Abstract
Background
Rheumatoid arthritis primarily affects the working-age population and may cause key functional and work limitations. As the disease progresses, individuals become increasingly unable to conduct daily activities, which has a substantial personal and socioeconomic impact. Fairly recent prior studies showed that patients with RA stop working 20 years earlier than age-matched controls. Factors related to sociodemographic, clinical, care and disease profiles might affect the loss of work capacity. The purpose of this study was to assess the factors associated with the prevalence of working patients with rheumatoid arthritis in the municipality of Blumenau.
Methods
A cross-sectional, population-based study was conducted between July 2014 and January 2015, with 296 individuals aged 20 years or older, male and female, living in Blumenau, Santa Catarina state, Brazil, and diagnosed with rheumatoid arthritis according to the 1987 American College of Rheumatology criteria. The prevalence of working patients with RA was assessed by employment status self-reporting during the interview. The chi-squared test, Wald test and Poisson regression analysis were used to test the possible associations between the independent variables and outcome.
Results
The prevalence of working patients with rheumatoid arthritis was 44.3%. Patients aged 20 to 59 years had a 90% higher prevalence of outcome than subjects aged 60 years or older. The prevalence of working patients was 132% and 73% higher among individuals with low income and high functional disability, measured using the Health Assessment Questionnaire (HAQ), respectively.
Conclusion
The prevalence of working RA patients was highest among adult patients with low income and high functional disability. The first variable is directly related to the individual characteristic, the second reflects the socioeconomic context of the patient, and the third reflects the degree of disability caused by the disease, which may be modifiable by health professionals.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic, autoimmune, and systemic inflammatory disease characterized by symmetrical synovitis of the peripheral joints. Inflammation of the synovial membranes causes pain, edema and stiffness and, if untreated, may lead to joint destruction and a loss of functional capacity [1, 2]. RA occurs in 0.24% to 1% of the population, predominantly among women between the fourth and sixth decades of life [3, 4]. According to a multicenter study, the prevalence of RA in Brazil is similar, ranging from 0.2 to 1% of the population [5].
RA primarily affects the working-age population and may cause key functional and work limitations [6]. As the disease progresses, individuals become increasingly unable to conduct daily activities, which has a substantial personal and socioeconomic impact [7, 8]. Studies report that 40% of patients with early-onset disease and 60% of patients with advanced disease were unable to work [9, 10].
Fairly recent prior studies showed that patients with RA stop working 20 years earlier than age-matched controls [11]. Researchers who conducted a study in Germany concluded that 59% of patients continued working until 12 months after diagnosis, whereas 17% stopped working and received disability payments, and 9% lost their jobs because of RA but received no disability pension [12]. Another study, conducted in the state of São Paulo, showed that 30% of patients were actually employed and that the others were homemakers, on leaves of absence or unemployed [13].
Factors related to sociodemographic, clinical, care and disease profiles might affect the loss of work capacity. Early diagnosis combined with disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) is the most effective method to reduce the prevalence of disability [13]. Other predictors, such as age, education level, the presence of comorbidities and the use of biopharmaceuticals may also be associated with disease progression [13, 14].
Studies on RA among working-age populations are increasingly conducted in developed countries. However, few studies considering this approach in Brazil were identified. Among them, a study conducted in the state of São Paulo determined that 30% of such patients were actively working, 34% were unemployed, 31% were retirees, and 5% were working retirees [15].
To collect additional data on this subject, the present study aimed to assess the percentage of and the possible factors associated with working patients with RA in Blumenau.
Methods
This cross-sectional, population-based study was conducted between July 2014 and January 2015, with 296 individuals aged 20 years or older, male and female, living in the municipality of Blumenau in the south region of Brazil and diagnosed with rheumatoid arthritis according to the 1987 American College of Rheumatology criteria. According to the United Nations Development Program (UNDP), this municipality had a Human Development Index (HDI) of 0.806 in 2010, ranking 25th among Brazilian municipalities [16]. The number of inhabitants in the study age group corresponded to 221,839 people, which is equivalent to 71.7% of the municipality population [17].
