Abstract
Background
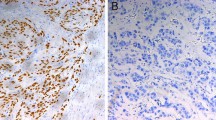
A reliable marker of chemoradiosensitivity that would enable appropriate and individualized treatment of thoracic squamous cell esophageal cancer has long been sought. We investigated whether regenerating gene (REG) Iα is such a marker.
Methods
We assessed expression of REG Iα in untreated endoscopic biopsy specimens and examined the correlation between REG Iα expression and the clinical responses to definitive chemoradiotherapy and prognosis. We also examined the relationship between REG Iα expression in the resected tumor and the prognosis of patients who received esophagectomy for thoracic squamous cell esophageal cancer.
Results
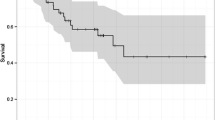
Among the 42 patients treated with definitive chemoradiotherapy, 8 of the 23 REG I-positive patients (35%) showed complete responses to chemoradiotherapy, while only one of the 19 REG I-negative patients did so. The survival rate among the REG I-positive patients was significantly better than among the REG I-negative patients. For the 76 patients treated surgically, there was no significant difference in the survival rates among the REG I-positive and REG I-negative patients.
Conclusions
REG Iα expression in squamous cell esophageal carcinoma may be a reliable marker of chemoradiosensitivity. We anticipate that it will enable us to provide more appropriate and individualized treatment to patients of advanced esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ando N, Ozawa S, Kitagawa Y, et al. Improvement in the results of surgical treatment of advanced squamous esophageal carcinoma during 15 consecutive years. Ann Surg 2002; 232:225–32
Law S, Kwong D, Wong KF, et al. Improvement in treatment results and long-term survival of patients with esophageal cancer: Impact of chemoradiation and change in treatment strategy. Ann Surg 2003; 238:339–47
Suntharalingam M. Definitive chemoradiation in the management of locally advanced esophageal cancer. Semin Radiat Oncol 2006; 17:22–8
Ohtsu A, Boku N, Muro K, et al. Definitive chemoradiotherapy for T4 and/or M1 lymph node squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus. J Clin Oncol 1999; 17:2915–21
Hironaka S, Ohtsu A, Boku N, et al. Nonrandomized comparison between definitive chemoradiotherapy and radical surgery in patients with T(2–3) N(any) M(0) squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus. Int J Radiat Oncol 2003; 57:425–33
Tahara M, Ohtsu A, Hironaka S, et al. Clinical impact of criteria for complete response (CR) of primary site to treatment of esophageal cancer. Jpn J Clin Oncol 2005; 35:316–23
Ishikura S, Nihei K, Ohtsu A, et al. Long-term toxicity after definitive chemoradiotherapy for squamous cell carcinoma of the thoracic esophagus. J Clin Oncol 2003; 21:2697–702
Motoyama S, Sugiyama T, Ueno Y, et al. REGI expression predicts long-term survival among locally advanced thoracic squamous cell esophageal cancer patients treated with neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy followed by esophagectomy. Ann Surg Oncol 2006; 13:1724–31
Motoyama S, Saito R, Kitamura M, et al. Outcome of active surgery during intensive follow-up for second primary malignancy after esophagectomy for thoracic squamous cell esophageal carcinoma. J Am Coll Surg 2003; 197:914–20
Sato Y, Motoyama S, Maruyama K, et al. A second malignancy is the major cause of death among thoracic squamous cell esophageal cancer patients negative for lymph node involvement. J Am Coll Surg 2005; 201:188–93
Terazono K, Yamamoto H, Takasawa S, et al. A novel gene activated in regenerating islets. J Biol Chem 1988; 263:2111–4
Zhang YW, Ding LS, Lai MD. Reg gene family and human disease. World J Gastroenterol 2003; 9:2635–41
Sanchez D, Figarella C, Marchand-Pinatel S, et al. Preferential expression of RegIβ gene in human adult pancreas. Biochem Biop Res Co 2001; 284:729–37
Cash HL, Whitham CV, Hooper LV. Refolding, purification, and characterization of human and murine Reg III proteins expressed in escherichia coli. Protein Expres Purif 2006; 48:151–9
Kobayashi S, Akiyama T, Nata K, et al. Identification of a receptor for Reg (Regenerating gene) protein, a pancreatic β-cell regeneration factor. J Biol Chem 2000; 275:10723–6
Nanakin A, Fukui H, Fujii S, et al. Expression of the REG IV gene in ulcerative colitis. Lab Invest 2007; 87:304–14
