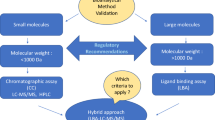
Abstract
The continued globalization of pharmaceutics has increased the demand for companies to know and understand the regulations that exist across the globe. One hurdle facing pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies developing new drug candidates is interpreting the current regulatory guidance documents and industry publications associated with bioanalytical method validation (BMV) from each of the different agencies throughout the world. The objective of this commentary is to provide our opinions on the best practices for reference standards and key reagents, such as metabolites and internal standards used in the support of regulated bioanalysis based on a review of current regulatory guidance documents and industry white papers for BMV.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Global Bioanalytical Consortium: http://www.globalbioanalysisconsortium.org/. Accessed 22 Oct 2013.
O’Hara D, Theobald V, Egan A, Usansky J, Krishna M, TerWee J, et al. “Ligand binding assays in the 21st century laboratory: recommendations for characterization and supply of critical reagents”. AAPS J. 2012;14(2):316–28.
Rup B, O’Hara D. Critical ligand binding reagent preparation/selection: when specificity depends on reagents. AAPS J. 2007;9(2):E148–55.
Nowatzke W, Woolf E. Best practices during bioanalytical method validation for the characterization of assay reagents and the evaluation of analyte stability in assay standards, quality controls, and study samples. AAPS J. 2007;9(2):E117–22.
O’Hara D, Theobald V. Life cycle management of critical ligand-binding reagents. Bioanalysis. 2013;5(21):2679–96.
Staack R, Stracke J, Stubenrauch K, Vogel R, Schleypen J, Papadimitriou A. Quality requirements for critical assay reagents used in bioanalysis of therapeutic proteins: what bioanalysts should know about their reagents. Bioanalysis. 2011;3(5):523–34.
Guidance for industry on bioanalytical method validation, US Department of Health and Human Services FDA (CDER) and (CVM) May 2001.
Guidance for the industry bioanalytical method validation, draft guidance, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Food and Drug Administration Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER) Center for Veterinary Medicine (CVM). September 2013 Biopharmaceutics Revision 1.
Guidance for industry safety testing of drug metabolites, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services Food and Drug Administration Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER), February 2008 Pharmacology and Toxicology.
EMA guideline for bioanalytical method validation, 21 July 2011, Effective 1 February 2012 EMEA/CHMP/EWP/192217/2009.
ANVISA, RDC no 27, May 27, 2012, Guideline for bioanalytical method validation, D.O.U. 22–05–2012–2012.
Draft guideline on bioanalytical method validation in pharmaceutical development, 15 April 2013, MHLW, Japan.
ICH Q2B; Text on validation of analytical procedures. Methodology, International Conference on Harmonization of Technical Requirements for the Registration of Drugs for Human Use, Geneva, Switzerland, March 1997.
Findlay JWA, Smith WC, Lee JW, Nordblom GD, Das I, DeSilva BS, et al. Validation of immunoassays for bioanalysis: a pharmaceutical industry perspective. J Pharmaceut BioMed Anal. 2000;21(6):1249–73.
DeSilva B, Smith W, Weiner R, Kelley M, Smolec J, Lee B, et al. Recommendations for the bioanalytical method validation of ligand-binding assays to support pharmacokinetic assessments of macromolecules. Pharm Res. 2003;20(11):1885–900.
Viswanathan CT, Bansal S, Booth B, DeStephano AJ, Rose MJ, Salistad J, et al. Quantitative bioanalytical methods validation and implementation: best practices for chromatographic and ligand binding assays. AAPS J. 2007;9(1):E30–42.
Lee JW, Devanararayan V, Barrett YC, Weiner R, Allinson J, Fountain S, et al. Fit-for purpose method development and validation for successful biomarker measurement. Pharm Res. 2006;23(2):312–28.
Chau C, Rixe O, McLeod H, et al. Validation of analytic methods for biomarkers used in drug development. Clin Cancer Tes. 2008;14:5967–76.
National Institute for Biological Standards and Controls: http://www.nibsc.org/products/reference_standards.aspx. Accessed 22 Oct 2013.
WHO International Biological Reference Preparations: http://www.who.int/biologicals/reference_preparations/. Accessed 22 Oct 2013.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Guest editors: Binodh DeSilva and Philip Timmerman
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bower, J.F., McClung, J.B., Watson, C. et al. Recommendations and Best Practices for Reference Standards and Reagents Used in Bioanalytical Method Validation. AAPS J 16, 352–356 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1208/s12248-014-9566-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1208/s12248-014-9566-y