The formula for calculating the sample size required to estimate the prevalence of an event in a simple random sample was used considering the following parameters: 0.5% RA prevalence (1110 patients), 50% prevalence of exposure and unknown outcome, 5% sample error and 95% confidence level. The effective calculated sample size was 286 individuals. The participants were recruited from all primary care centers (Unidades Básicas de Saúde – UBS), the specialty outpatient clinic and the specialty pharmacy of the municipality.
Sample loss occurred when households were visited twice, once on the weekend and again in the evening, and no resident was at home, the resident had moved or refused to participate in the study on both occasions. The data collection team consisted of a local supervisor docent and 8 medical academics of the Regional University of Blumenau (Universidade Regional de Blumenau – FURB) previously trained to conduct structured interviews at home and, if necessary, by telephone. Quality control was performed in 20% of respondents, who were interviewed for the second time using a short questionnaire.
The dependent variable analyzed was the employment status at the time of the interview, considering the prevalence of working patients with RA, in any type of occupation, the outcome. Conversely, the independent variables were selected based on the sociodemographic, clinical, care and disease profiles. The following sociodemographic variables were analyzed: sex, age in completed years, ranging from 20 to 59 years for adults and 60 years or older for the elderly, in accordance with the status of the elderly/Ministry of Health (Ministério da Saúde – MS), current monthly personal income, ranging from 0 to 2 and greater than 2 minimum wages, education in years of completed study and self-reported skin color, categorized as white, brown, black, yellow or indigenous (IBGE). The clinical variable analyzed was the presence of comorbidities. The care variables analyzed were consultations with another rheumatologist during their treatment, number of consultations with a rheumatologist in the last 12 months, type of medical care classified into two groups, the Unified Health System (Sistema Único de Saúde – SUS; free, public healthcare system) and Public-Private Healthcare (supplementary healthcare system), defined according to the MS, in addition to private healthcare (fee-for-service care), and diagnostic delay in months, which was calculated by subtracting the date of the medical diagnosis by the date of the onset of symptoms. Lastly, the disease-related variables were total disease time in months, current use of DMARDs (methotrexate, sulfasalazine, leflunomide and antimalarial drugs), current use of anti-TNF immunobiologicals (adalimumab, etanercept, infliximab), Health Assessment Questionnaire (HAQ) score, ranging from 0 to 1 (mild disability) and from 1.1 to 3 (moderate and severe disability), presence of rheumatoid factor lower than or equal to 60 (negative or low titer) or higher than 60 (high titer) and, finally, the presence of radiographic changes (joint erosion) in the hands.
The data were entered into a system developed for this study in an Excel file format, and the final file was subsequently exported to the software Stata 10.0 (Stata Corporation, College Station, United States). The distribution of the variables of interest was analyzed using the mean, standard deviation and median for continuous variables, and the frequency and percentage for categorical variables. To test the association between the employment status and the independent variables, the chi-squared test and, where appropriate, the Wald test were used. Then, crude and Poisson regression analyses were performed to assess the association between the study factors and the dependent variables, estimating the crude and adjusted prevalence ratios (PRs), the respective 95% confidence intervals and the p value.
All variables with p value < 0.20 in the crude analysis were considered for entry into the final model. The variables that maintained a p value ≤0.05 or that fitted the final model remained in the adjusted regression model. The researchers chose to sequentially include sociodemographic, clinical, care and disease-related variables in the regression model.
This research study was submitted to the research ethics committees of the University of São Paulo (Universidade de São Paulo – USP) and of the FURB (protocol numbers 339/13 and 133/12, respectively) and approved; all participants signed the informed consent form.
Results
A total of 336 patients were identified. After excluding deceased patients and those who refused to participate in the study or patients without data for the dependent variable, 296 patients were included in the study. Those individuals who were unemployed, pensioners, housewives or regular or RA-unrelated disability retirees were excluded from the analysis of the dependent variable data, which resulted in an effective final sample of 185 patients (Fig. 1).
