Abstract
Background
Undernutrition is a major public health issue highlighted by the 2015 Sustainable Development Goals, with target 2.2 aiming to ‘end hunger’ by 2030. On-going surveillance is essential detecting nutritional stress in a population and is key to planning consequent interventions. Whilst methodologies of nutritional surveillance systems vary across different settings, organisations and even within the same country, the direct evidence-base underpinning these practices is limited. This paper aims therefore to: 1) compare the performance of different anthropometric indices/measurements for detecting change in the nutritional situation at population level; 2) discuss their properties and appropriateness for use in a surveillance system.
Methods
This systematic literature review considered peer-reviewed and grey literature. Evidence was compiled from standard electronic databases, websites and snowballing. The search was performed in November 2015 by a single reviewer using the following terms to capture two concepts: 1) Undernutrition and 2) Nutrition surveillance. The search was limited to children under five and the period considered started in 1980. Languages included English and French. Articles had to assess whether the changes or trend observed at population level were statistically significant. All study designs were included.
Results
A total of 4563 articles were retrieved from the electronic database search. Most articles (3137, 89%) were not directly relevant based on title and abstract; 39 articles were reviewed in full. A total of 17 articles met the inclusion criteria and an additional 4 papers were added after snowballing. A number of measures and indices such as weight, weight-for-height/length, triceps skinfold and middle-upper arm circumference performed well in the detection of short term changes in the nutritional situation of a population. Height/Length-for-age responded the most to long term change. Applying a standard set of criteria (simplicity, acceptability, cost, independence of age, reliability and accuracy) to determine which is the most appropriate measure or index identified middle-upper arm circumference as the one with the greatest net benefits.
Conclusions
Limited available evidence suggests that mid-upper arm circumference is the best measure to detect short term changes in the nutritional state of a population: this should receive higher priority in surveillance systems.
Similar content being viewed by others
Background
Undernutrition is a major public health issue highlighted by the 2015 Sustainable Development Goals, target 2.2 aspiring to end hunger by 2030 [1]. United Nations Children's Emergency Fund’s (UNICEF) latest report on the State of the World’s Children [2] estimates that nearly half of all deaths in children under five are attributable to under-nutrition: this translates into the about three million young lives a year.
On-going surveillance is essential detecting nutritional stress in a population, whether caused by natural or conflict related hazards. It is key to the planning of interventions. It provides information on trends and allows interpretation of malnutrition prevalence as compared to expected seasonal changes, i.e. what is normal for that population at that time of the year, and/or, in the absence of baseline data, to determine arbitrary benchmarks for gravity of the nutritional situation [3–5].
Methodologies used by nutritional surveillance systems vary across different settings, organisations and even within the same country [6, 7]. They usually rely on repeated cross-sectional anthropometric surveys [8–10]. They can also use clinic-based monitoring or sentinel sites selected to represent a particular population with specific livelihood systems or areas where the population is most at risk [10]. Common national surveys include government led Demographic and Health Surveys (DHS) and UNICEF’s Multiple Indicator Cluster Surveys (MICS) that are conducted in approximately 100 countries every three to ten years [11, 12]. Many organizations also routinely use the Standardized Monitoring and Assessment of Relief and Transitions (SMART) methodology to conduct surveys at camp, district, regional or national level [13].
Children under five years are more at risk of malnutrition and more vulnerable to external shocks. It is therefore common practice to use the nutritional status of the under-5-years population to draw conclusions about the situation of the whole population [14]. Commonly used anthropometric indices or measurements for nutrition surveillance are: weight-for-height/length (WFH/L) (wasting); Mid-Upper Arm Circumference (MUAC) (acute malnutrition); Oedema (Oedematous malnutrition, also known as kwashiorkor); height/length-for-age (L/HFA) (stunting) and weight-for-age (WFA) (underweight) (Table 1). Other less common indices or measurements include weight, height, birth weight, MUAC-for-Age, triceps skinfold thickness (TSF), TSF-for-Age, subscapular skinfold (SSF), head circumference and Muscular Circumference (MC) (MC = MUAC-π x TSF). To calculate nutritional indices, e.g. WFH/L, L/HFA and WFA, child’s anthropometric measurements are compared to a well-fed, healthy reference population (main ones being the Harvard Growth curves in the 60s, the National Centre for Health Statistics (NCHS) reference distribution from 1978, the 2000 US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) growth charts and the World Health Organisation (WHO) standards from 2006). The child’s measurement deviation from the central values of this distribution, as percentage of the reference median or standard deviations (SD or Z-scores) below or above the reference mean have been used as estimates of anthropometric status. Measurements are then used directly or are compared to a specific threshold (e.g. MUAC < 115 mm is used to diagnose severe acute malnutrition). Table one presents the most commonly used measurement and indices in children under five.
