Abstract
A 59 year old patient was referred to our department to detect disease activity related to clinical symptoms of tiredness, weight loss and an elevated serum serotonine, suspicious of a neuro-endocrine tumour. A 18F-fluoro-l-dihydroxy-phenylalanine (FDOPA) PET/CT scan was performed, which showed focally increased uptake in the terminal ileum and in a mesenterial lymph node. Additionally, an area of intense uptake was observed intracranially. Histological analysis confirmed the presence of a WHO grade I meningioma. Few cases of FDOPA PET uptake in meningiomas have been published, underlining it is as a rare finding. Awareness of this potential finding is crucial to avoid misinterpretation as intracerebral metastasis.
Similar content being viewed by others
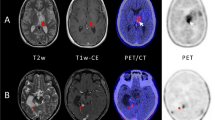
A 59 year old patient was referred to our department to detect disease activity related to clinical symptoms of tiredness, weight loss and an elevated serum serotonine, suspicious of a neuro-endocrine tumour. A 18F-fluoro-l-dihydroxy-phenylalanine (FDOPA) PET/CT scan was performed, which showed focally increased uptake in the terminal ileum and in a mesenterial lymph node (Fig. 1). Additionally, an area of intense uptake was observed intracranially (Fig. 2a, left frontal region). The atypical location of the uptake suggested the presence of a mengioma (Fig. 2b). Based on this PET finding, MRI was performed (2C), which showed an extra-axial mass with extensive contrast enhancement on T1 weighted imaging and a ‘dural tail’, typical of meningioma. Additional findings on MRI were midline shift and edema. Histological analysis confirmed the presence of a WHO grade I meningioma.
After oral administration of 75 mg carbidopa, 300 MBq of 18F-FDOPA was injected intravenously. Images were acquired 60 min after injection on a 64-slice PET/CT camera (mCT Biograph, Siemens Medical Solutions, Knoxville, TN USA,) whole body. Increased uptake was noted in the terminal ileum (left arrow) and in the mesentery (right arrow), as shown in figure 1a (CT only) and 1b (fused PET/CT images)
FDOPA PET has been used in the evaluation of brain tumours, among other PET techniques using amino acid tracers such as 11C-methionine and -(2-[18F]fluoroethyl)-l-tyrosine (FET) (Becherer et al. 2003; Fueger et al. 2010; Schiepers et al. 2007). The increased uptake of FDOPA is related to the L amino acid transporter (LAT). The LAT facilitates amino acid transport in tumour cells, which in turn use it for protein synthesis. In meningiomas, high LAT1 expression has been described (Zitron et al. 2013). Consequently, increased uptake of FDOPA may be observed in these tumours. In addition, increased uptake of other amino acid PET tracers in meningiomas has been described, including a series of 10 meningiomas which showed increased uptake of -[11C]methyl-L-tryptophan (AMT) (Zitron et al. 2013). as well as of somatostatin radiolabelled analogs (Soto-Montenegro et al. 2014).
Conclusions
Few cases of FDOPA PET uptake in meningiomas have been published (Calabria et al. 2016), underlining it is as a rare finding. Awareness of this potential finding is crucial to avoid misinterpretation as intracerebral metastasis.
Abbreviations
- AMT:
-
Methyl-L-tryptophan
- FDOPA:
-
Fluoro-l-dihydroxy-phenylalanine
- FET:
-
Fluoroethyl)-l-tyrosine
- LAT:
-
L amino acid transporter
References
Becherer A, Karanikas G, Szabo M, Zettinig G, Asenbaum S, Marosi C et al (2003) Brain tumour imaging with PET: a comparison between [18F]fluorodopa and [11C]methionine. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 30(11):1561–1567
Calabria FF, Chiaravalloti A, Calabria EN, Grillea G, Schillaci O (2016) 18F-DOPA PET/CT and MRI findings in a patient with multiple Meningiomas. Clin Nucl Med 41(8):636–637
Fueger BJ, Czernin J, Cloughesy T, Silverman DH, Geist CL, Walter MA et al (2010) Correlation of 6-18F-fluoro-L-dopa PET uptake with proliferation and tumor grade in newly diagnosed and recurrent gliomas. J Nucl Med 51(10):1532–1538
Schiepers C, Chen W, Cloughesy T, Dahlbom M, Huang SC (2007) 18F-FDOPA kinetics in brain tumors. J Nucl Med 48(10):1651–1661
Soto-Montenegro ML, Pena-Zalbidea S, Mateos-Perez JM, Oteo M, Romero E, Morcillo MA et al (2014) Meningiomas: a comparative study of 68Ga-DOTATOC, 68Ga-DOTANOC and 68Ga-DOTATATE for molecular imaging in mice. PLoS One 9(11):e111624
Zitron IM, Kamson DO, Kiousis S, Juhasz C, Mittal S (2013) In vivo metabolism of tryptophan in meningiomas is mediated by indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1. Cancer Biol Ther 14(4):333–339
Acknowledgments
The publication of this article was supported by funds of the European Association of Nuclear Medicine (EANM).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
GNS: writing of the manuscript, lay-out, images. AWJMG, RHJAS, RAJOD: review of the article, providing comments. All authors read and approved the final mansucript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
About this article
Cite this article
Stormezand, G.N., Glaudemans, A.W.J.M., Slart, R.H.J.A. et al. Incidental meningioma detected with [18F]-FDOPA PET/CT. European J Hybrid Imaging 2, 23 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1186/s41824-018-0041-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s41824-018-0041-3