In the sociodemographic analysis, females (82.7%) and adults (71.9%) accounted for most individuals, with a mean age of 54.5 years, ranging from 26 to 79 years and with a standard deviation (SD) of 10.4. The mean income was 1.9 minimum wages (SD: 1.4). Approximately one-third of the subjects had education ranging from 0 to 4 years of completed study, with a mean education of 7.9 years (SD: 4.3). Regarding the care variables, the diagnostic delay was longer than or equal to 4 months in 74.1% of the sample and the mean diagnostic delay time was 27.6 months, ranging from 1 to 240 months (SD: 45). Most respondents stated that they visited another rheumatologist (72.4%), with a mean of 3.4 visits in the last 12 months (SD: 2.4). Regarding the type of care, private or public-private healthcare was predominant (55.9%). The analysis of the disease variables showed that most subjects had a disease time longer than or equal to 25 months (89.9%), with a mean of 127.8 months, ranging from 2 to 420 months (SD: 95.8; Table 1).
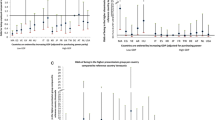
The crude analysis showed an increase in outcome with the decrease in age and among low-income individuals. The prevalence of working patients with RA was 64%, 37% and 66% higher among patients with up to 4 years of education, comorbidities and a higher HAQ score, respectively. Due to confounding between education and income in the adjusted analysis, the variables education and comorbidities lost significance and were excluded from the final model, which consisted of age, income and HAQ. The prevalence of working patients was 90% higher among adults than among the elderly. The prevalence of working patients was 132% higher among low-income individuals than among those earning more than 2 minimum wages. The prevalence of working patients was 73% higher among individuals with high functional disability, assessed using the HAQ (Table 2).
Discussion
The present study showed that job retention among RA patients in the city of Blumenau was 44.3%. Higher percentages of working RA patients were identified among low-income adult RA patients with high functional disability. The first variable is directly related to individual characteristics, the second reflects the socioeconomic context of the patient and the third reveals the degree of disability caused by RA.
Studies conducted in Germany and the Netherlands found 41% and 40% working RA patients, respectively [12, 18]. Furthermore, a systematic review of North American data found rates of working RA patients ranging from 22% to 76% [19]. Regarding the Brazilian data, a study conducted in Sorocaba found a prevalence of 46% working RA patients, similar to that found in the present study [20]. However, another study conducted in São Paulo found a 31% prevalence of such working patients, possibly due to different inclusion criteria and sampling and to the use of secondary data from medical records [13].
Age is a non-modifiable predictive factor of work disability. Our study confirmed this finding because the prevalence of working RA patients among elderly individuals was almost twice as high as that among adults. Synergistically, two systematic reviews of cohort studies on disability also reported the existence of this relationship [21, 22].
A study with 878 patients, conducted in the Netherlands, showed that a low socioeconomic status was related to worsened disease activity, physical and mental health and quality of life [23]. Similarly, a Latin American cohort with 1093 patients from 14 countries, including Brazil, concluded that low and middle incomes were associated with increased disease activity and higher HAQ scores [24]. Notably however, this association has not been consistently reported [25].
In contrast to the aforementioned findings, our study found a prevalence of working RA patients among low-income individuals who was 132% higher than that among individuals with a higher income. This finding suggests social inequality because the prevalence of working RA patients was expected to be higher among individuals with a higher income considering that higher income is usually associated with easier access to information, medical consultations and pharmacological treatments. This finding may be due to circumstances directly related to the individual, such as a lack of access to information, lack of knowledge of the right to disability retirement, limited legal expenses, lack of payment to social security and the need to work to avoid income loss.
Regarding the HAQ, the results showed that the prevalence of working RA patients was 73% higher among individuals with high disability than among individuals with a low HAQ score. This finding may be related to low-income patients with increased inflammatory activity of the disease and, therefore, increased disability [24]. Although this variable had a lower sample number than the others, an association with outcome was observed. An English study of two cohorts, totaling 244 patients, described HAQ as the most important factor of work disability [26].
