Abstract
Background
The accuracy of sentinel lymph node biopsy (SLNB) after neoadjuvant therapy (NAT) has been improved with the placement of a clip in the positive node prior to treatment. Several methods have been described for clipped node excision during SLNB after NAT. We assessed the feasibility of intraoperative ultrasound (IOUS)-guided excision of the clipped node during SLNB and investigated whether the accuracy of SLNB is improved.
Methods
After approval by the Institutional Ethics Committee, all breast cancer patients undergoing NAT had an US-visible clip placed in the positive node. The ILINA trial consisted of IOUS-guided excision of the clipped node along with SLNB and axillary lymph node dissection (ALND).
Results
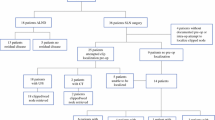
Forty-six patients had a clip placed in the positive node. In two (4.3%) cases, the clip could not be seen prior to surgery and the patient underwent ALND; however, the clipped node was successfully removed by IOUS-guided excision in 44 patients. Thirty-five patients (79.5%) underwent SLNB along with IOUS-guided excision of the clipped node and ALND, and were subsequently included in the ILINA trial. Nine patients were not included (five patients with SLNB only and four patients with ALND without SLNB). SLNB matched the clipped node in 27 (77%) patients. The false negative rate for the ILINA protocol was 4.1% (95% confidence interval 0.1–21.1%).
Conclusions
IOUS-guided excision of the axillary clipped node after NAT was feasible, safe, and successful in 100% of cases. The ILINA trial is accurate in predicting axillary nodal status after NAT.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gralow JR, Burstein HJ, Wood W, et al. Preoperative therapy in invasive breast cancer: pathologic assessment and systemic therapy issues in operable disease. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26(5):814–9.
Kaufmann M, Hortobagyi GN, Goldhirsch A, et al. Recommendations from an international expert panel on the use of neoadjuvant (primary) systemic treatment of operable breast cancer: an update. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24(12):1940–9.
van Deurzen CH, Vriens BE, Tjan-Heijnen VC, et al. Accuracy of sentinel node biopsy after neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer patients: a systematic review. Eur J Cancer 2009;45(18):3124–30.
Xing Y, Foy M, Cox DD, Kuerer HM, Hunt KK, Cormier JN. Meta-analysis of sentinel lymph node biopsy after preoperative chemotherapy in patients with breast cancer. Br J Surg. 2006;93(5):539–46.
Dominici LS, Negron Gonzalez VM, Buzdar AU, et al. Cytologically proven axillary lymph node metastases are eradicated in patients receiving preoperative chemotherapy with concurrent trastuzumab for HER2-positive breast cancer. Cancer 2010;116(12):2884–9.
Kuerer HM, Sahin AA, Hunt KK, et al. Incidence and impact of documented eradication of breast cancer axillary lymph node metastases before surgery in patients treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Ann Surg. 1999;230(1):72–8.
Boughey JC, Suman VJ, Mittendorf EA, et al. Sentinel lymph node surgery after neoadjuvant chemotherapy in patients with node-positive breast cancer: the ACOSOG Z1071 (Alliance) clinical trial. JAMA 2013;310(14):1455–61.
Boileau JF, Poirier B, Basik M, et al. Sentinel node biopsy after neoadjuvant chemotherapy in biopsy-proven node-positive breast cancer: the SN FNAC study. J Clin Oncol. 2015;33(3):258–64.
Chagpar AB, Middleton LP, Sahin AA, et al. Accuracy of physical examination, ultrasonography, and mammography in predicting residual pathologic tumor size in patients treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Ann Surg. 2006;243(2):257–64.
Yuan Y, Chen XS, Liu SY, Shen KW. Accuracy of MRI in prediction of pathologic complete remission in breast cancer after preoperative therapy: a meta-analysis. Am J Roentgenol. 2010;195(1):260–8.
