Abstract
Background
Laparoscopic thermal ablation is a common alternative to surgical resection in treating hepatic tumors, particularly in those located in difficult-to-reach locations.
Objective
The aim of this study was to compare the safety and long-term efficacy of laparoscopic radiofrequency ablation (RFA) and microwave ablation (MWA) in treating hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
Method
From February 2009 to May 2015, data from patients with HCC nodules who had undergone either laparoscopic MWA or laparoscopic RFA were examined. Complications, complete ablation rates, local tumor progression (LTP) rates, and disease-free and cumulative survival rates were compared between the two treatment groups.
Results
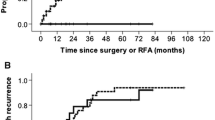
A total of 154 patients with HCC (60 MWA and 94 RFA) were treated via the laparoscopic approach. Major complication rates were identified as 1 and 2 % in the RFA and MWA groups, respectively (p = 0.747). Complete ablation rates were 95 % for both treatment groups (p = 0.931), and LTP rates were 21.2 % for RFA and 8.3 % for MWA (p = 0.034). Disease-free survival rates at 5 years were 19 % in the RFA group and 12 % in the MWA group (p = 0.434), while cumulative survival rates at 5 years were 50 % in the RFA group and 37 % in the MWA group (p = 0.185).
Conclusion
Laparoscopic RFA and MWA appear to be safe in the treatment of early-stage HCC. The LTP rates were lower in the laparoscopic MWA group compared with the laparoscopic RFA group, but their respective overall and disease-free survival rates remained similar.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Colombo M, Sangiovanni A. Treatment of hepatocellular caricnoma: beyond international guidelines. Liver Int. 2015; 35 Suppl 1:129–38.
Livraghi T, Meloni F, Di Stasi M, Rolle E, Solbiati L, Tinelli C, et al. Sustained complete response and complications rates after radiofrequency ablation of very early hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhosis: is resection still the treatment of choice? Hepatology. 2008;47:82–89.
Forner A, Llovet JM, Bruix J. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet. 2012;379:1245–55.
De Lope CR, Tremosini S, Forner A, Reig M, Bruix J. Management of HCC. J Hepatol. 2012;56 Suppl 1:S75–87.
Li L, Zhang J, Liu X, Li X, Jiao B, Kang T. Clinical outcomes of radiofrequency ablation and surgical resection for small hepatocellular carcinoma: a meta-analysis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012;27:51–58.
Huang J, Yan L, Cheng Z, et al. A randomized trial comparing radiofrequency ablation and surgical resection for HCC conforming to Milan criteria. Ann Surg. 2010;252:903–12.
Cho YC, Kim JK, Kim WT, Chung JW. Hepatic resection versus radiofrequency ablation for very early stage hepatocellular carcinoma: a Markov model analysis. Hepatology. 2010;51:1284–90.
Kuang M, Xie XY, Huang C, et al. Long-term outcome of percutaneous ablation in very early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma. J Gastrointest Surg. 2011;15:2165–71.
Wang JH, Wang CC, Hung CH, Chen CL, Lu SN. Survival comparison between surgical resection and radiofrequency ablation for patients in BCLC very early/early stage hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 2012;56:412–8.
Ke S, Ding XM, Qian XJ, Zhou YM, Cao BX, Gao K, et al. Radiofrequency ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma sized >3 and <5 cm: is ablative margin of more than 1 cm justified?. World J Gastroenterol. 2013;14:7389–7398.
Huang HW. Influence of blood vessel on the thermal lesion formation during radiofrequency ablation for liver tumors. Med Phys. 2013;40:073303.
Lu DSK, Raman SS, Limanond P, Aziz D, Economou J, Busuttil R, et al. Influence of large peritumoral vessels on outcome of radiofrequency ablation of liver tumors. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2003;14:1267–1274.
Lubner MG, Brace CL, Ziemlewicz TJ, Hinshaw JL, Lee FT. Microwave ablation of hepatic malignancy. Semin Intervent Radiol. 2013;30:56–66.
Huang S, Yu J, Liang P, Yu X, Cheng Z, Han Z, et al. Percutaneous microwave ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma adjacent to large vessels: a long-term follow-up. Eur J Radiol. 2014;83:552–558.
Chung MH, Wood TF, Tsioulias GJ, Rose DM, Bilchik AJ. Laparoscopic radiofrequency ablation of unresectable hepatic malignancies. A phase 2 trial. Surg Endosc. 2001;15:1020–6.
Santambrogio R, Opocher E, Costa M, Cappellani A, Montorsi M. Survival and intra-hepatic recurrences after laparoscopic radiofrequency of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with liver cirrhosis. J Surg Oncol. 2005;89:218–26.
Ballem N, Berber E, Pitt T, Siperstein A. Laparoscopic radiofrequency ablation of unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: long-term follow-up. HPB (Oxford) 2008;10:315–20.
De la Serna S, Vilana R, Sanchez-Cabus S, et al. Results of laparoscopic radiofrequency ablation of HCC. Could the location of the tumor influence a complete response to treatment? A single European experience. HPB (Oxford). 2015;17:387–93.
