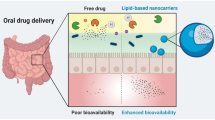
Abstract
Among many, the oral route of delivery is considered to be the most favorable route with the highest patient compliance. The main issue with oral delivery is the environmental vulnerability of gastro intestinal tract (G.I.T). The bioavailability could further decrease when drug has poor aqueous solubility and permeability through biological membrane. This drawback could be resolved by employing drug-phospholipid complex strategy, as they utilize mechanism which is similar to the absorption mechanism of nutritional constituents form G.I.T. The drug-phospholipid complexes are considered ideal for oral delivery as they are biodegradable and non-toxic, which enable them to be employed as solubilizer, emulsifier, and as a matrix forming excipient for dugs with poor solubility and/or permeability. The present review compiles the basic know how about the phospholipids and the mechanism through which it improves the bioavailability of drugs. Further, it also compiles the crucial formulation aspects and methods of preparations of drug-phospholipid complex along with its physical and in silico characterization techniques. The increase in number of recent reports involving the utilization of drug-phospholipid complex to improve oral bioavailability of drugs thus explains how vital the strategy is for a successful oral delivery.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Veber DF, Johnson SR, Cheng H-Y, Smith BR, Ward KW, Kopple KD. Molecular properties that influence the oral bioavailability of drug candidates. J Med Chem. 2002;45(12):2615–23.
Kuche K, Maheshwari R, Tambe V, Mak K-K, Jogi H, Raval N, et al. Carbon nanotubes (CNTs) based advanced dermal therapeutics: current trends and future potential. Nanoscale. 2018;10(19):8911–37.
Yan C, Gu J, Lv Y, Shi W, Jing H. Improved intestinal absorption of water-soluble drugs by acetylation of G2 PAMAM dendrimer nanocomplexes in rat. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2017;7(3):408–15.
Kirtane AR, Narayan P, Liu G, Panyam J. Polymer-surfactant nanoparticles for improving oral bioavailability of doxorubicin. J Pharm Investig. 2017;47(1):65–73.
Pandey SC, Kaur R, Gangadharapp H, Sachin J. Self-emulsifying drug delivery system: a review. RJPT. 2018;1(4):313–23.
Vilas PC, Gujarathi NA, Rane BR, Pawar SP. A Review on self microemulsifying drug delivery system. Pharma Sci Monit. 2013;4(1):3628–48.
Andonova V, Peneva P. Characterization methods for solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN) and nanostructured lipid carriers (NLC). Curr Pharm Des. 2017;23(43):6630–42.
Semalty A, Semalty M, Rawat BS, Singh D, Rawat M. Pharmacosomes: the lipid-based new drug delivery system. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2009;6(6):599–612.
J-n Y, Zhu Y, Wang L, Peng M, S-s T, Cao X, et al. Enhancement of oral bioavailability of the poorly water-soluble drug silybin by sodium cholate/phospholipid-mixed micelles. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2010;31(6):759.
Gnananath K, Nataraj KS, Rao BG. Phospholipid complex technique for superior bioavailability of Phytoconstituents. Adv Pharm Bull. 2017;7(1):35–42.
Singh RP, Gangadharappa H, Mruthunjaya K. Phospholipids: unique carriers for drug delivery systems. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol. 2017;39:166–79.
Marsh D. General features of phospholipid phase transitions. Chem Phys Lipids. 1991;57(2–3):109–20.
Seimiya T, Ohki S. Ionic structure of phospholipid membranes, and binding of calcium ions. Biochim Biophys Acta (BBA)-Biomembr. 1973;298(3):546–61.
Sosenko IR, Innis SM, Frank L. Intralipid increases lung polyunsaturated fatty acids and protects newborn rats from oxygen toxicity. Pediatr Res. 1991;30(5):413–7.
de Boer JF, Kuipers F, Groen AK. Cholesterol transport revisited: A new Turbo mechanism to drive cholesterol excretion. Trends Endocrin Met. 2017;29(2):123–33.
Mills PC, Chen Y, Hills YC, Hills BA. Comparison of surfactant lipids between pleural and pulmonary lining fluids. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2006;19(4):292–6.
Cevc G. Phospholipids handbook: CRC press; 1993.
Li J, Wang X, Zhang T, Wang C, Huang Z, Luo X, et al. A review on phospholipids and their main applications in drug delivery systems. Asian J Pharm Sci. 2015;10(2):81–98.
Intermolecular JI. Surface forces. San Diego: Academic press; 1992.
