Abstract
Background
TWIST1 is a basic helix–loop–helix (bHLH) transcription factor that has been involved in tumor progression and metastasis in several cancer types, although no evidence has been provided yet on its implication in colorectal carcinogenesis.
Methods
We examined the expression pattern of TWIST1 messenger RNA (mRNA) in 54 colorectal cancer biopsies compared with each respective adjacent normal mucosa by real-time reverse-transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) methodology.
Results
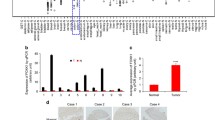
TWIST1 mRNA was found significantly overexpressed in colorectal cancer samples compared to nontumorous colon mucosa (P < 0.0001). Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis demonstrated that TWIST1 mRNA levels are significantly increased in patients with nodal invasion and, interestingly, a significant correlation with patient sex was also found.
Conclusions
Evidence for upregulation of TWIST1 mRNA in colorectal cancer is provided, suggesting its implication in the onset of malignant progression of this disease. In addition, significant higher levels of TWIST1 mRNA were found in men than in women, suggesting a possible transcriptional regulation of TWIST1 by sexual hormones. The use of TWIST1 as a new prognostic marker of advanced malignancy, and as a potential therapeutic target in colorectal cancer, is proposed.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, et al. Cancer statistics, 2008. CA Cancer J Clin 2008
Nelson H, Petrelli N, Carlin A et al. Guidelines 2000 for colon and rectal cancer surgery. J Natl Cancer Inst 2001; 93:583–96
O;Connell JB, Maggard MA, Ko CY. Colon cancer survival rates with the new American Joint Committee on Cancer sixth edition staging. J Natl Cancer Inst 2004; 96:1420–5
Compton CC, Greene FL. The staging of colorectal cancer: 2004 and beyond. CA Cancer J Clin 2004; 54:295–308
Wright FC, Law CH, Last L et al. Lymph node retrieval and assessment in stage II colorectal cancer: a population-based study. Ann Surg Oncol 2003; 10:903–9
Hebrok M, Wertz K, Fuchtbauer EM. M-twist is an inhibitor of muscle differentiation. Dev Biol 1994; 165:537–44
Chen ZF, Behringer RR. twist is required in head mesenchyme for cranial neural tube morphogenesis. Genes Dev 1995; 9:686–99
Vernon AE, LaBonne C. Tumor metastasis: a new twist on epithelial-mesenchymal transitions. Curr Biol 2004; 14:R719–21
Yang J, Mani SA, Donaher JL et al. Twist, a master regulator of morphogenesis, plays an essential role in tumor metastasis. Cell 2004; 117:927–39
Ma L, Teruya-Feldstein J, Weinberg RA. Tumour invasion and metastasis initiated by microRNA-10b in breast cancer. Nature 2007; 449:682–8
Maestro R, Dei Tos AP, Hamamori Y et al. Twist is a potential oncogene that inhibits apoptosis. Genes Dev 1999; 13:2207–17
Rosivatz E, Becker I, Specht K et al. Differential expression of the epithelial-mesenchymal transition regulators snail, SIP1, and twist in gastric cancer. Am J Pathol 2002; 161:1881–91
Valsesia-Wittmann S, Magdeleine M, Dupasquier S et al. Oncogenic cooperation between H-Twist and N-Myc overrides failsafe programs in cancer cells. Cancer Cell 2004; 6:625–30
Elias MC, Tozer KR, Silber JR et al. TWIST is expressed in human gliomas and promotes invasion. Neoplasia 2005; 7:824–37
Yuen HF, Chan YP, Wong ML, et al. Up-regulation of TWIST in oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma is associated with neoplastic transformation and distant metastasis. J Clin Pathol 2007; 60:510–12
Ohuchida K, Mizumoto K, Ohhashi S, et al. Twist, a novel oncogene, is upregulated in pancreatic cancer: clinical implication of Twist expression in pancreatic juice. Int J Cancer 2007; 120:1634–40
Watanabe O, Imamura H, Shimizu T et al. Expression of twist and wnt in human breast cancer. Anticancer Res 2004; 24:3851–6
Hoek K, Rimm DL, Williams KR et al. Expression profiling reveals novel pathways in the transformation of melanocytes to melanomas. Cancer Res 2004; 64:5270–82
Kwok WK, Ling MT, Lee TW et al. Up-regulation of TWIST in prostate cancer and its implication as a therapeutic target. Cancer Res 2005; 65:5153–62