Nutritional surveillance generally measures point estimates/prevalence or incidence of malnutrition. However, treating nutritional indices as continuous variables can also give very useful information on trends and gravity levels; for example, a decrease in the mean and distribution of WFH, MUAC or weight has been recognised as a sign of a worsening nutritional situation [15–17].
Though they are commonly used, there is a very limited direct evidence-based exploring the usefulness of the different indices at detecting change in nutritional status of a population. This review aims to 1) compare the performance of the different anthropometric indices/measurements in the detection of change in the nutritional situation at population level (long term i.e. over a year and short term i.e. few months/season) and 2) discuss their properties and appropriateness for use in a surveillance system.
Methods
This systematic literature review considered peer-reviewed and grey literature. Evidence was compiled from standard electronic databases, websites and snowballing (reference list from relevant primary studies and review articles).
Exclusion criteria
The search excluded paper on adults and adolescents and was limited to children under five. Articles prior to 1980 were not considered. Languages included English and French. Articles had to assess whether the changes or trend observed at population level were statistically significant. All study designs were included.
Search strategy
The peer-reviewed literature search was conducted using Embase, Global Health and Medline. The search was performed in November 2015 by a single reviewer using the following terms to capture two concepts: 1) Undernutrition: ((arm or midarm or mid-arm or mid-upper arm) and circumference) or MUAC or weight-for-height or weight-for-length or WHZ or WHM or weight- for- age or WAZ or height- for-age or length-for-age or HAZ or kwashiorkor or oedema or WAM or HAM or weight or height or anthropometry or anthropometric indices or anthropometric indicators or stunting or wasting or acute malnutrition or marasmus or underweight AND 2) Nutrition surveillance: Nutrition$ assessment or nutrition$ survey or nutrition$ surveillance or nutrition$ situation or malnutrition prevalence or nutrition$ monitoring or nutrition$ screening or nutrition$ evaluation or nutrition$ early warning system or nutrition$ change or nutrition$ variation or nutrition$ impact or season$ change or season$ variation.
Grey literature undertaken by searching the following websites: Emergency Nutrition Network (ENN), The United Nations System Standing Committee on Nutrition and the Community-based Management of Acute Malnutrition (CMAM) forum [18–20].
Data extraction, analysis and reporting
Returned citations were downloaded to Endnote software and a five-stage screening process applied (see Fig. 1). Articles that met the inclusion criteria were selected and data abstracted in an excel sheet. The following data were extracted from each paper: i) study authors, ii) year; iii) study country and collection period, iv) setting, (v) type of study, vi) sample size, vii) age group, viii) independent variables, ix) dependent variables, x) reference and unit, xi) outcome of the study. The outcome of the study included prevalence, means and Odd Ratios (OR) with associated p-values. Descriptive analysis was used and the systematic review methodology adheres to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) statement [21]. We did not register the review protocol and this review does not include a bias analysis. Papers included were too different to be able to do a synthesis and very few of them had as objective to assess performance of different anthropometric measurements or indices in the detection of change in the nutritional status of the study population.
Results
Performance of nutritional measurement/indices to detect changes in nutritional situations
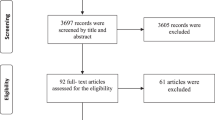
A total of 4563 articles were retrieved from the electronic database search (1837 articles from Embase, 1102 from articles Global Health and 1624 articles from Medline) out of which 1033 duplicates were excluded leaving 3530 articles to review. A large majority of articles (3137, 89%) were found out of topic and 39 articles were left for full review. A total of 17 articles met the inclusion criteria. All potential articles found in the grey literature had been published and therefore included in the above search. An additional 4 papers were added after snowballing. A total of 21 articles were included in this review. Figure 1 flow diagram summarises the search.