Santambrogio R, Barabino M, Bruno S, et al. Long-term outcome of laparoscopic ablation therapies for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: a single European center experience of 426 patients. Surg Endosc 2016;30:2103–13.
Lo CM, Lai ECS, Liu CL, Fan ST, Wong J. Laparoscopy and laparoscopic ultrasonography avoid exploratory laparotomy in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann Surg. 1998;227:527–32.
Kim PN, Choi D, Rhim H, et al. Planning ultrasound for percutaneous radiofrequency ablation to treat (<3 cm) hepatocellular carcinomas detected on computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging: a multicenter prospective study to assess factors affecting ultrasound visibility. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2012;23:627–634.
Kim JE, Kim YS, Rhim H, et al. Outcomes of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma referred for percutaneous radiofrequency ablation at a tertiary center: analysis focused on the feasibility with the use of ultrasonography guidance. Eur J Radiol. 2011;79:e80–4.
Rhim H, Lee MH, Kim YS, Choi D, Lee WJ, Lim HK. Planning sonography to assess the feasibility of percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of hepatocellular carcinomas. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2008;190:1324–1330.
Machi J. Intraoperative and laparoscopic ultrasound. Surg Oncol Clin N Am. 1999;8:205–226.
Santambrogio R, Bianchi P, Pasta A, Palmisano A, Montorsi M. Ultrasound-guided interventional procedures fo the liver during laparoscopy. Technical considerations. Surg Endosc. 2002;16:349–54.
Santambrogio R, Opocher E. Diagnostic laparoscoy and allied technology. In: Calise F, Casciola G, editors. Minimally invasive surgery of the liver (updates in surgery). Milan:Springer-Verlag; 2013. p. 83–94.
National Cancer Institute. Cancer therapy evaluation program: common toxicity evaluation manual. Version 2.0. 1999. http://www.ctep.cancer.gov/reporting/ctc.html.
Dindo D, Demartines N, Clavien PA. Classification of surgical complications. A new proposal with evaluation in a cohort of 633 patients and results of a survey. Ann Surg. 2004;240:205–13.
Ahmed M. Image-guided tumor ablation: standardization of terminology and reporting criteria—a 10-year update. Radiology. 2014;273:241–260.
Mulier S, Ni Y, Jamart J, Ruers T, Marchal G, Michel L. Local recurrence after hepatic radiofrequency coagulation. Multivariate meta-analysis and review of contributing factors. Ann Surg. 2005;242:158–171.
Livraghi T, Meloni F, Solbiati L, Zanus G; Collaborative Italian Group using AMICA system. Complications of microwave ablation for liver tumors: results of a multicenter study. Cardiovasc Interv Radiol. 2012;35:868–874.
Bertot LC, Sato M, Tateishi R, Yoshida H, Koike K. Mortality and complication rates of percutaneous ablative techniques for the treatment of liver tumors: a systematic review. Eur Radiol. 2011;21:2584–96.
Chinnaratha MA, Chuang MA, Fraser RJ, Woodman RJ, Wigg AJ. Percutaneous thermal ablation for primary hepatocellular carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016;31:294–301.
Poulou LS, Botsa E, Thanou I, Ziakas PD, Thanos L. Percutaneous microwave ablation vs radiofrequency ablation in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Hepatol. 2015;7:1054–1063.
Lencioni R, De Baere T, Martin RC, Nutting CW, Narayanan G. Image-guided ablation of malignant liver tumors: recommendations for clinical validation of novel thermal or non-thermal technologies—a Western perspective. Liver Cancer. 2015;4:208–2014.
Dodd JD, Dodd NA, Lanctot AC, Glueck DA. Effect of variation of portal venous blood flow on radiofrequency and microwave ablations in a blood-perfused bovine liver model. Radiology. 2013;267:129–36.
Ohmoto K, Yoshioka N, Tomiyama Y, et al. Comparison of therapeutic effects between radiofrequency ablation and percutaneous microwave coagulation therapy for small hepatocellular carcinoma. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009;24:223–7.
Ding J, Jing X, Liu J, Wang Y, Wang F, Wang Y, et al. Comparison of two different thermal techniques for the treatment of hepatocelllular carcinoma. Eur J Radiol. 2013;82:1379–84.
Chinnaratha MA, Sathananthan D, Pateria P, et al High local recurrence of early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma after percutaneous thermal ablation in routine clinical practice. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015;27:349–54.
Takahashi S, Kudo M, Chung H, et al. Initial treatment response is essential to improve survival in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma who underwent curative radiofrequency ablation therapy. Oncology. 2007;72 Suppl 1:98–103.
Disclosures
Roberto Santambrogio, Jason Chiang, Matteo Barabino, Franca Maria Meloni, Emanuela Bertolini, Fabio Melchiorre, and Enrico Opocher have no conflicts of interest or financial ties to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Santambrogio, R., Chiang, J., Barabino, M. et al. Comparison of Laparoscopic Microwave to Radiofrequency Ablation of Small Hepatocellular Carcinoma (≤3 cm). Ann Surg Oncol 24, 257–263 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-016-5527-2
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-016-5527-2