McMahon HT, Gallop JL. Membrane curvature and mechanisms of dynamic cell membrane remodelling. Nature. 2005;438(7068):590–6.
Phillips R, Theriot J, Kondev J, Garcia H. Physical biology of the cell: Garland. Science. 2012.
Sharma S, Roy RK. Phytosomes: an emerging technology. Int J Pharm Res Dev. 2010;2(5):1–7.
Kapoor B, Gupta R, Singh SK, Gulati M, Singh S. Prodrugs, phospholipids and vesicular delivery-an effective triumvirate of pharmacosomes. Adv Colloid Interf Sci. 2018;253:35–65.
Carey MC, Small DM. The characteristics of mixed micellar solutions with particular reference to bile. Am J Med. 1970;49(5):590–608.
Gangwar M, Singh R, Goel R, Nath G. Recent advances in various emerging vescicular systems: an overview. Asian Pac J Trop Biomed. 2012;2(2):S1176–S88.
Bhingare U, Khadabadi S, Shinde N. Pharmacosomes: A novel drug delivery system. Int J. 2014;3(1):14–20.
Gavhane YN, Yadav AV. Loss of orally administered drugs in GI tract. Saudi Pharm J. 2012;20(4):331–44.
Jena SK, Singh C, Dora CP, Suresh S. Development of tamoxifen-phospholipid complex: novel approach for improving solubility and bioavailability. Int J Pharm. 2014;473(1–2):1–9.
van Hoogevest P. Review–an update on the use of oral phospholipid excipients. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2017;108:1–12.
Chaudhri O, Small C, Bloom S. Gastrointestinal hormones regulating appetite. Phil Trans R Soc London B: Biol Sci. 2006;361(1471):1187–209.
Marieb EN, Hoehn K. Human anatomy and physiology. 8e éd ed. San Francisco: Benjamin Cummings; 2010.
Kossena GA, Charman WN, Wilson CG, O’Mahony B, Lindsay B, Hempenstall JM, et al. Low dose lipid formulations: effects on gastric emptying and biliary secretion. Pharm Res. 2007;24(11):2084–96.
Higgins J, Fielding C. Lipoprotein lipase. Mechanism of formation of triglyceride-rich remnant particles from very low density lipoproteins and chylomicrons. Biochemistry. 1975;14(11):2288–93.
Harde H, Das M, Jain S. Solid lipid nanoparticles: an oral bioavailability enhancer vehicle. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2011;8(11):1407–24.
Nestel P, Havel R, Bezman A. Sites of initial removal of chylomicron triglyceride fatty acids from the blood. J Clin Invest. 1962;41(10):1915–21.
Semalty A, Semalty M, Singh D, Rawat M. Phyto-phospholipid complex of catechin in value added herbal drug delivery. J Incl Phenom Macrocycl Chem. 2012;73(1–4):377–86.
Alexander A, Ajazuddin S, Verma T, Swarna MJ, Patel S. Mechanism responsible for mucoadhesion of mucoadhesive drug delivery system: a review. Int J Appl Biol Pharm Technol. 2011;2(1):434–45.
Behra A, Giri TK, Tripathi DK, Ajazuddin AA. An exhaustive review on recent advancement in pharmaceutical bioadhesive used for systemic drug delivery through oral mucosa for achieving maximum pharmacological response and effect. Int J Pharmacol. 2012;8(5):283–305.
Afanas’eva YG, Fakhretdinova E, Spirikhin L, Nasibullin R. Mechanism of interaction of certain flavonoids with phosphatidylcholine of cellular membranes. Pharm Chem J. 2007;41(7):354–6.
Li N, Ye Y, Yang M, Jiang X, Ma J. Pharmacokinetics of baicalin-phospholipid complex in rat plasma and brain tissues after intranasal and intravenous administration. Die Pharmazie-an international. J Pharm Sci. 2011;66(5):374–7.
Yue P-F, Yuan H-L, Li X-Y, Yang M, Zhu W-F. Process optimization, characterization and evaluation in vivo of oxymatrine–phospholipid complex. Int J Pharm. 2010;387(1–2):139–46.
Maryana W, Rachmawati H, Mudhakir D. Formation of Phytosome containing Silymarin using thin layer-hydration technique aimed for Oral delivery. Mater Today Proc. 2016;3(3):855–66.
Qin X, Yang Y, T-t F, Gong T, X-n Z, Huang Y. Preparation, characterization and in vivo evaluation of bergenin-phospholipid complex. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2010;31(1):127–36.