Over half of the articles included were published in the 2000s (12, 57%), a fifth (4, 19%) in the 90s and a quarter (5, 24%) in the 80s which translates recent interest in the topic. Although the African continent is overrepresented (52% of studies), we believe this does not affect the generalisability of the findings as we are interested in the capacity to detect change within the same population. Most studies were conducted in rural areas (15, 71%) while few were implemented in urban (3, 14%) or both urban and rural (3, 14%) settings. Different types of design were used to conduct the studies included which made it difficult to compare outcomes. Longitudinal (9, 43%) and repeated cross sectional studies (7, 33%) were the predominant types. Most studies examined the effect of seasonality on malnutrition (17, 80%). Different sets and numbers of dependent variable as well as different references and types of analysis were used which made comparison and generalisations difficult. The main dependent variable analysed was weight-for-height/length (18, 86%) followed by weight-for-age (13, 62%), height/length-for-Age (13, 62%) and mid-upper arm circumference (6, 29%). Most studies included three or more dependent variables. Half (10, 50%) of the analysis treated dependent variables as continuous (mean) and binary (prevalence). Just over half of the analyses (11, 55%) used the NCHS reference and Z-score was the most common unit (14, 67%) (Table 2). The detailed characteristics of each study can be found in the extraction sheet Table 3.
Table 4 presents the summary of the study outcome for each measurement/index. Means and/or prevalence of the measurement and/or indices examined in the 21 papers generally varied significantly between seasons or before/after external hazards. Few studies showed no or few differences. Egata et al. [22] showed no difference in mean WFH and mean MUAC. They argued that good food security was common regardless of the seasonal variation. Huong et al. [23] found no change in weight, height, WFA, H/LFA and WFH/L but the small sample sizes (around 200 children 24 to 59 months) involved as well as the design of the study (repeated cross sectional studies) were not ideal to detect differences. Loutan et al. [24] showed no differences in WFH and MUAC but had a very small sample size (around 30 children under five years).
Out of the 21 studies included, 4 (19%) compared the change in mean and/or prevalence of several measurements/indices. Benefice et al. [25] presented variations of mean MUAC, WFH, TSF and MC in a longitudinal study in rural Senegal. Mean WFH/L was the only index that was not changing significantly and TSF showed the largest differences. Briend et al. [15] examined the effect of seasonal change as well as the change between the first two years of the study and the last two on weight, WFA, H/LFA, WFH/L, and MUAC. This study revealed that Weight, MUAC and WFH were the nutritional indices that changed the most between seasons. Mean H/LFA, WFA and MUAC were significantly higher during last 2 years. This was more pronounced for HFA. In a study assessing the fluctuations of the mean weight, height increment, WFA, HFA, WFH, MUAC-for-Age and TSF-for-Age, Brown et al. [26] found that TSF-for-Age had the greatest seasonal change. WFA and MUAC-for-Age followed the same patterns and magnitude while WFH had greater range but similar coefficient of variation as MUAC and smaller than WFA. Finally, Garenne et al. [27] study looked at seasonal changes of mean WFA, WFH, MUAC, TSF, weight, height, BMI, MC, SSF and HC. The highest contrast value was observed for mean MUAC which made it the best measurement for the detection of short term changes. Mean weight, height and head circumference had the highest responsiveness. Responsiveness was defined as a measure of the change over a semester compared with the variation of the indicator in the population (change divided by the standard deviation of the same indicator). These indices were the most appropriate to monitor growth velocity of children in a stable situation (Table 4).
Unsurprisingly, H/LFA was mainly out of phase compared to other measures of undernutrition and was a good measure of long term change (Briend et al. [15], Brown et al. [26], Huong et al. [23], Marin et al. [28], Martin-Prevel et al. [29], Miller et al. [30], Panter-Brick et al. [31]) (Table 4).
The capacity to detect change in the nutritional status of the population did not seem to differ whether the anthropometric measurements/indices were treated as continuous or binary. However, the sample size requirement differs whether assessing the mean of a continuous variable or looking at the prevalence of a binary variable. Using means allows for smaller sample size which has important implications in terms of logistics, costs and timeliness. This was confirmed in Briend et al. [15] paper.
Discussion
This literature review shows that short term changes in the nutritional status of a population can be detected using weight, WFH/L, MUAC or TSF while H/LFA is a good measure of long term change. In addition to its responsiveness to nutritional stress, a number of important criteria need to be taken into account to identify the most appropriate and relevant measure or index to be used to detect changes: simplicity, acceptability, cost, independence of age, reliability and accuracy, sensitivity and specificity [32].