Lee TK, Poon RT, Yuen AP et al. Twist overexpression correlates with hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis through induction of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Clin Cancer Res 2006; 12:5369–76
Hosono S, Kajiyama H, Terauchi M, et al. Expression of Twist increases the risk for recurrence and for poor survival in epithelial ovarian carcinoma patients. Br J Cancer 2007
Kyo S, Sakaguchi J, Ohno S et al. High Twist expression is involved in infiltrative endometrial cancer and affects patient survival. Hum Pathol 2006; 37:431–8
Zhang Z, Xie D, Li X, et al. Significance of TWIST expression and its association with E-cadherin in bladder cancer. Hum Pathol 2007; 38:598–606
Yan-Qi Z, Xue-Yan G, Shuang H et al. Expression and significance of TWIST basic helix-loop-helix protein over-expression in gastric cancer. Pathology 2007; 39:470–5
Shibata K, Kajiyama H, Ino K, et al. Twist expression in patients with cervical cancer is associated with poor disease outcome. Ann Oncol 2007
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods 2001; 25:402–8
Gallego-Ortega D, Ramirez De Molina A, Gutierrez R et al. Generation and characterization of monoclonal antibodies against choline kinase alpha and their potential use as diagnostic tools in cancer. Int J Oncol 2006; 29:335–40
Markowitz SD, Dawson DM, Willis J et al. Focus on colon cancer. Cancer Cell 2002; 1:233–6
Leptin M. twist and snail as positive and negative regulators during Drosophila mesoderm development. Genes Dev 1991; 5:1568–76
Yang J, Mani SA, Weinberg RA. Exploring a new twist on tumor metastasis. Cancer Res 2006; 66:4549–52
Bates RC, Mercurio AM. The epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) and colorectal cancer progression. Cancer Biol Ther 2005; 4:365–70
Vesuna F, van Diest P, Chen JH et al. Twist is a transcriptional repressor of E-cadherin gene expression in breast cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2008; 367:235–41
Kampman E, Bijl AJ, Kok C et al. Reproductive and hormonal factors in male and female colon cancer. Eur J Cancer Prev 1994; 3:329–36
Brand RM, Jones DD, Lynch HT et al. Risk of colon cancer in hereditary non-polyposis colorectal cancer patients as predicted by fuzzy modeling: Influence of smoking. World J Gastroenterol 2006; 12:4485–91
Zi X, Guo Y, Simoneau AR et al. Expression of Frzb/secreted Frizzled-related protein 3, a secreted Wnt antagonist, in human androgen-independent prostate cancer PC-3 cells suppresses tumor growth and cellular invasiveness. Cancer Res 2005; 65:9762–70
Guo Y, Zi X, Koontz Z, et al. Blocking Wnt/LRP5 signaling by a soluble receptor modulates the epithelial to mesenchymal transition and suppresses met and metalloproteinases in osteosarcoma Saos-2 cells. J Orthop Res 2007; 25:964–71
Bienz M, Clevers H. Linking colorectal cancer to Wnt signaling. Cell 2000; 103:311–20
Hsu HH, Cheng SF, Chen LM et al. Over-expressed estrogen receptor-alpha up-regulates hTNF-alpha gene expression and down-regulates beta-catenin signaling activity to induce the apoptosis and inhibit proliferation of LoVo colon cancer cells. Mol Cell Biochem 2006; 289:101–9
Acknowledgements
This work has been supported by MEyC (SAF2004-0577 and SAF2005-06195-C02-01), EU grant (LSHG-CT-2006-037278), Ministerio de Sanidad (RD06/0020/0016), Fundación Mutua Madrileña, and the PRICYT Program from Comunidad de Madrid (S-BIO/0280/2006) to JCL. Fátima Valdés-Mora is the recipient of fellowship AP-2004-4640 from MEyC. David Gallego-Ortega is the recipient of fellowship FPI-2004 from CAM.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Fátima Valdés-Mora and Teresa Gómez del Pulgar have equally contributed to this article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Valdés-Mora, F., Gómez del Pulgar, T., Bandrés, E. et al. TWIST1 Overexpression is Associated with Nodal Invasion and Male Sex in Primary Colorectal Cancer. Ann Surg Oncol 16, 78–87 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-008-0166-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-008-0166-x