Guo B, Liu H, Li Y, Zhao J, Yang D, Wang X, et al. Application of phospholipid complex technique to improve the dissolution and pharmacokinetic of probucol by solvent-evaporation and co-grinding methods. Int J Pharm. 2014;474(1–2):50–6.
Sikarwar MS, Sharma S, Jain AK, Parial S. Preparation, characterization and evaluation of marsupsin–phospholipid complex. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2008;9(1):129–37.
Li Y, Yang D-J, Chen S-L, Chen S-B, AS-C C. Comparative physicochemical characterization of phospholipids complex of puerarin formulated by conventional and supercritical methods. Pharm Res. 2008;25(3):563–77.
Dora CP, Kushwah V, Katiyar SS, Kumar P, Pillay V, Suresh S, et al. Improved oral bioavailability and therapeutic efficacy of erlotinib through molecular complexation with phospholipid. Int J Pharm. 2017;534(1–2):1–13.
Cui F, Shi K, Zhang L, Tao A, Kawashima Y. Biodegradable nanoparticles loaded with insulin–phospholipid complex for oral delivery: preparation, in vitro characterization and in vivo evaluation. J Control Release. 2006;114(2):242–50.
Murugan V, Mukherjee K, Maiti K, Mukherjee PK. Enhanced oral bioavailability and antioxidant profile of ellagic acid by phospholipids. J Agric Food Chem. 2009;57(11):4559–65.
Dora CP, Kushwah V, Katiyar SS, Kumar P, Pillay V, Suresh S, et al. Improved metabolic stability and therapeutic efficacy of a novel molecular gemcitabine phospholipid complex. Int J Pharm. 2017;530(1–2):113–27.
Kumar P, Choonara YE, Pillay V. In silico affinity profiling of neuroactive polyphenols for post-traumatic calpain inactivation: a molecular docking and atomistic simulation sensitivity analysis. Molecules. 2014;20(1):135–68.
Larkin P. Infrared and Raman spectroscopy: principles and spectral interpretation. Amsterdam: Elsevier; 2017.
Singh C, Bhatt TD, Gill MS, Suresh S. Novel rifampicin–phospholipid complex for tubercular therapy: synthesis, physicochemical characterization and in-vivo evaluation. Int J Pharm. 2014;460(1–2):220–7.
Rajan S, Kang S-Y, Gutowsky HS, Oldfield E. Phosphorus nuclear magnetic resonance study of membrane structure. Interactions of lipids with protein, polypeptide, and cholesterol. J Biol Chem. 1981;256(3):1160–6.
Jin Y, Wunderlich B. Single-run heat capacity measurement by DSC: principle, experimental and data analysis. Thermochim Acta. 1993;226:155–61.
Chandrasekaran B, Abed SN, Al-Attraqchi O, Kuche K, Tekade RK. Computer-aided prediction of pharmacokinetic (ADMET) properties. In: Dosage Form Design Parameters. Amsterdam: Elsevier; 2018. p. 731–55.
Ngwuluka NC, Choonara YE, Kumar P, du Toit LC, Khan RA, Pillay V. A novel pH-responsive interpolyelectrolyte hydrogel complex for the oral delivery of levodopa. Part I. IPEC modeling and synthesis. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2015;103(3):1077–84.
Wang L, Hao Y, Liu N, Ma M, Yin Z, Zhang X. Enhance the dissolution rate and oral bioavailability of pranlukast by preparing nanosuspensions with high-pressure homogenizing method. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2012;38(11):1381–9.
Hao Y, Wang L, Li J, Liu N, Feng J, Zhao M, et al. Enhancement of solubility, transport across Madin-Darby canine kidney monolayers and oral absorption of pranlukast through preparation of a pranlukast-phospholipid complex. J Biomed Nanotechnol. 2015;11(3):469–77.
Schuetz EG, Schinkel AH, Relling MV, Schuetz JD. P-glycoprotein: a major determinant of rifampicin-inducible expression of cytochrome P4503A in mice and humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 1996;93(9):4001–5.
Qin L, Niu Y, Wang Y, Chen X. Combination of phospholipid complex and submicron emulsion techniques for improving Oral bioavailability and therapeutic efficacy of water-insoluble drug. Mol Pharm. 2018;15(3):1238–47.
Immordino ML, Brusa P, Rocco F, Arpicco S, Ceruti M, Cattel L. Preparation, characterization, cytotoxicity and pharmacokinetics of liposomes containing lipophilic gemcitabine prodrugs. J Control Release. 2004;100(3):331–46.
Elnaggar YS, Shehata EM, Galal S, Abdallah OY. Self-emulsifying preconcentrates of daidzein–phospholipid complex: design, in vitro and in vivo appraisal. Nanomedicine. 2017;12(8):893–910.