You S, Kang DK, Jung YS, An YS, Jeon GS, Kim TH. Evaluation of lymph node status after neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer patients: comparison of diagnostic performance of ultrasound, MRI and (1)(8)F-FDG PET/CT. Br J Radiol. 2015;88(1052):20150143.
Kuehn T, Bauerfeind I, Fehm T, et al. Sentinel-lymph-node biopsy in patients with breast cancer before and after neoadjuvant chemotherapy (SENTINA): a prospective, multicentre cohort study. Lancet Oncol. 2013;14(7):609–18.
Mittendorf EA, Caudle AS, Yang W, et al. Implementation of the American College of Surgeons Oncology Group z1071 trial data in clinical practice: is there a way forward for sentinel lymph node dissection in clinically node-positive breast cancer patients treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy? Ann Surg Oncol. 2014;21(8):2468–73.
Donker M, Straver ME, Wesseling J, et al. Marking axillary lymph nodes with radioactive iodine seeds for axillary staging after neoadjuvant systemic treatment in breast cancer patients: the MARI procedure. Ann Surg. 2015;261(2):378–82.
Caudle AS, Yang WT, Krishnamurthy S, et al. Improved axillary evaluation following neoadjuvant therapy for patients with node-positive breast cancer using selective evaluation of clipped nodes: implementation of targeted axillary dissection. J Clin Oncol. 2016;34(10):1072–8.
Choy N, Lipson J, Porter C, et al. Initial results with preoperative tattooing of biopsied axillary lymph nodes and correlation to sentinel lymph nodes in breast cancer patients. Ann Surg Oncol. 2015;22(2):377–82.
Wilson LL, Giuliano AE. Sentinel lymph node mapping for primary breast cancer. Curr Oncol Rep. 2005;7(1):12–7.
Rubio IT, Esgueva-Colmenarejo A, Espinosa-Bravo M, Salazar JP, Miranda I, Peg V. Intraoperative ultrasound-guided lumpectomy versus mammographic wire localization for breast cancer patients after neoadjuvant treatment. Ann Surg Oncol. 2016;23(1):38–43.
Edge SB, Byrd DR, Compto CC, Fritz AG, Greene FL, Trotti A. AJCC cancer staging manual. 7th ed. New York: Springer; 2010.
Rahusen FD, Bremers AJ, Fabry HF, van Amerongen AH, Boom RP, Meijer S. Ultrasound-guided lumpectomy of nonpalpable breast cancer versus wire-guided resection: a randomized clinical trial. Ann Surg Oncol. 2002;9(10):994–8.
Krekel NM, Haloua MH, Lopes Cardozo AM, et al. Intraoperative ultrasound guidance for palpable breast cancer excision (COBALT trial): a multicentre, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2013;14(1):48–54.
Ramos M, Diaz JC, Ramos T, et al. Ultrasound-guided excision combined with intraoperative assessment of gross macroscopic margins decreases the rate of reoperations for non-palpable invasive breast cancer. Breast 2013;22(4):520–4.
James TA, Harlow S, Sheehey-Jones J, et al. Intraoperative ultrasound versus mammographic needle localization for ductal carcinoma in situ. Ann Surg Oncol. 2009;16(5):1164–9.
Krekel NM, Lopes Cardozo AM, Muller S, Bergers E, Meijer S, van den Tol MP. Optimising surgical accuracy in palpable breast cancer with intra-operative breast ultrasound: feasibility and surgeons’ learning curve. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2011;37(12):1044–50.
Nguyen TT, Hieken TJ, Glazebrook KN et al. Localizing the clipped node in patients with node positive breast cancer treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy: early learning experience and challenges. Ann Surg Oncol. https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-017-6023-z (Epub 1 Aug 2017)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosure
All authors declare that they have no potential conflicts of interest to declare.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Siso, C., de Torres, J., Esgueva-Colmenarejo, A. et al. Intraoperative Ultrasound-Guided Excision of Axillary Clip in Patients with Node-Positive Breast Cancer Treated with Neoadjuvant Therapy (ILINA Trial). Ann Surg Oncol 25, 784–791 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-017-6270-z
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-017-6270-z