Abstract
Background
High-dose interleukin (IL)-2 is an effective agent for the treatment of metastatic malignant melanoma and renal cell carcinoma. This study evaluated the outcomes of patients receiving two commonly used intravenous IL-2 schedules that have never been directly compared.
Methods
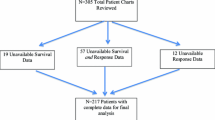
Forty-seven metastatic malignant melanoma and renal cell carcinoma patients were identified from a prospective database who underwent high-dose IL-2 therapy (720,000 or 600,000 IU/kg) during 1999 to 2003. Disease-specific survival (DSS) was calculated by the Kaplan-Meier method with the log-rank test on an intention-to-treat basis. Multivariate Cox regression analysis of prognostic variables associated with outcome was performed. Factors associated with initial response and prevention of disease progression were determined.
Results
Objective response (5 partial and 5 mixed) or disease stabilization was noted in 9 (20%) and 10 (22%), respectively, of 46 assessable patients after 1 course of therapy. Four patients (22%) achieved disease-free status after the third course of IL-2 (n = 1) or surgical resection of confined metastatic disease (n = 3). At 19.1 months’ median follow-up, factors associated with improved DSS included an initial clinical response to IL-2 therapy (P < .001) and a higher administered dose (P = .04). Patients who received 720,000 IU/kg were more likely to experience an initial major objective response (P = .03) and disease stabilization (P = 0.03) independent of the tumor treated. Objective response early in the course of therapy was the only independent predictor of tumor-related mortality (P = .004).
Conclusions
The initial clinical response to IL-2 therapy is an independent predictor of improved outcome associated with DSS and the 720,000 IU/kg dose. These results support further prospective trials with increased IL-2 dose schedules in a larger cohort of patients.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
SA Rosenberg JC Yang SL Topalian et al. (1994) ArticleTitleTreatment of 283 consecutive patients with metastatic melanoma or renal cell cancer using high-dose bolus interleukin 2 JAMA 271 907–13 Occurrence Handle10.1001/jama.271.12.907 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByuC28nhsFQ%3D Occurrence Handle8120958
J Dutcher (2002) ArticleTitleCurrent status of interleukin-2 therapy for metastatic renal cell carcinoma and metastatic melanoma Oncology (Huntingt) 16 IssueID11 Suppl 13 4–10
S Agarwala (2003) ArticleTitleImproving survival in patients with high-risk and metastatic melanoma: immunotherapy leads the way Am J Clin Dermatol 4 333–46 Occurrence Handle12688838
G Fyfe RI Fisher SA Rosenberg M Sznol DR Parkinson AC Louie (1995) ArticleTitleResults of treatment of 255 patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma who received high-dose recombinant interleukin-2 therapy J Clin Oncol 13 688–96
MB Atkins MT Lotze JP Dutcher et al. (1999) ArticleTitleHigh-dose recombinant interleukin 2 therapy for patients with metastatic melanoma: analysis of 270 patients treated between 1985 and 1993 J Clin Oncol 17 2105–16 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXkvVSmur4%3D Occurrence Handle10561265
MB Atkins L Kunkel M Sznol SA Rosenberg (2000) ArticleTitleHigh-dose recombinant interleukin-2 therapy in patients with metastatic melanoma: long-term survival update Cancer J Sci Am 6 IssueIDSuppl 1 S11–4 Occurrence Handle10685652
RI Fisher SA Rosenberg G Fyfe (2000) ArticleTitleLong-term survival update for high-dose recombinant interleukin-2 in patients with renal cell carcinoma Cancer J Sci Am 6 IssueIDSuppl 1 S55–7 Occurrence Handle10685660
SA Rosenberg JC Yang DE White SM Steinberg (1998) ArticleTitleDurability of complete responses in patients with metastatic cancer treated with high-dose interleukin-2: identification of the antigens mediating response Ann Surg 228 307–19 Occurrence Handle10.1097/00000658-199809000-00004 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1cvhtlyntA%3D%3D Occurrence Handle9742914
MT Lotze AE Chang CA Seipp C Simpson JT Vetto SA Rosenberg (1986) ArticleTitleHigh-dose recombinant interleukin 2 in the treatment of patients with disseminated cancer. Responses, treatment-related morbidity, and histologic findings JAMA 256 3117–24 Occurrence Handle10.1001/jama.256.22.3117 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:BiiD287ivFY%3D Occurrence Handle3491225
MT Lotze YL Matory AA Rayner et al. (1986) ArticleTitleClinical effects and toxicity of interleukin-2 in patients with cancer Cancer 58 2764–72 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:BiiD2M7islY%3D Occurrence Handle3490903