Regarding education, the prevalence of working RA patients among the group with more than 4 years of study was 64% higher in the crude analysis; however, when subjected to adjusted analysis, the variable lost significance. Despite this result, a systematic review of studies on RA found a significant association between higher levels of education and the prevalence of working patients [21]. The same result was found regarding the presence of comorbidities, which was initially 37% higher among working RA patients, although the lack of a significant association was subsequently assessed. A Saudi study also found no significant association between the prevalence of working patients and the presence of comorbidities, although comorbidities were found in 95% of the subjects [27]. Conversely, a longitudinal study conducted in the United States with patients from the National Data Bank for Rheumatic Diseases, a national database for rheumatologic diseases, found progression of work disability, particularly in individuals with cardiovascular disease and a high number of comorbidities [28].
Regarding the sociodemographic profile variables, although sex and self-reported skin color were not significantly associated with the outcome (possibly due to the predominance of white over brown and black individuals in the sample), studies describing significant associations between these variables and the prevalence of working patients have been reported in the literature. A study showed that women had a higher risk for being out of the labor force, whereas men were more likely to continue working and to report negative workplace experiences [29].
Regarding the care variables, a Brazilian study showed that diagnostic delay may increase the prevalence of loss of work capacity and found a mean diagnostic delay of 39 months [20]. Although a lower mean diagnostic delay was found in our study (27.6 months), the importance of this variable for early treatment is noteworthy.
Regarding the disease variables, disease time is directly related to decreased prevalence of working RA patients. A cohort of Swedish patients with RA followed for 15 years showed that after 5, 10 and 15 years of disease, 65%, 61% and 56% of the individuals were actively working, respectively [30]. The lack of association and the decreased prevalence of outcome in our study may be related to the sample, which predominantly consisted of patients with established RA (> 2 years), to the mean disease time of approximately 10 years and to the fact that most subjects had higher levels of education.
Although the prevalence of working RA patients was not associated with the use of DMARDs or anti-TNF biologicals, several studies showing that these drugs may decrease the number of sick-leave days have been published [31,32,33]. The work capacity of patients may approximate that of healthy individuals during early treatment [34, 35].
The study limitations might include methodological differences caused by the lack of consistency in defining work disability [10], specific population characteristics, the very high HDI of the municipality of Blumenau (which differs from the rest of the country), the sample losses of some variables such as the HAQ score (which would likely be more significantly associated with the prevalence of working RA patients in a larger sample), possible memory biases of the respondents and reverse causation typical of cross-sectional studies.
The strengths of the study were the representative sample of the population of the municipality where the study was conducted (encompassing all social classes), the interviews conducted through pre-structured questionnaires by trained staff and the quality control of the interviews. The labor market context presumably had no effect on the results because the unemployment rate in Brazil in the study period ranged from 4.3% to 5.3%, in contrast to Blumenau, which had a 2% unemployment rate in 2014. Furthermore, the state of Santa Catarina had the lowest unemployment rate of all Brazilian states in 2015 (IBGE).
Conclusion
This study analyzed the prevalence of RA patients in the labor market in a southern region of Brazil. A higher prevalence of working RA patients was found among adult, low-income individuals with high functional disability. We suggest new population-based studies to improve the consistency of information on the employment status of patients with RA and to signal future budgetary impacts on social security.
Abbreviations
- DMARDs:
-
Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs
- FURB:
-
Regional University of Blumenau
- HAQ:
-
Health assessment questionnaire
- HDI:
-
Human development index
- MH:
-
Ministry of Health
- PR:
-
Prevalence ratios
- RA:
-
Rheumatoid arthritis
- SD :
-
Standard deviation
- SUS:
-
Unified Health System
- UBS:
-
Primary care centers
- UNPD:
-
United Nations Development Program
References
Cheung PP, Dougados M, Andre V, Balandraud N, Chales G, Chary-Valckenaere I, et al. Improving agreement in assessment of synovitis in rheumatoid arthritis. Jt Bone Spine. 2013;80(2):155–9.
Mota LMH, Laurindo IMM, Neto LL dos S, FAC L, Viana SL, Mendlovitz PS, et al. Diagnóstico por imagem da artrite reumatoide inicial. Rev Bras Reumatol. 2012;52(5):761–6.