Simplicity
Any index that includes an age component requires that age be ascertained accurately and it is widely acknowledged that determining age correctly is problematic in many developing countries [33–36]. The use of multi-component indices (i.e. WFA, HFA, WFH, MUAC-for-Age, TSF-for-Age) is usually more complex [33, 37]. Moreover, transporting and carrying weight scales as well as height/length board is more logistically challenging than for MUAC tapes.
Acceptability
The measurement of weight, height and MUAC is widely accepted and commonly performed in nutrition surveillance and interventions. A study reported that younger children tended to become upset and agitated during both weight and height measurement but not during MUAC measurement [37]. TSF index is not currently used for surveillance or programming and would probably not be as acceptable as the measures above as it requires the measurement of the width of a fold of skin taken over the triceps muscle using a skinfold caliper.
Cost
The measurement of height and weight requires fairly costly equipment [37–39] while the MUAC tool – a tape measure – is cheap and easy to transport. A caliper is also relatively costly and may be harder to procure.
Independence of age
One way to ascertain age-independence is to adjust indices for age (i.e. WFA, HFA, MUAC-for-Age) but the issue of the accuracy of age remains. MUAC is relatively age and sex independent among 1–5 year olds [32, 37, 40–43] as well as WFH [39, 44]. It was also shown that MUAC alone, without correction for age, was a better predictor of death than indices based on height, weight and age [41–43, 45].
Reliability and accuracy
Although weight and height alone were shown to be more precisely measured [46–49], it was reported that MUAC has a better reliability than WFH and shows better performance in screening programmes [50]. It was also shown that in field conditions, minimally trained workers make fewer and smaller errors in screening children with MUAC than with WFH [37]. Indices usually require finding values in tally sheets or calculations that can lead to further errors. A recent paper shows that MUAC is more reliable than WFH [51] and another that MUAC outperforms weight-based measures of nutritional status in children with diarrhoea [52]. It was also shown to be less affected by dehydration than WFH [53]. As mentioned above, any index requiring the age (i.e. WFA or HFA) of the child is likely to be less accurate.
Sensitivity and specificity (to mortality)
MUAC is increasingly recognised as a very useful index of nutritional status [50]. There is a consensus that MUAC is a better predictor of mortality than WFH [40, 45, 54–60] and it was recently reported that using MUAC alone is preferable for identifying high-risk malnourished children [61].
Table 5 summarises the characteristics of all relevant measures and indices reviewed. We focus on measures and indices that are currently in use in nutrition programming and nutrition surveillance (i.e. we did not discuss TSF, TSF-for-Age, MUAC-for-Age, MC, birth weight). Table 5 highlights the advantages of using MUAC over other measures or indices detecting short term changes.
These findings are consistent with the increasing interest in MUAC-only nutrition programming and use for admission and discharge to feeding programmes [62–66]. This concordance makes the findings of this review applicable and of interest to international policy makers and programme managers.
Limitations
We acknowledge the limitations to our review, the most important being:
-
1)
Great heterogeneity (population; setting; study design; methods; time periods; primary research question) between the studies found: this makes it difficult to carry out any quantitative analysis/meta-analysis to compare the performance of different measures and indices
-
2)
A single reviewer performed the search which may have lead to errors or omissions
-
3)
Publication bias: studies that were unable to assess changes or trends at population level are less likely to be published
-
4)
The observational nature of the studies: it is not possible to directly ‘test’ the performance of one indicator against another in an interventional study
-
5)
There is no gold standard measure of population nutritional status. Where no change is observed, we cannot know whether there really was no change in the population or whether a real change was simply not detected by indices used (i.e. not sensitive enough)
-
6)
We did not look at over-nutrition. MUAC might not be the best index when measuring obesity, an increasing problem even in resource poor settings [67].
Strengths
Balancing these limitations, a major strength of our review is that we explore a highly policy/practice-relevant question using a systematic approach. By highlighting the overall limited evidence base we hope to stimulate both more and better-quality future research in this area. We also provide a framework whereby policy makers and managers can think about the different aspects of indicator performance: different indicators may suit different questions and in choosing which is ‘best’ it is vital to consider context. Different aspects of malnutrition may be better monitored by different sets of indictors such as in DHS or MICS. The measurement or index to use also depends on the nature and intensity of the crises. In some crises where diets might still be sufficient to maintain weight but have lost adequacy in micronutrient, the change in stunting might be significant but not in wasting. This has been the case in recent conflicts [68]. Finally, we highlight an indicator – MUAC - that is still missing from many major surveys such as DHS. This is an important gap given MUAC’s good performance for detecting short term changes in population nutritional status. This has major implications for early warning systems or other assessments systems which only allow for limited field data collection because of time or budget constraints.
