Applied Geography, 1990, 10(3): 205–221.
Sutherland, R. A., The potential for reference site resampling in estimating sediment redistribution and assessing landscape stability by the caesium-137 method, Hydrological Processes, 1998, 12(7): 995–1007.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, Y., Liu, J., Zhuang, D. et al. Distribution characteristics of 137Cs in wind-eroded soil profile and its use in estimating wind erosion modulus. Chin.Sci.Bull. 50, 1155–1159 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1360/04wd0312
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1360/04wd0312