DR Parkinson JS Abrams PH Wiernik et al. (1990) ArticleTitleInterleukin-2 therapy in patients with metastatic malignant melanoma: a phase II study J Clin Oncol 8 1650–6 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:By6D3M7ltFI%3D Occurrence Handle2213101
JA Gollob KG Veenstra RA Parker et al. (2003) ArticleTitlePhase I trial of concurrent twice-weekly recombinant human interleukin-12 plus low-dose IL-2 in patients with melanoma or renal cell carcinoma J Clin Oncol 21 2564–73 Occurrence Handle10.1200/JCO.2003.12.119 Occurrence Handle12829677
RO Dillman AA O’Connor L Simpson NM Barth LA VanderMolen P Vanderplas (2003) ArticleTitleDoes continuous-infusion interleukin-2 increase survival in metastatic melanoma? Am J Clin Oncol 26 141–5 Occurrence Handle10.1097/00000421-200304000-00008 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXntV2jtL4%3D Occurrence Handle12714884
WD Quan SuffixJr FM Quan (2003) ArticleTitleOutpatient experience with moderate dose bolus interleukin-2 in metastatic malignant melanoma and kidney cancer J Immunother 26 286–90 Occurrence Handle10.1097/00002371-200305000-00012 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXksVOnu7c%3D Occurrence Handle12806282
D McDermott L Flaherty JI Clark et al. (2001) ArticleTitleA randomized phase III trial of high-dose interleukin-2 (HD IL2) versus subcutaneous (SC) IL2/interferon (IFN) in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma (RCC) (abstract) Proc Am Soc Clin Oncol 20 172
U Keilholz SH Goey CJ Punt et al. (1997) ArticleTitleInterferon alfa-2a and interleukin-2 with or without cisplatin in metastatic melanoma: a randomized trial of the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer Melanoma Cooperative Group J Clin Oncol 15 2579–88 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXkslyms74%3D Occurrence Handle9215828
LE Flaherty M Atkins J Sosman et al. (2001) ArticleTitleOutpatient biochemotherapy with interleukin-2 and interferon alfa-2b in patients with metastatic malignant melanoma: results of two phase II cytokine working group trials J Clin Oncol 19 3194– 202 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXltlShtLc%3D Occurrence Handle11432886
MB Atkins (2002) ArticleTitleInterleukin-2: clinical applications Semin Oncol 29 IssueID3 Suppl 7 12–7 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38Xltlaqtrg%3D
JM Tourani C Pfister N Tubiana et al. (2003) ArticleTitleSubcutaneous interleukin-2 and interferon alfa administration in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma: final results of SCAPsIII, a large, multicenter, phase II, nonrandomized study with sequential analysis design—the Subcutaneous Administration Propeukin Program Cooperative Group J Clin Oncol 21 3987–94 Occurrence Handle10.1200/JCO.2003.02.073 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2cXpsVajsbs%3D Occurrence Handle14581421
J Atzpodien K Neuber D Kamanabrou et al. (2002) ArticleTitleCombination chemotherapy with or without s.c. IL-2 and IFN-alpha: results of a prospectively randomized trial of the Cooperative Advanced Malignant Melanoma Chemoimmunotherapy Group (ACIMM) Br J Cancer 86 179–84 Occurrence Handle10.1038/sj.bjc.6600043 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38Xit1aqsbg%3D Occurrence Handle11870502
JC Yang RM Sherry SM Steinberg et al. (2003) ArticleTitleRandomized study of high-dose and low-dose interleukin-2 in patients with metastatic renal cancer J Clin Oncol 21 3127–32 Occurrence Handle10.1200/JCO.2003.02.122 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2cXpsVWqtb8%3D Occurrence Handle12915604
U Keilholz AM Eggermont (2000) ArticleTitleThe emerging role of cytokines in the treatment of advanced melanoma. For the EORTC Melanoma Cooperative Group Oncology 58 89–95 Occurrence Handle10.1159/000012085 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXis1Siur4%3D Occurrence Handle10705235
JA Sparano RI Fisher M Sunderland et al. (1993) ArticleTitleRandomized phase III trial of treatment with high-dose interleukin-2 either alone or in combination with interferon alfa-2a in patients with advanced melanoma J Clin Oncol 11 1969–77 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByuD3MritFM%3D Occurrence Handle8410122
O Eton SS Legha AY Bedikian et al. (2002) ArticleTitleSequential biochemotherapy versus chemotherapy for metastatic melanoma: results from a phase III randomized trial J Clin Oncol 20 2045–52 Occurrence Handle10.1200/JCO.2002.07.044 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XjvVKmsrg%3D Occurrence Handle11956264