Future research should look at cost-effectiveness and logistics issues of different systems as this is critical to successful and sustained large-scale rollout of any system. Especially with the large number of sustainable development goals, there is increasing pressure to make efficient use of resources.
Conclusions
A number of measures and indices such as weight, WFH, TSF and MUAC perform well in the detection of short term changes in the nutritional situation of a population. However, after applying a set of criteria which are critical to successful large-scale rollout (simplicity; acceptability; cost; independence of age; reliability; and accuracy) MUAC stands out strongly as the best measure to use in nutritional surveillance systems to detect short term changes in the nutritional status of a population.
Abbreviations
- CDC:
-
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
- CMAM:
-
Community-based Management of Acute Malnutrition
- DHS:
-
Demographic and Health Surveys
- ENN:
-
Emergency Nutrition Network
- FSNAU:
-
Food Security and Nutrition Analysis Unit
- H/LFA:
-
Height/Length-For-Age
- MUAC:
-
Middle-Upper Arm Circumference
- MICS:
-
Multiple Indicator Cluster Surveys
- NCHS:
-
National Centre for Health Statistics
- SMART:
-
Standardized Monitoring and Assessment of Relief and Transitions
- SSF:
-
Subscapular Skinfold
- TSF:
-
Triceps SkinFold
- UNICEF:
-
United Nations Children's Fund’s
- WFA:
-
Weight-For-Age
- WFH/L:
-
Weight-For-Height/Length
- WHO:
-
World Health Organization
References
Sustainable Development Goals [08/08/2016]. Available from: https://sustainabledevelopment.un.org/
The State of the World’s Children [Internet]. UNICEF. 2015 [cited 07/11/2016]. Available from: http://www.unicef.org/sowc2016/.
The Integrated Food Security Phase Classification (IPC) [03/03/2016]. Available from: http://www.ipcinfo.org.
WHO. Physical status: the use and interpretation of anthropometry. Report of a WHO Expert Committee [Technical Report] 1995.
Tuffrey V, Hall A. Methods of nutrition surveillance in low-income countries. Emerg Themes Epidemiol. 2016;13:4.
Busili A, J. Frize, and J. Shoham. A Review of Nutrition Information Systems in Kenya. Save the Children UK, 2004.
Darcy JaCH. According to need? Needs assessment and decision-making in the humanitarian sector. 2003 September 2003. Report No.
Young H, Borrel A, Holland D, Salama P. Public nutrition in complex emergencies. Lancet. 2004;364(9448):1899–909.
Young HJ, S. The meaning and measurement of acute malnutrition in emergencies: a primer for decision-makers. Humanitarian Practices Network. 2006; 56
Shoham J, Watson F, Dolan C. The use of Nutritional Indicators in Surveillance Systems. International Public Nutrition Resource Group. 2001
The Demographic and Health Surveys Program (The DHS Program). Available from: http://www.dhsprogram.com/(accessed 12 Nov 2014).
UNICEF. Multiple Indicator Cluster Survey (MICS) http://www.unicef.org/statistics/index_24302.html (accessed 12 Nov 2014).
SMART. Measuring Mortality, Nutritional Status, and Food Security in Crisis Situations: SMART methodology2006.
WFP, CDC. A Manual: Measuring and Interpreting Malnutrition and Mortality. 2005
Briend A, Hasan KZ, Aziz KM, Hoque BA, Henry FJ. Measuring change in nutritional status: a comparison of different anthropometric indices and the sample sizes required. Eur J Clin Nutr. 1989;43(11):769–78.
Myatt M, Duffield A. Weight-for-height and MUAC for estimating the prevalence of acute malnutrition. Global nutrition cluster meeting report: IASC Global Nutrition Cluster, 2007
Mude ABC, McPeak JG, Kaitho R, Kristjanson P. Empirical forecasting of slow-onset disasters for improved emergency response: an application to Kenya’s arid north. Food Policy. 2009;34(4):329–39.
