Summary
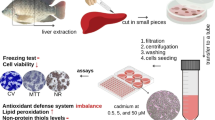
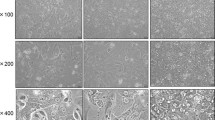
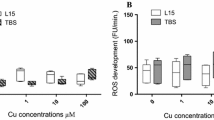
We established an in vitro hepatocyte primary culture system from Oreochromis niloticus, a tropical fish species of great economical importance, and evaluated its ability to express albumin, a liver-specific protein, consistently for a period of 3 wk. Serum requirements for fish hepatocyte cultures were assessed. A one-step in situ perfusion of tilapia liver retrogradely followed by collagenase liver dissociation and subsequent washing produced nearly 90% homogenous viable hepatocytes, as shown by trypan blue exclusion test. Mixed primary monolayer and aggregate hepatocyte cultures achieved by 10% fetal calf serum medium supplements expressed consistent levels of albumin. The results of light and electron microscopy showed that the hepatocytes did not significantly proliferate (P<0.05) but remained viable for at least 3 wk. The results of this study show that in vitro cultures of mixed primary hepatocyte monolayers and aggregates established from Nile tilapia may be useful models for studying transient cellular stress induction.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blair, J. B.; Miller, M.; Pack, D.; Barnes, R.; Teh, S. J.; Hinton, D. E. Isolated trout liver cells: establishing short-term primary cultures exhibiting cell-to-cell interactions. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. 26A:237–249; 1990.
Bradford, M. M. A rapid and sensitive method of the quantification of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 72:248–254; 1976.
Cao, Y.-A.; Blair, J. A.; Ostrander, G. K. The initial report of the establishment of primary liver cell cultures from Medaka (Oryzias latipes). Fish Biol. J. Medaka 8:47–56; 1996.
Chen, J.-Y.; Tsai, H.-L.; Chang, C.-Y.; Wang, J.-I.; Shen, S.-C.; Wu, J.-L. Isolation and characterization of tilapia (Oreochromis mossambicus) insulin-like growth factors gene and proximal promoter region. DNA Cell Biol. 17:359–376; 1998.
Flouriot, G.; Vaillant, C.; Salbert, G.; Pelissero, C.; Guiraud, J. M.; Valotaire, Y. Monolayer and aggregate cultures of rainbow trout hepatocytes: long-term and stable liver-specific expression in aggregates. J. Cell Sci. 105:407–416; 1993.
Klaunig, J. E.; Ruch, J. R.; Golblatt, P. J. Trout hepatocyte culture isolation and primary culture. In Vitro 21:221–228; 1985.
Laemmli, U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685; 1970.
Lipsky, M.; Sheridan, T. R.; Benett, R. Comparison of trout hepatocyte culture on different substrates. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. 22A:360–362; 1986.
Ostrander, G. K.; Blair, J. B.; Stark, B. A., et al. Long-term epithelial cells from rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) liver. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. 31A:367–378; 1995.
Rabergh, C. M. I.; Kane, A. S.; Reimschuessel, R., et al. Viability and induction of tyrosine aminotransferase in rainbow trout hepatocytes cultured on laminin and polylysine in serum-free medium. Methods Cell Sci. 17:207–215; 1995.
Sachs, L. Angewandte statistik. Berlin, Germany: Springer; 1997.
Schmid, A. C.; Reinecke, M.; Kloas, W. Primary cultured hepatocytes of the bony fish, Oreochromis mossambicus, the tilapia: a valid tool for physiological studies on IGF-1 expression in liver. J. Endocrinol. 166:265–273; 2000.
Scholz, S.; Braunbeck, T.; Segner, H. Viability and differential function of rainbow trout lever cells in primary culture: coculture with two permanent fish cells. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. 34A:762–771; 1998.
Segner, H.; Blair, J. B.; Wirtz, G., et al. Cultured trout liver cells: utilization of substrates and response to hormones. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. 30A:306–311; 1994.
Wu, F. J.; Friend, J. R.; Remmel, R. P.; Cerra, F. B.; Hu, W. S. Enhanced cytochrome P450 1A1 activity of self-assembled rat hepatocyte spheroids. Cell Transplant. 8:233–246; 1999.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jung'a, J.O., Mitema, E.S. & Gutzeit, H.O. Establishment and comparative analyses of different culture conditions of primary hepatocytes from Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) as a model to study stress induction in vitro. In Vitro Cell.Dev.Biol.-Animal 41, 1–6 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1290/0410068.1
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1290/0410068.1