R Ridolfi V Chiarion-Sileni M Guida et al. (2002) ArticleTitleCisplatin, dacarbazine with or without subcutaneous interleukin-2, and interferon alpha-2b in advanced melanoma outpatients: results from an Italian multicenter phase III randomized clinical trial J Clin Oncol 20 1600–7 Occurrence Handle10.1200/JCO.20.6.1600 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XivFeitrk%3D Occurrence Handle11896110
SA Rosenberg JC Yang DJ Schwartzentruber et al. (1999) ArticleTitleProspective randomized trial of the treatment of patients with metastatic melanoma using chemotherapy with cisplatin, dacarbazine, and tamoxifen alone or in combination with interleukin-2 and interferon alfa-2b J Clin Oncol 17 968–75 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXhvFGgu7Y%3D Occurrence Handle10071291
M Atkins S Lee L Flaherty J Sosman VK Sondak JM Kirkwood (2003) ArticleTitleA prospective randomized phase III trial of concurrent biochemotherapy (BCT) with cisplatin, vinblastine, dacarbazine (CVD), IL-2 and interferon alpha-2b (IFN) versus CVD alone in patients with metastatic melanoma (E3695): an ECOG-coordinated intergroup trial (abstract) Proc Am Soc Clin Oncol 22 708
DJ Schwartzentruber (2001) ArticleTitleGuidelines for the safe administration of high-dose interleukin-2 J Immunother 24 287–93 Occurrence Handle10.1097/00002371-200107000-00004 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXntFGntrY%3D Occurrence Handle11565830
LE Flaherty (2000) ArticleTitleRationale for intergroup trial E-3695 comparing concurrent biochemotherapy with cisplatin, vinblastine, and DTIC alone in patients with metastatic melanoma Cancer J Sci Am 6 IssueIDSuppl 1 S15–20 Occurrence Handle10685653
RN Schwartz L Stover J Dutcher (2002) ArticleTitleManaging toxicities of high-dose interleukin-2 Oncology (Huntingt) 16 IssueID11 Suppl 13 11–20
US Kammula DE White SA Rosenberg (1998) ArticleTitleTrends in the safety of high dose bolus interleukin-2 administration in patients with metastatic cancer Cancer 83 797–805 Occurrence Handle10.1002/(SICI)1097-0142(19980815)83:4<797::AID-CNCR25>3.0.CO;2-M Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXls1ansbo%3D Occurrence Handle9708948
RE Royal SM Steinberg RS Krouse et al. (1996) ArticleTitleCorrelates of response to IL-2 therapy in patients treated for metastatic renal cancer and melanoma Cancer J Sci Am 2 91–98 Occurrence Handle9166506
E Chang SA Rosenberg (2001) ArticleTitlePatients with melanoma metastases at cutaneous and subcutaneous sites are highly susceptible to interleukin-2-based therapy J Immunother 24 88–90 Occurrence Handle10.1097/00002371-200101000-00010 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3M7ls1SisQ%3D%3D Occurrence Handle11211152
U Keilholz P Martus CJ Punt et al. (2002) ArticleTitlePrognostic factors for survival and factors associated with long-term remission in patients with advanced melanoma receiving cytokine-based treatments: second analysis of a randomised EORTC Melanoma Group trial comparing interferon-alpha2a (IFNalpha) and interleukin 2 (IL-2) with or without cisplatin Eur J Cancer 38 1501–11 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0959-8049(02)00123-5 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XltFWiurc%3D Occurrence Handle12110497
RL White SuffixJr DJ Schwartzentruber A Guleria et al. (1994) ArticleTitleCardiopulmonary toxicity of treatment with high dose interleukin-2 in 199 consecutive patients with metastatic melanoma or renal cell carcinoma Cancer 74 3212–22 Occurrence Handle7982185
GQ Phan P Attia SM Steinberg DE White SA Rosenberg (2001) ArticleTitleFactors associated with response to high-dose interleukin-2 in patients with metastatic melanoma J Clin Oncol 19 3477–82
J Atzpodien H Kirchner U Jonas et al. (2004) ArticleTitleInterleukin-2- and interferon alfa-2a-based immunochemotherapy in advanced renal cell carcinoma: a prospectively randomized trial of the German Cooperative Renal Carcinoma Chemoimmunotherapy Group (DGCIN) J Clin Oncol 22 1188–94 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2cXpsVGktL8%3D Occurrence Handle14981107
Acknowledgments
Supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health (K08–79881), the National Cancer Institute (R01-093696), and the Doris Duke Charitable Foundation (T98052).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Published by Springer Science+Business Media, Inc. © 2005 The Society of Surgical Oncology, Inc.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Spanknebel, K., Cheung, K.Y., Stoutenburg, J. et al. Initial Clinical Response Predicts Outcome and Is Associated With Dose Schedule in Metastatic Melanoma and Renal Cell Carcinoma Patients Treated With High-Dose Interleukin 2. Ann Surg Oncol 12, 381–390 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1245/ASO.2005.03.063
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1245/ASO.2005.03.063