Hoy D, March L, Brooks P, Blyth F, Woolf A, Bain C, et al. The global burden of rheumatoid arthritis: estimates from the global burden of disease 2010 study. Ann Rheum Dis. 2014;73(6):968–74.
Gabriel SE. The epidemiology of rheumatoid arthritis. Rheum Dis Clin N Am. 2001;27:269–81.
Marques WV, Cruz VA, Rego J, da Silva NA. Influência das comorbidades na capacidade funcional de pacientes com artrite reumatoide. Rev Bras Reumatol. 2015;56(1):14–21.
Schoels M, Wong J, Scott DL, Zink A, Richards P, Landewé R, et al. Economic aspects of treatment options in rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic literature review informing the EULAR recommendations for the management of rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2010;69(6):995–1003.
Kwoh CK, Simms RW, Anderson LG, Erlandson DM, Greene JM, Moncur C, et al. Guidelines for the management of rheumatoid arthritis: American College of Rheumatology ad hoc Committee on clinical guidelines. Arthritis Rheum. 1996;39(5):713–22.
Diretrizes P. Projeto Diretrizes Artrite Reumatóide : Diagnóstico e Tratamento Projeto Diretrizes; 2002. p. 1–15.
Han C, Smolen J, Kavanaugh A, St. Clair EW, Baker D, Bala M. Comparison of employability outcomes among patients with early or long-standing rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Care Res. 2008;59(4):510–4.
Verstappen SMM, Bijlsma JWJ, Verkleij H, Buskens E, Blaauw AAM, ter Borg EJ, et al. Overview of work disability in rheumatoid arthritis patients as observed in cross-sectional and longitudinal surveys. Arthritis Rheum 2004;51(3):488–497.
Woolf AD, Pfleger B. Burden of major musculoskeletal conditions. Bull World Health Organ. 2003;81(9):646–56.
Merkesdal S, Ruof J, Schffski O, Bernitt K, Zeidler H, Mau W. Indirect medical costs in early rheumatoid arthritis: composition of and changes in indirect costs within the first three years of disease. Arthritis Rheum. 2001;44(3):528–34.
Louzada P, Souza BDB, Toledo RA, Ciconelli RM. Análise descritiva das caracteríticas demográficas e clínicas de pacientes com artrite reumatóide no estado de São Paulo. Brazil Rev Bras Reumatol. 2007;47(2):84–90.
Vilsteren van M, Boot CR, Knol DL, van Schaardenburg D, Voskuyl AE, Steenbeek R, et al. Productivity at work and quality of life in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2015;16(1):107.
De Abreu MM, Kowalski SC, Ciconelli RM, Ferraz MB. Avaliação do perfil sociodemográfico, clínico-laboratorial e terapêutico dos pacientes com artrite reumatóide que participaram de projetos de pesquisa na Escola Paulista de Medicina, nos últimos 25 anos. Rev Bras Reumatol. 2006;46(2):103–9.
Programa das Nações Unidas - PNUD. Atlas do Desenvolvimento Humano no Brasil 2003. Available from: http://www.pnud.org.br/atlas. [Accessed in 21 Feb 2016].
Instituto Brasileiro de Geografia e Estatística-IBGE. Sinopse do Censo Demográfico de 2010/2011. Available from: http://www.ibge.gov.br/home/estatistica/populacao/censo2010/. [Accessed in 21 Feb 2016].
Young A, Dixey J, Kulinskaya E, Cox N, Davies P, Devlin J, et al. Which patients stop working because of rheumatoid arthritis? Results of five years’ follow up in 732 patients from the early RA study (ERAS). Ann Rheum Dis. 2002;61(4):335–40.
Cooper NJ. Economic burden of rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic review. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2000;39(1):28–33.
de Melo Jr VA, Aguiar FA, Baleroni TCG, Novaes GS. Análise temporal entre início dos sintomas, avaliação reumatológica e tratamento com drogas modificadoras de doença em pacientes com artrite reumatóide. Revista da Faculdade de Ciências Médicas de Sorocaba. 2008;10(2):12–5.