Ma H, Chen H, Sun L, Tong L, Zhang T. Improving permeability and oral absorption of mangiferin by phospholipid complexation. Fitoterapia. 2014;93:54–61.
Zhou H, Han Y-m, Zheng Y-m, Xu X-y, Fu S-q, Wang L-I, et al. Preparative procedure of inclusion compound of mangiferin-HP-β-CD. J Chongqing Inst Technol (Nat Sci). 2009;9:011.
Li Y, Ren X, Lio C, Sun W, Lai K, Liu Y, et al. A chlorogenic acid-phospholipid complex ameliorates post-myocardial infarction inflammatory response mediated by mitochondrial reactive oxygen species in SAMP8 mice. Pharmacol Res. 2018;130:110–22.
Maheshwari R, Kuche KN, Advankar A, Soni N, Raval N, Sharma PA, et al. Natural Ingredients/Botanical Extracts for the Nutraceutical Industry. In: Flavors for Nutraceutical and Functional Foods. Boca Raton: CRC Press; 2018. p. 95–142.
Wu J-Y, Li Y-J, Han M, Hu X-B, Yang L, Wang J-M, et al. A microemulsion of puerarin–phospholipid complex for improving bioavailability: preparation, in vitro and in vivo evaluations. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2018;44(8):1336–41.
Ge L, He X, Zhang Y, Zhang Y, Chai F, Jiang L, et al. A dabigatran etexilate phospholipid complex nanoemulsion system for further oral bioavailability by reducing drug-leakage in the gastrointestinal tract. Nanomedicine. 2018;14(4):1455–64.
Pouton CW, Porter CJ. Formulation of lipid-based delivery systems for oral administration: materials, methods and strategies. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2008;60(6):625–37.
Constantinides PP. Lipid microemulsions for improving drug dissolution and oral absorption: physical and biopharmaceutical aspects. Pharm Res. 1995;12(11):1561–72.
Pouton CW. Formulation of poorly water-soluble drugs for oral administration: physicochemical and physiological issues and the lipid formulation classification system. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2006;29(3–4):278–87.
Čerpnjak K, Zvonar A, Gašperlin M, Vrečer F. Lipid-based systems as promising approach for enhancing the bioavailability of poorly water-soluble drugs. Acta Pharma. 2013;63(4):427–45.
Walstra P. Principles of emulsion formation. Chem Eng Sci. 1993;48(2):333–49.
Ruan J, Liu J, Zhu D, Gong T, Yang F, Hao X, et al. Preparation and evaluation of self-nanoemulsified drug delivery systems (SNEDDSs) of matrine based on drug–phospholipid complex technique. Int J Pharm. 2010;386(1–2):282–90.
Wu H, Long X, Yuan F, Chen L, Pan S, Liu Y, et al. Combined use of phospholipid complexes and self-emulsifying microemulsions for improving the oral absorption of a BCS class IV compound, baicalin. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2014;4(3):217–26.
Wei D, Zhang X. Solubility of puerarin in the binary system of methanol and acetic acid solvent mixtures. Fluid Phase Equilib. 2013;339:67–71.
Xia H-j, Zhang Z-h, Jin X, Hu Q, Chen X-y, Jia X-b. A novel drug–phospholipid complex enriched with micelles: preparation and evaluation in vitro and in vivo. Int J Nanomedicine. 2013;8:545.
Munyendo WL, Zhang Z, Abbad S, Waddad AY, Lv H, Baraza LD, et al. Micelles of TPGS modified apigenin phospholipid complex for oral administration: preparation, in vitro and in vivo evaluation. J Biomed Nanotechnol. 2013;9(12):2034–47.
Jin X, Zhang Z-h, Sun E, Qian Q, X-b T, X-b J. Preparation of a nanoscale baohuoside I-phospholipid complex and determination of its absorption: in vivo and in vitro evaluations. Int J Nanomedicine. 2012;7:4907.
Beg S, Raza K, Kumar R, Chadha R, Katare O, Singh B. Improved intestinal lymphatic drug targeting via phospholipid complex-loaded nanolipospheres of rosuvastatin calcium. RSC Adv. 2016;6(10):8173–87.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Guest Editor: Sanyog Jain
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kuche, K., Bhargavi, N., Dora, C.P. et al. Drug-Phospholipid Complex—a Go Through Strategy for Enhanced Oral Bioavailability. AAPS PharmSciTech 20, 43 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1208/s12249-018-1252-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1208/s12249-018-1252-4