Shinozaki S, Nakamura T, Iimura M, et al. Upregulation of Reg Iα and GW112 in the epithelium of inflamed colonic mucosa. Gut 2001; 48:623–29
Ose T, Kadowaki Y, Fukuhara H, et al. Reg I—knockout mice reveal its role in regulation of cell growth that is required in generation and maintenance of the villous structure of small intestine. Oncogene 2007; 26:349–59
Harada K, Zen Y, Kanemori Y, et al. Human REGI gene is up-regulated in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma and its precursor lesions. Hepatology 2001; 33:1036–42
Macadam RC, Sarela AI, Farmery SM, et al. Death from early colorectal cancer is predicted by the presence of transcripts of the REG gene family. Br J Cancer 2000; 83:188–95
Yonemura Y, Sakurai S, Yamamoto H, et al. REG gene expression is associated with the infiltrating growth of gastric carcinoma. Cancer 2003; 98:1394–400
Dhar DK, Udagawa J, Ishihara S, et al. Expression of regenerating gene I in gastric adenocarcinomas. Cancer 2004; 100:1130–6
Takehara A, Eguchi H, Ohigashi H, et al. Novel tumor marker REG4 detected in serum of patients with resectable pancreatic cancer and feasibility for antibody therapy targeting REG4. Cancer Sci 2006; 97:1191–7
Takeuchi H, Ozawa S, Ando N, et al. Cell-cycle regulators and the Ki-67 labeling index can predict the response to chemoradiotherapy and the survival of patients with locally advanced squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus. Ann Surg Oncol 2003; 10:792–800
Shintani S, Mihara M, Ueyama Y, et al. Cyclin D1 overexpression associates with radiosensitivity in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Cancer 2001; 96:159–65
Martin JMC, Balkenende A, Verschoor T, et al. CyclinD1 overexpression enhances radiation-induced apoptosis and radiosensitivity in a breast tumor cell line. Cancer Res 1999; 59:1134–40
Schneider S, Uchida K, Brabender J, et al. Downregulation of TS, DPD, ERCC1, GST-Pi, EGFR, and HER2 gene expression after neoadjuvant three-modality treatment in patients with esophageal cancer. J Am Coll Surg 2005; 200:336–44
Kawamata H, Furihata T, Omotehara F, et al. Identification of genes differentially expressed in a newly isolated human metastasizing esophageal cancer cell line, T.Tn-AT1, by cDNA microarray. Cancer Sci 2003; 94:699–706
Kan T, Yamasaki S, Kondo K, et al. A new specific gene expression in squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus detected using representational difference analysis and cDNA microarray. Oncology 2006; 70:25–33
Yoshitake Y, Nakatsura T, Monji M, et al. Proliferation potential-related protein, an ideal esophageal cancer antigen for immunotherapy, identified using complementary DNA microarray analysis. Clin Cancer Res 2004; 10:6437–48
Shao L, Hittelman WN, Lin J, et al. Deficiency of cell cycle checkpoints and DNA repair system predispose individuals to esophageal cancer. Mutat Res-Fund Mol M 2006; 602:143–50
Kastan MB, Bartek J. Cell-cycle checkpoints and cancer. Nature 2004; 432:316–23
Miyata H, Doki Y, Shinozaki H, et al. CDC25B and p53 are independently implicated in radiation sensitivity for human esophageal cancers. Clin Cancer Res 2000; 6:4859–65
Sheridan MT, O’Dwyer T, Seymour CB, et al. Potential indicators of radiosensitivity in squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. Radiat Oncol Invest 1997; 5:180–6
Takasawa S, Ikeda T, Akiyama T, et al. CyclinD1 activation through ATF-2 in Reg-induced pancreatic β-cell regeneration. FEBS Lett 2006; 580:585–91
Bishnupuri KS, Luo Q, Korzenik JR, et al. Dysregulation of Reg gene expression occurs early in gastrointestinal tumorigenesis and regulates anti-apoptotic genes. Cancer Biol Ther 2006; 5:1714–20
Sekikawa A, Fukui H, Fujii S, et al. REG Iα protein may function as a trophic and/or anti-apoptotic factor in the development of gastric cancer. Gastroenterology 2005; 128:642–53
Bishnupuri KS, Luo Q, Murmu N, et al. Reg IV activates the epidermal growth factor receptor/Akt/AP-1 signaling pathway in colon adenocarcinomas. Gastroenterology 2006; 130:137–49
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hayashi, K., Motoyama, S., Sugiyama, T. et al. REG Iα is a Reliable Marker of Chemoradiosensitivity in Squamous Cell Esophageal Cancer Patients. Ann Surg Oncol 15, 1224–1231 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-008-9810-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-008-9810-8