De Croon EM, Sluiter JK, Nijssen TF, Dijkmans BA, Lankhorst GJ, Frings-Dresen MH. Predictive factors of work disability in rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic literature review. Ann Rheum Dis. 2004;63:1362–7.
Detaille SI, Heerkens YF, Engels JA, van der Gulden JW, van Dijk FJ. Common prognostic factors of work disability among employees with a chronic somatic disease: a systematic review of cohort studies. Scand J Work Environ Health. 2009;35:261–81.
Jacobi CE, Mol GD, Boshuizen HC, Rupp I, Dinant HJ, Van Den Bos GAM. Impact of socioeconomic status on the course of rheumatoid arthritis and on related use of health care services. Arthritis Rheum. 2003;49(4):567–73.
Massardo L, Pons-Estel BA, Wojdyla D, Cardiel MH, Galarza-Maldonado CM, Sacnun MP, et al. Early rheumatoid arthritis in Latin America: low socioeconomic status related to high disease activity at baseline. Arthritis Care Res. 2012;64(8):1135–43.
Liao KP, Karlson EW. Classification and epidemiology of rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology. 2011;5:823–8.
Barrett EM, Scott DG, Wiles NJ, et al. The impact of rheumatoid arthritis on employment status in the early years of disease: a UK community-based study. Rheumatology. 2000;39:1403–9.
Janoudi N, Almoallim H, Husien W, Noorwali A, Ibrahim A. Work ability and work disability evaluation in Saudi patients with rheumatoid arthritis: special emphasis on work ability among housewives. Saudi Med J. 2013;34(11):1167–72.
Michaud K, Wallenstein G, Wolfe F. Treatment and nontreatment predictors of health assessment questionnaire disability progression in rheumatoid arthritis: a longitudinal study of 18,485 patients. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2011;63(3):366–72.
Kaptein SA, Gignac MA, Badley EM. Differences in the workforce experiences of women and men with arthritis disability: a population health perspective. Arthritis Rheum. 2009;61:605–13.
Eberhardt K, Larsson BM, Nived K, Lindqvist E. Work disability in rheumatoid arthritis--development over 15 years and evaluation of predictive factors over time. J Rheumatol. 2007;34:481–7.
Augustsson J, Neovius M, Cullinane-Carli C, et al. Patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with tumour necrosis factor antagonists increase their participation in the workforce: potential for significant long-term indirect cost gains (data from a population-based registry). Ann Rheum Dis. 2010;69:126–31.
Sokka T. Work disability in early rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2003;21:S71–4.
Puolakka K, Kautiainen H, Möttönen T, Hannonen P, Korpela M, Julkunen H, et al. Impact of initial aggressive drug treatment with a combination of disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs on the development of work disability in early rheumatoid arthritis: a five-year randomized followup trial. Arthritis Rheumatism. 2004;50:55–62.
Tiippana-Kinnunen T, Paimela L, Peltomaa R, Kautiainen H, Laasonen L, Leirisalo-Repo M. Work disability in Finnish patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a 15-year follow-up. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2014;32:88–94.
Puolakka K, Kautiainen H, Mattonen T. Predictors of productivity loss in early rheumatoid arthritis: a year follow up study. Ann Rheum Dis. 2005;64:130–3.
Availability of data and materials
All data generated and analysed during this article are part of the project: Cohort study of patients with rheumatoid arthritis of the municipality of Blumenau.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
RKSG and MRCN contributed to elaboration, literature review, statistical analysis and article writing. LCS, MOV and PHM contributed to writing and literature review. All approved final version for submission in journal.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Submitted to the research ethics committee of the University of São Paulo (USP) and Blumenau Regional University Foundation (FURB) (protocol n°.339 / 13 and 133/12, respectively).
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
About this article
Cite this article
Gomes, R.K.S., Schreiner, L.C., Vieira, M.O. et al. Staying in the labor force among patients with rheumatoid arthritis and associated factors in Southern Brazil. Adv Rheumatol 58, 14 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1186/s42358-018-0009-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s42358-018-0009-9