Emergency Nutrition Network (ENN). Available from: http://www.ennonline.net/
United Nation Systems Standing Committee on Nutrition (UNSCN). Available from: http://www.unscn.org/.
Community-based Management of Acute Malnutrition (CMAM) forum. Available from: http://www.cmamforum.org/.
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman D. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. BMJ (Online). 2009;339(7716):332–6.
Egata G, Berhane Y, Worku A. Seasonal variation in the prevalence of acute undernutrition among children under five years of age in east rural Ethiopia: a longitudinal study. BMC Public Health. 2013;13:864.
le Huong T, le Xuan TT, le Phuong H, Huyen DT, Rocklov J. Diet and nutritional status among children 24–59 months by seasons in a mountainous area of Northern Vietnam in 2012. Glob Health Action. 2014;7:23121.
Loutan L, Lamotte JM. Seasonal variations in nutrition among a group of nomadic pastoralists in Niger. Lancet. 1984;1(8383):945–7.
Benefice E, Chevassus-Agnes S, Barral H. Nutritional situation and seasonal variations for pastoralist populations of the Sahel. Ecol Food Nutr. 1984;14:229–47.
Brown KH, Black RE, Becker S. Seasonal changes in nutritional status and the prevalence of malnutrition in a longitudinal study of young children in rural Bangladesh. Am J Clin Nutr. 1982;36(2):303–13.
Garenne M, Maire B, Fontaine O, Briend A. Adequacy of child anthropometric indicators for measuring nutritional stress at population level: a study from Niakhar, Senegal. Public Health Nutrition. 2012:1–7
Marin CM, Segura JL, Bern C, Freedman DS, Lescano AG, Benavente LE, et al. Seasonal change in nutritional status among young children in an urban shanty town in Peru. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1996;90(4):442–5.
Martin-Prevel Y, Delpeuch F, Traissac P, Massamba JP, Adoua-Oyila G, Coudert K, et al. Deterioration in the nutritional status of young children and their mothers in Brazzaville, Congo, following the 1994 devaluation of the CFA franc. Bull World Health Organ. 2000;78(1):108–18.
Miller J, Ritchie B, Cuong T, Beggs S, Lada CO, Whetter K, et al. Seasonal variation in the nutritional status of children aged 6 to 60 months in a resettlement village in West Timor. Asia Pac J Clin Nutr. 2013;22(3):449–56.
Panter-Brick C. Seasonal growth patterns in rural Nepali children. Ann Hum Biol. 1997;24(1):1–18.
Myatt M, Khara T, Collins S. A review of methods to detect cases of severely malnourished children in the community for their admission into community-based therapeutic care programs. Food Nutr Bull. 2006;27(3 Suppl):S7–23.
Hamer C, Kvatum K, Jeffries D, Allen S. Detection of severe protein-energy malnutrition by nurses in The Gambia. Arch Dis Child. 2004;89(2):181–4.
Jelliffe EFPJD. The arm circumference as a public health index of protein-calorie malnutrition of early childhood. J Trop Pediatr. 1969;15(4):177–260.
Bairagi R, Ahsan RI. Inconsistencies in the findings of child nutrition surveys in Bangladesh. Am J Clin Nutr. 1998;68(6):1267–71.
Bairagi R, Edmonston B, Khan AD. Effects of age misstatement on the utility of age-dependent anthropometric indicators of nutritional status in rural Bangladesh. Am J Public Health. 1987;77(3):280–2.
Velzeboer MI, Selwyn BJ, Sargent 2nd F, Pollitt E, Delgado H. The use of arm circumference in simplified screening for acute malnutrition by minimally trained health workers. J Trop Pediatr. 1983;29(3):159–66.
Davis LE. Epidemiology of famine in the Nigerian crisis: rapid evaluation of malnutrition by height and arm circumference in large populations. Am J Clin Nutr. 1971;24(3):358–64.
Ross DA, Taylor N, Hayes R, McLean M. Measuring malnutrition in famines: are weight-for-height and arm circumference interchangeable? Int J Epidemiol. 1990;19(3):636–45.
Alam N, Wojtyniak B, Rahaman MM. Anthropometric indicators and risk of death. Am J Clin Nutr. 1989;49(5):884–8.
Bairagi R. On validity of some anthropometric indicators as predictors of mortality. Am J Clin Nutr. 1981;34(11):2592–4.
Briend A, Zimicki S. Validation of arm circumference as an indicator of risk of death in one to four year old children. Nutr Res. 1986;6:249–61.
Rasmussen J, Andersen A, Fisker A, Ravn H, Sodemann M, Rodrigues A, et al. Mid-upper-arm-circumference and mid-upper-arm circumference z-score: The best predictor of mortality. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2012;66(9):998–1003.
Waterlow JC. Classification and definition of protein-calorie malnutrition. Br Med J. 1972;3(5826):566–9.
Briend A, Dykewicz C, Graven K, Mazumder RN, Wojtyniak B, Bennish M. Usefulness of nutritional indices and classifications in predicting death of malnourished children. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed). 1986;293(6543):373–5.
Sicotte M, Ledoux M, Zunzunegui MV, Ag Aboubacrine S, Nguyen VK, Atarao group. Reliability of anthropometric measures in a longitudinal cohort of patients initiating ART in West Africa. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2010;10:102.
Ulijaszek SJ, Kerr DA. Anthropometric measurement error and the assessment of nutritional status. Br J Nutr. 1999;82(3):165–77.
Mwangome MK, Berkley JA. The reliability of weight-for-length/height Z scores in children. Matern Child Nutr. 2014;10(4):474–80.
Ayele B, Aemere A, Gebre T, Tadesse Z, Stoller NE, See CW, et al. Reliability of measurements performed by community-drawn anthropometrists from rural Ethiopia. PLoS ONE. 2012;7(1):e30345.
Cluster) II-ASCN. Transitioning to the WHO Growth Standards: Implications for Emergency Nutrition Programmes. 2008.
Mwangome MK, Fegan G, Mbunya R, Prentice AM, Berkley JA. Reliability and accuracy of anthropometry performed by community health workers among infants under 6 months in rural Kenya. Tropical Med Int Health. 2012;17(5):622–9.
Modi P, Nasrin S, Hawes M, Glavis-Bloom J, Alam NH, Hossain MI, et al. Midupper Arm circumference outperforms weight-based measures of nutritional status in children with diarrhea. J Nutr. 2015;145(7):1582–7.
Mwangome MK, Fegan G, Prentice AM, Berkley JA. Are diagnostic criteria for acute malnutrition affected by hydration status in hospitalized children? A repeated measures study. Nutr J. 2011;10:92.
Briend A, Garenne M, Maire B, Fontaine O, Dieng K. Nutritional status, age and survival: the muscle mass hypothesis. Eur J Clin Nutr. 1989;43(10):715–26.
Briend A, Wojtyniak B, Rowland MG. Arm circumference and other factors in children at high risk of death in rural Bangladesh. Lancet. 1987;2(8561):725–8.
de Onis M, Onyango AW, Borghi E, Garza C, Yang H. Comparison of the World Health Organization (WHO) Child Growth Standards and the National Center for Health Statistics/WHO international growth reference: implications for child health programmes. Public Health Nutr. 2006;9(7):942–7.
Young HJ, S. Review of Nutrition and Mortality Indicators for the Integrated Food Security Phase Classification (IPC): Reference Levels and Decision-Making. 2009
Akinbami FO, Hamzat TH, Orimadegun AE, Tongo O, Oyeyemi L, Okafor O, et al. Body mass composition: a predictor of admission outcomes among hospitalized Nigerian under 5 children. Asia Pac J Clin Nutr. 2010;19(3):295–300.
Berkley J, Mwangi I, Griffiths K, Ahmed I, Mithwani S, English M, et al. Assessment of severe malnutrition among hospitalized children in rural Kenya: comparison of weight for height and mid upper arm circumference. JAMA. 2005;294(5):591–7.
Vella V, Tomkins A, Borghesi A, Migliori GB, Ndiku J, Adriko BC. Anthropometry and childhood mortality in northwest and southwest Uganda. Am J Public Health. 1993;83(11):1616–8.
Briend A, Maire B, Fontaine O, Garenne M. Mid-upper arm circumference and weight-for-height to identify high-risk malnourished under-five children. Matern Child Nutr. 2012;8(1):130–3.
Collins S, Sadler K, Dent N, Khara T, Guerrero S, Myatt M, et al. Key factors in the success of community-based management of severe malnutrition. Food and nutrition bulletin. 2006:49–79
Dale NM, Myatt M, Prudhon C, Briend A. Using Mid-upper Arm circumference to End treatment of severe acute malnutrition leads to higher weight gains in the most malnourished children. PLoS ONE. 2013;8(2):e55404. no pagination.
en-net. Mid-Upper Arm Circumference and Weight-for-Height Z-Score as Indicators of Severe Acute Malnutrition: A Consultation of Operational Agencies and Academic Specialists to Understand the Evidence, Identify Knowledge Gaps and to Inform Operational Guidance..Emergency Nutrition Network. 2012.
Goossens S, Bekele Y, Yun O, Harczi G, Ouannes M, Shepherd S. Mid-upper Arm circumference based nutrition programming: evidence for a New approach in regions with high burden of acute malnutrition. PLoS ONE. 2012;7(11):e49320. no pagination.
WHO, WFP, UNICEF. Community-based management of severe acute malnutrition. Joint statement. WHO, WFP, UNICEF, 2007
Grijalva-Eternod CS. The Double Burden of Obesity and Malnutrition in a Protracted Emergency Setting: A Cross-Sectional Study of Western Sahara Refugees. PLoS Medicine. 2012;9(10):no pagination.
Rahim HFA, Wick L, Halileh S, Hassan-Bitar S, Chekir H, Watt G, et al. Maternal and child health in the occupied Palestinian territory. Lancet. 2009;373(9667):967–77.
Bairagi R. Is income the only constraint on child nutrition in rural Bangladesh? Bull World Health Organ. 1980;58(5):767–72.
Bechir M, Schelling E, Bonfoh B, Seydi M, Wade S, Moto DD, et al. Seasonal variations in the nutritional status of nomad and sedentary children less than 5 years of age living in the Sahel in Chad. [French] Evolution saisonniere du statut nutritionnel des enfants nomades et sedentaires de moins de cinq ans dans le Sahel au Tchad. Med Trop. 2010;70(4):353–8.
Block SA, Kiess L, Webb P, Kosen S, Moench-Pfanner R, Bloem MW, et al. Macro shocks and micro outcomes: child nutrition during Indonesia’s crisis. Econ Hum Biol. 2004;2(1):21–44.
Branca F, Pastore G, Demissie T, Ferro-Luzzi A. The nutritional impact of seasonality in children and adults of rural Ethiopia. Eur J Clin Nutr. 1993;47(12):840–50.
Chikhungu LC, Madise NJ. Seasonal variation of child under nutrition in Malawi: is seasonal food availability an important factor? Findings from a national level cross-sectional study. BMC Public Health. 2014;14:1146.
Hillbruner C, Egan R. Seasonally, household food security, and nutritional status in Dinajpur Bangladesh. Food Nutr Bull. 2008;29(3):221–31.
Meshram II, Balakrishna N, Arlappa N, Mallikarjun Rao K, Laxmaiah A, Brahmam GN. Prevalence of undernutrition, its determinants, and seasonal variation among tribal preschool children of Odisha state, India. Asia Pac J Public Health. 2014;26(5):470–80.
Shell-Duncan B. Impact of seasonal variation in food availability and disease stress on the health status of nomadic Turkana children: a longitudinal analysis of morbidity, immunity, and nutritional status. Am J Hum Biol. 1995;7:339–55.
Wright J, Vaze P, Russell G, Gundry SW, Ferro-Luzzi A, Mucavele P, et al. Seasonal aspects of weight-for-age in young children in Zimbabwe. Public Health Nutr. 2001;4(3):757–64.
Acknowledgements
We would like to acknowledge Jane Falconer (LSHTM) for assisting with the peer-reviewed search. No funding bodies had any role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Office of U.S. Foreign Disaster Assistance (OFDA) and the World Food Programme (WFP) (grant number ITDCZD07). OFDA and WFP had no role in the design, analysis or writing of this article.
Availability of data and materials
All of the data are stated within the manuscript.
Authors’ contribution
SF is the main author and was involved in all stages from the conception and design, literature search, analysis and interpretation to drafting the article and writing the final version to be published. CP, MK and FC were involved in the conception and design as well as in critically revising different draft versions and approving the version to be published. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Competing interests
No financial or non-financial competing interests.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver (http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
About this article
Cite this article
Frison, S., Kerac, M., Checchi, F. et al. Anthropometric indices and measures to assess change in the nutritional status of a population: a systematic literature review. BMC Nutr 2, 76 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40795-016-0104-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1186/s40795-016-0104-4